MN30067BestPracticeforCashPooling
advertisement

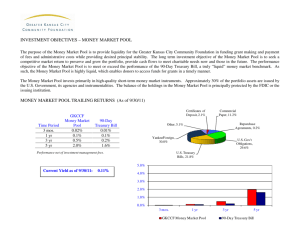
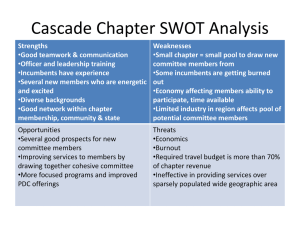
Best Practice for Cash Pooling: A Custom Made Solution? Beatrice Wassing, Handelsbanken - 28 Oct 2011 A flexible cash pooling solution can be custom made, allowing for ongoing alterations and improvements to meet not only the corporate's current needs but also their future requirements. The most successful bank in delivering a flexible solution will be the one who collaborates closely with its clients for the future development of cash pooling. How useful was this article? One of the most talked about topics at global cash management forums during the past few years has been the crucial issue of knowing exactly where your cash is at all times - this has been particularly true during the current financial situation. Even though the topic of managing and pooling cash to ensure access has been on the radar for many years, researchers, corporates and banks still struggle with the definition of cash pooling and how to apply best practices for pooling cash on a domestic and global level. While many banks and financial networks, such as treasury journals and online forums, focus on the need for identifying new techniques, tools and standards for pooling cash, such as notional pooling or cash concentration, few address the importance of a dynamic and flexible cash pool solution that can be adjusted to the nature of the business. In addition to size and location of the corporate, the cash flow environment and account structure are influenced by the scope of globalisation, the treasury organisation, foreign exchange (FX) exposure and management, tax and legal, pricing, and systems environment, to name some of the most important business factors. A cash pool solution for a corporate should therefore, in all cases, be unique in its set-up and features. Change of Focus The benefits of establishing a cash pool, as described by most banks, are the maximum utilisation of internal liquidity before using external sources, interest optimisation and control of cash. However, while the benefits are easily communicated to customers, best practices on how to operate the suggested cash pool solution on a daily basis are challenging. Common questions raised by companies when setting the parameters for a cash pool, whether domestic or global, are: (5=high) 1 2 3 4 5 rate People who read this article also recently read: Local-global Bank Partnerships: Improving the Efficiency of Crossborder Liquidity Management Optimising Liquidity and Working Capital Management: Strategic Positions and Options Taking Liquidity Risk Management to the Next Level Hedging FX Exposures: Which Strategy is Right for Your Business? Liquidity Risk Management and the Changing Risk Landscape Email this article recipient email: send Comment on this Article: "An excellent article, Beatrice. I would like to stress the point about tailormade solutions. No tw..." Add your question/ comment How to act on the different solutions offered by the market? How to integrate the cash pool with other business areas? How other corporates of different or similar nature run their cash pools? Consequently, a bank must often act as a consultant to help customers create a cash pool solution that is fitted to the daily business operations and adjusted for all of the influencing factors mentioned above. Many banks, particularly in Scandinavia and Europe, have developed and established frequently used models and techniques for cash pooling. The successful bank is therefore the one that has advanced from offering efficient and modern cash pool tools, including online dialogues to manage the cash pool, to offering custom made solutions instead. A Custom Made Cash Pool Solution With the challenge of offering a tailored cash pool solution, the bank should offer several important functions to fit the purpose and usage of the pool. These functions include the possibility to combine different techniques such as notional pooling and cash concentration, also known as hybrid pooling, the possibility to: connect the pool with accounts held with other banks, to choose from different interest calculation models, and to build account structures and smaller pools within the structure. Cash pools should be available with multi-currency functionality and with an overlay credit facility with or without intraday overdraw capacity. The geographic coverage for a notional or hybrid pool should include as many countries as possible. On a more detailed account level, functions such as internal interest calculation and limits, selectable coverage controls, an assortment of capitalisation periods, several account levels, as well as summary levels and a selection of different market base rates, should be offered to meet customer requirements. As for the daily operations, automatic reconciliation of interest bookings and cash pool transactions should be facilitated by setting unique reference codes on balance and transaction statements such as MT940s. Several parameters for a cash concentration set-up can defined, such as target amount, frequency and minimum amount, all of which banks should be able to offer their customers. Cash concentration techniques should include at least the possibility to set up zero-balancing, target, threshold, topping, and interval balancing sweeps, all with unique reference coding. In addition, audit reports and recommendations for accounting practices should be made available. Finally, an online cash pool management tool is crucial. This tool should offer the client a range of choices in terms of viewing the cash pool, for example limited to country, currency, company, account level or type, etc. The account overview should be available to retrieve on at least an annual basis. Other functions are reports and specifications on interest capitalisation and accrued interests, on all account levels. Access to the cash pool online tool is limited by assigning mandates accordingly. Usually, full access to the cash pool is given to treasury departments, while subsidiaries and other business functions usually have a limited view of the cash pool. Within the online tool, cash concentration transfers can be