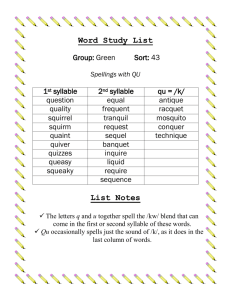
Calling the Phones
advertisement

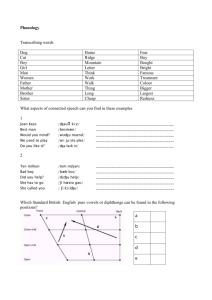
The Final Battle 1. Calling the Phones 6. Phono + Tactics 2. Phonology fill in the blank 7. Feature Features 3. On the Spot Minimal Pairs 8. Act It Out 4. Name that Phonological 9. Eawy Phonetic Rule 5. Set Up the Syllable Pwocesses 10. Toddler Syntax Table of Content 1. Calling the Phones 2. Phonology fill in the blank 3. On the Spot Minimal Pairs 4. Name that Phonological Rule 5. Set Up the Syllable 6. Phone+O+Tactics 7. Feature Features 8. Acting Out 9. Eawy Pwonetic Pwocesses 10. Toddler Syntax Calling the Phones Duel - One against one Each team chooses two participants. When giving your answer you will be awarded -2 pt for the SOUND -2 pt for the SYMBOL (on board) - 1 pt for an EXAMPLE Which sound is it? 1. I am a “plosive”. 2. I am “velar” 3. I am “voiceless” What am I? [k] Which sound is it? 1. I am a “nasal”. 2. I am “bilabial” 3. I am “voiced” What am I? [m] Which sound is it? 1. I am a “plosive”. 2. I am “alveolar” 3. I am “voiceless” What am I? [t] Which sound is it? 1. I am an “approximant” [w] 2. I am “velar” and “labial” 3. To pronounce me, you must have rounded lips. What am I? Which sound is it? 1. I am “alveolar” [l] 2. I am “voiced”, but can also be voiceless in certain circumstances. 3. I am a “lateral approximant”. 4. I am a “liquid”. What am I? Which sound is it? 1. I am “alveolar”. 2. I am a “nasal” 3. I am “voiced” What am I? [n] Which sound is it? 1. I am a “fricative”. 2. I am “glottal” 3. I am “voiceless” What am I? [h] Which sound is it? 1. I am an “affricate”. 2. I am “voiceless” What am I? [ʧ] Which sound is it? 1. I am “plosive”. 2. I am “bilabial” 3. I am “voiced” What am I? [b] Phonology Fill in the Blank Individual Questions Each team chooses one participant Phonology Fill in the Blank No human language exploits all phonetic ___________. Phonology Fill in the Blank Every language makes its own particular selection from the range of all possible ________________. Phonology Fill in the Blank The task of ______________ is to discover and describe the systematic phonological patterns found in individual languages. Phonology Fill in the Blank __________ correspond to articulatory or acoustic categories such as [voice] or [strident] They are the smallest building block of phonological structure Phonology Fill in the Blank The three major phonological units are: Phonology Fill in the Blank Segments are said to _________ when their presence alone may distinguish forms with different meaning from each other Ex: sip [sɪp] and zip [zɪp] Phonology Fill in the Blank Two forms with distinct meaning that differ by only one segment found in the same position in each form, are said to be __________ _______. Phonology Fill in the Blank Segments that contrast with each other in a particular language are said to belong to separate ____________ of that language. On the Spot Minimal Pairs Individual Questions Each team chooses one participants On the Spot Minimal Pairs Find minimal pairs to prove that /f/ and /v/ are in fact phonemes of English. On the Spot Minimal Pairs Find minimal pairs to prove that /b/ and /m/ are in fact phonemes of English. On the Spot Minimal Pairs Find minimal pairs to prove that /z/ and /s/ are in fact phonemes of English. On the Spot Minimal Pairs Find minimal pairs to prove that /l/ and /r/ are in fact phonemes of English. Name the Phonological Rule Group Question (all groups work at once) First group to answer Time limit (60 seconds) Possibility of stealing other groups points Name that Phonological Rule Blue [blu] Gleam [glim] Slip [slɪp] Flog [flɒg] Leaf [lif] Plow Clap Clear Play [pl̥aʊ] [kl̥æp] [kl̥ɪər] [pl̥eɪ] /l/ Answer In English, we find the voiceless allophones /l̥/after voiceless stops, and voiced allophones /l/elsewhere. Name the Phonological Rule Brew [bru] Green [grin] Drip [drɪp] Frog [rɒg] Shrimp [ʃrɪmp] Prow Trip Creep Pray [pr̥aʊ] [tr̥ɪp] [kr̥ip] [pr̥eɪ] /r/ Answer In English, glides have voiceless allophones after voiceless stops, and voiced allophones elsewhere. Name that Phonological Rule Beauty [bjuti] Putrid [pj̥utrɪd] Dwayne [dweɪn] Twin Gwen [gwɛn] View [vju] Swim [swɪm] Thwack [θwæk] [tw̥ɪn] Quick [kw̥ɪk] Cute [kj̥ut] /j//w/ Answer In English, liquids have voiceless allophones after voiceless stops, and voiced allophones elsewhere. Name that Phonological Rule Eyes Lies Tried Tribe House Loud Cow [aɪz] [laɪz] [tr̥aɪd] [tr̥aɪb] [haʊz] [laʊd] [kaʊ] Ice Lice Trite Tripe House [ʌɪs] [l ʌɪs] [tr̥ʌɪt] [tr̥ʌɪp] [hʌʊs] /aɪ//aʊ/ Answer • [aj] before the class of voiced consonants or in word final position • [ʌ j] before the class of voiceless consonants Name that Phonological Rule Save Abe Made Maze Age Haig [sev] [eb] [med] [mez] [edʒ] [eg] Safe Ape Mate Mace H Ache [sĕf] [ĕp] [mĕt] [mĕs] [ĕtʃ] [ĕk] /e/ Answer In English, /e/ is short when followed by a voiceless consonant. Name that Phonological Rule Tenth [tɛn̪θ] Know [noʊ] Month[mʌn̪θ] Annoy [ənɔɪ] Panther Onion [ʌnyən] [pæn̪θər] Chrysanthemum [krɪsæn̪θəməm] Nun [nʌn] /n/ Answer In English, /n/ becomes dental when it precedes /θ/. Name that Phonological Rule Skill [skɪl] Kill Ask Cass [æsk] Ski [ski] School [skul] Skull [skʌl] Ink [ɪŋk] King Cool Key Cull [khɪl] h [k æs] [khɪŋ] [khul] [khi] h [k əl] /k/ Answer Voiceless oral stops (/k/) are aspirated when it is syllable initial, and unaspirated elsewhere * Name that Phonological Rule Lit [lɪt] Lame [leɪm] Let [lɛt] Lick [lɪk] Lay [leɪ] Leak [lik] Low [ɫoʊ] Law [ɫɔ] Loot [ɫut] Lull [ɫʌɫ] All [ɔɫ] Feel [fiɫ] Answer In English, [l] occurs in the initial position before a front vowel. In English, [ɫ] occurs in the initial position before a central or back vowel or in the word final position Set Up the Syllable One participant per team On the Board Time limit (30 seconds) One group at a time but other groups work on the question at desk Since there will be a possibility of steeling points Draw the Syllable Tree for this word Syllable: Set Up the Syllable Lullaby: Set Up the Syllable Finding: Set Up the Syllable Hopelessly: Phone + O + tactics Individual questions Multiple choice questions Time limit (10 seconds) Definition: The set of constraints on how sequences of segments pattern. Phonemes Phonology Phonotactics Phonetics Phone me … baby! Which one of these series of sounds not possible in English in the onset position? s+t+r t+w s + k +r s +d+r s+p+l Which one of these words don’t fill an accidental gap of English? Ptato Zena Kodik Tacoo Washik Which one of these words could be considered an systemic gap of English? Shaz Zif Drodif Strik Tdriff Feature Features Individual questions Each team chooses one participant Answers on board + Time limit (10 seconds) Each question worth up to 5 points Features of this segment? /n/ [ [ [ [ [ consonantal] syllabic] sonorant] continuant] voice] Features of this segment? /f/ [ [ [ [ [ consonantal] syllabic] sonorant] continuant] voice] Features of this segment? /s/ [ [ [ [ [ consonantal] syllabic] sonorant] continuant] voice] Features of this segment? /g/ [ [ [ [ [ consonantal] syllabic] sonorant] continuant] voice] Theorizing Group exercise All groups at the same time One sheet of paper Time limit (30 seconds) 2 Points per right answer Match the theory with the statement. 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. a. b. c. d. e. Acting Out Group discussion Each team chooses a participant to represent their team First Team To show your understanding of the term, act this out: BABBLING Second Team To show your understanding of the term, act this out: LISP Third Team Only using materials in class, act this out: OVEREXTENTION Fourth Team Only using materials in class, act this out: UNDEREXTENTION Eawy Pwonetic Pwocesses Individual questions Each team chooses one participant What kind of early phonetic process is used in this example: Syllable deletion Syllable simplification Substitution Assimilation Maintenance of the same cons./vowel What kind of early phonetic process is used in this example: Syllable deletion Syllable simplification Substitution Assimilation Maintenance of the same cons./vowel What kind of early phonetic process is used in this example: Syllable deletion Syllable simplification Substitution Assimilation Maintenance of the same cons./vowel What kind of early phonetic process is used in this example: Syllable deletion Syllable simplification Substitution Assimilation Maintenance of the same cons./vowel Toddler Syntax Individual questions Each team chooses one participant What syntax stage? ‘Mom gone’. Combine important words with crucial semantic relationships What syntax stage? ‘I teasing Mummy.’ Contains utterances that are generally longer than two words but lack bound morphemes and most functional categories What syntax stage? ‘Puppy’. A single word to express a whole sentencelike meaning What syntax stage? ‘See cow’ Combine important words with crucial semantic relationships Please wait while we tally the scores ... And fourth place goes to ... And third place goes to ... And second place goes to ... Congratulations to our winning team !!!