Gifted and Talented Education
advertisement

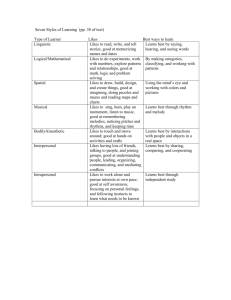
Gifted and Talented Education & Kid Pix STATE GOAL FOR SERVICES FOR GIFTED STUDENTS Students who participate in services designed for gifted students will demonstrate skills in self-directed learning, thinking, research, and communication as evidenced by the development of innovative products and performances that reflect individuality and creativity and are advanced in relation to students of similar age, experience, or environment. High school graduates who have participated in services for gifted students will have produced products and performances of professional quality as part of their program services. What is Giftedness? 1. General intellectual ability or talent. Laypersons and educators alike usually this in terms of a high intelligence test score--usually two standard deviations above the mean-on individual or group measures. Parents and teachers often recognize students with general intellectual talent by their wide-ranging fund of general information and high levels of vocabulary, memory, abstract word knowledge, and abstract reasoning. Other sources generally cite IQ scores and their labels something like: 85-99 Lower normal 100-114 Upper normal 115-129 Bright 130-144 Gifted 145-159 Highly gifted 160-above Profoundly gifted 2. Specific academic aptitude or talent. Students with specific academic aptitudes are identified by their outstanding performance on an achievement or aptitude test in one area such as mathematics or language arts. The organizers of talent searches sponsored by a number of universities and colleges identify students with specific academic aptitude who score at the 97th percentile or higher on standard achievement tests and then give these students the Scholastic Aptitude Test (SAT). Remarkably large numbers of students score at these high levels. 3. Creative and productive thinking. This is the ability to produce new ideas by bringing together elements usually thought of as independent or dissimilar and the aptitude for developing new meanings that have social value. Characteristics of creative and productive students openness to experience, setting personal standards for evaluation, ability to play with ideas, willingness to take risks, preference for complexity, tolerance for ambiguity, positive self-image, and the ability to become submerged in a task. Creative and productive students are identified through the use of tests such as the Torrance Test of Creative Thinking or through demonstrated creative performance. 4. Leadership ability. Leadership can be defined as the ability to direct individuals or groups to a common decision or action. Students who demonstrate giftedness in leadership ability use group skills and negotiate in difficult situations. Many teachers recognize leadership through a student's keen interest and skill in problem solving. Leadership characteristics self-confidence, responsibility, cooperation, a tendency to dominate, and the ability to adapt readily to new situations. These students can be identified through instruments such as the Fundamental Interpersonal Relations Orientation Behavior (FIRO-B). 5. Visual and performing arts. Gifted students with talent in the arts demonstrate special talents in visual art, music, dance, drama, or other related studies. These students can be identified by using task descriptions such as the Creative Products Scales, which were developed for the Detroit Public Schools by Patrick Byrons and Beverly Ness Parke of Wayne State University 6. Psychomotor ability. This involves kinesthetic motor abilities such as practical, spatial, mechanical, and physical skills. It is seldom used as a criterion in gifted programs. Blooms Taxonomy Knowledge • • • • • observation and recall of information knowledge of dates, events, places knowledge of major ideas mastery of subject matter Question Cues: list, define, tell, describe, identify, show, label, collect, examine, tabulate, quote, name, who, when, where, etc. Comprehension • • • • • • • understanding information grasp meaning translate knowledge into new context interpret facts, compare, contrast order, group, infer causes predict consequences Question Cues: summarize, describe, interpret, contrast, predict, associate, distinguish, estimate, differentiate, discuss, extend Application • • • • use information use methods, concepts, theories in new situations solve problems using required skills or knowledge Questions Cues: apply, demonstrate, calculate, complete, illustrate, show, solve, examine, modify, relate, change, classify, experiment, discover Analysis • • • • • seeing patterns organization of parts recognition of hidden meanings identification of components Question Cues: analyze, separate, order, explain, connect, classify, arrange, divide, compare, select, explain, infer Synthesis • • • • • use old ideas to create new ones generalize from given facts relate knowledge from several areas predict, draw conclusions Question Cues: combine, integrate, modify, rearrange, substitute, plan, create, design, invent, what it?, compose, formulate, prepare, generalize, rewrite Evaluation • • • • • • compare and discriminate between ideas assess value of theories, presentations make choices based on reasoned argument verify value of evidence recognize subjectivity Question Cues assess, decide, rank, grade, test, measure, recommend, convince, select, judge, explain, discriminate, support, conclude, compare, summarize Multiple Intelligences Multiple Intelligences • • • • • • • Verbal/Linguistic Intelligence Visual/Spatial Intelligence Musical Intelligence Logical/Mathematical Intelligence Bodily/Kinesthetic Intelligence Interpersonal Intelligence Intrapersonal Intelligence Verbal-Linguistic Is strong in: reading, writing, telling stories, memorizing dates, thinking in words. Likes to: read, write, talk, memorize, work at puzzles. Learns best through: reading, hearing and seeing words, speaking, writing, discussing and debating. Math-Logic Is strong in: math, reasoning, logic, problem-solving, patterns. Likes to: solve problems, question, work with numbers, experiment. Learns best through: working with patterns and relationships, classifying, categorizing, working with the abstract. Spatial Is strong in: reading, maps, charts, drawing, mazes, puzzles, imaging things, visualization. Likes to: design, draw, build, create, daydream, look at pictures. Learns best through: working with pictures and colors, visualizing, drawing. Bodily- Kinesthetic Is strong in: athletics, dancing, acting, crafts, using tools. Likes to: move around, touch and talk, body language. Learns best through: touching, moving, processing knowledge through bodily sensations. Musical Is strong in: singing, picking up sounds, remembering melodies, rhythms. Likes to: sing, hum, play an instrument, listen to music. Learns best through: rhythm, melody, singing, listening to music and melodies. Interpersonal Is strong in: understanding people, leading, organizing, communicating, resolving conflicts, selling. Likes to: have friends, talk to people, join groups. Learns best through: sharing, comparing, relating, interviewing, cooperating. Intrapersonal, Is strong in: understanding self, recognizing strengths and weaknesses, setting goals. Likes to: work alone, reflect, pursue interests. Learns best through: working alone, doing self-paced projects, having space, reflecting. Naturalist Is strong in: understanding nature, making distinctions, identifying flora and fauna. Likes to: be involved with nature, make distinctions. Learns best through: working in nature, exploring things, learning about plants and natural events. How Does Kid Pix Meet Your Needs?