managed and withdrawn, enabling the solution to be as flexible as possible in terms of being adjusted to cash flow alterations. Information about base rates and exchange rates is also essential. With all of the above, a successful bank can offer the customer a fully functional yet custom made cash pool solution with real-time access to all accounts included. The control is complete. To illustrate how a cash pool can be operated in different ways, two business case examples are described below. (The illustrations are simplifications of the set-up, not all of the participating accounts or countries are displayed.) Case study: Centralised Scandinavian Treasury The corporate is a middle-sized enterprise with operations in three Scandinavian countries. The treasury organisation is centralised and located in Sweden. A notional multi-currency cross-border pool with local pools in domestic currencies has been set up to include Sweden, Denmark and Norway (see Figure 1). The overlay notional account and intraday facility is based in Sweden but covers all participating accounts in real time. Interest is calculated per currency. The pool currency is Swedish kronor (SEK) so net disposable balance is always displayed in SEK on the top level, while subsidiaries view their part of the cash pool in Norwegian krone (NOK), Danish krone (DKK) and SEK respectively. As the operating business units in each country are mainly sales units fully owned by the group, except for in Sweden where a production factory is set up, excess liquidity is the common outcome of the banking day on most accounts. Therefore zero-balancing of sub-accounts to top account holder’s account (group yield account) have been set up in all local pools. The top account holder’s account balances in NOK and DKK is zero-balanced with an FX spot deal by central treasury once a week to acquire SEK. Outgoing payments during the day are made available with the removal of coverage checks and no internal interest calculation is applied as all sub-accounts are zerobalanced on a daily basis. Transaction statements are produced for the sub-accounts to enable reconciliation of payments and collections, while balance and transaction statement is generated for top account holder’s account as these accounts hold both end-of-day balances and cash pool interest transactions. As illustrated in Figure 1, this is an example of a hybrid pool where notional pooling has been combined with a zero-balancing routine. Figure 1: Example of a Hybrid Pool Source: Handelsbanken Case study: Regional Treasury based in Germany Figure 2 is an example of a multi-currency cash pool for a large global corporation. The parent company is based outside Europe and the regional treasury for Europe is located in Germany. The organisation covers different European areas where Scandinavia and UK is one isolated business area. The head office for this area is located in Sweden, undertaking strict directions from regional treasury in Germany who has complete overview of the cash pool. Subsidiaries only have access to their own accounts. Main cash flows are in euro but sales and production units are located in UK, Finland and Sweden leaving some flows in other currencies than euro. There is one production unit in Denmark invoicing in euro and DKK, while being invoiced in DKK. With several currency accounts in different countries, net balances are notionally aggregated to show one cash position per currency as well as the top level balance in euro. Interest is calculated per currency. Subsidiaries are independent in terms of daily cash management; however FX deals are managed from regional treasury. The parent company holds no accounts in the cash pool, except for the notional top level account in Sweden. Hence, group yield accounts are only used for internal interest compensation, leaving an aggregated balance accumulating on this account. As subsidiaries are mainly short on cash, internal limits are distributed and interest is paid to the group yield account monthly. The regional treasury settles these account balances with a monthly sweep to the top level. Excess funds in euro are pooled on a weekly basis to regional treasury in Germany which has a local euro cash pool. The Danish subsidiary’s euro account has an automatic target-balancing executed daily to be swept to the Swedish euro pool, leaving a target amount on the account. Figure 2: Example of a Multi-currency Cash Pool Source: Handelsbanken Pooling into the Future The two examples above illustrate the variation in the dynamics and purpose of a cash pool solution. As corporations are showing more interest for pooling solutions, particularly across the borders, banks will be challenged to meet customer requirements. Future opportunities lie in the offering of alternative interest compensation models, corporate administration of the cash pool online, new cash concentration features such as later cut-off times, tax and legal implications, geographic coverage, pricing models and last, but not least, more efficient documentation. On the corporate side, customers are already facing the challenge of finding ways to reduce currency accounts and to establish more efficient account structures, with cash pooling solutions being a part of that process. In Europe, companies have already begun to switch accounting currency from local currency to euro where possible, making way for other possibilities in terms of reducing FX risk and building cash pools dominated by euro flows. Still, using cash pools to manage liquidity and FX exposures will be hot topics for the years to come. As the techniques are developing and the banks are offering more global solutions, cash pooling will be an on going discussion for many companies. In addition, as tax and legal regulations are constantly changing, new possibilities and obstacles will arise in the management of cash. To summarise, a flexible cash pooling solution can be custom made, allowing for on going alterations and improvements to meet not only the current corporate needs but also their future requirements. The most successful bank in delivering such a flexible solution will be the one who collaborates closely with its clients for the future development of cash pooling.