What is a Lesson Plan?
advertisement

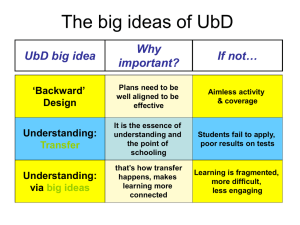
Nature & Importance of Lesson Planning By: Carol Gaerlan WHAT IS A LESSON PLAN? A LESSON PLAN IS: A model of organized learning events within a set period of time or session A projection of real lesson filled with concrete processes, assignments, and learning tools A blueprint on which to construct a learning process made up of clearly stated goals and objectives A tool that moves from theory to practice by carrying out a methodological approach (based on latest research) COMPARE THE STUDENTS WHY IS LESSON PLANNING IMPORTANT? The key to good teaching, purposeful class management and the achievement of sustained educational progress lies in effective preparation and planning. (Butt, 2008) Consistent effective lesson planning is essential for successful experiences in both teaching and learning process. (Serdyukov and Ryan, 2008) STAGES IN LESSON PLANNING PREPARATION Who is to be taught? By knowing the learners, the desired outcome can be determined and the teacher can identify the purpose of the lesson. DEVELOPMENT What is to be taught? This stage covers the substance of the lesson such as subject matter, instructional goals, specific learning objectives, concepts and skills. An effective activity or lesson plan begins with a specific objective. Bloom’s taxonomy provides good examples of appropriate action words to use in learning objectives. With this, the learning objective becomes studentfocused and outcomes oriented. IMPLEMENTATION How do you teach students? Methods or strategies employed Learning activities and methodological approach Materials and technology applications REFLECTION Will/ Is my lesson plan effective? the teacher evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of the lesson plan before implementing it and after it has been delivered •date, subject area, topic, grade level TYPES Description/ Introduction OF Materials and Tools Procedures Evaluation •instructional resources such as texts, visuals, handouts, etc. •educational technology •content presentation and activities •reflection and assessment (tests, quizzes, essays, etc. LESSON PLAN Goals and Objectives •may include academic and culturally relevant content standards, adaptations for diverse populations There are different ways to make a lesson plan. But ALL effective lesson plans have structure. DETAILED LESSON PLAN The detailed lesson plan has five parts: Objectives Subject Matter (topic, references, materials) Procedure (motivation, activity, routines, lesson proper) Evaluation Assignment Everything is written down like a script of a play. It contains what the teacher does and says and what the students are expected to say and do. EXAMPLES SEMI-DETAILED LESSON PLAN Has all the components of a detailed plan but does not include a complete description of pupils’ activity. It contains the important subject matter and a description of teaching-learning activities. (Beltran, 1992) BRIEF LESSON PLAN Only guide statements or brief explanation of the activities to be performed in each part are provided UNDERSTANDING BY DESIGN Jay McTighe describes UbD as a framework for curriculum planning, assessment by design and ultimately for teaching with the goal of understanding and transfer Grant Wiggins emphasizes that Ubd is not a philosophy and not an approach to teaching but a planning framework. There are 3 stages in UbD: Desired Results Assessment Evidence Learning Plan CONCLUSION Lesson planning is integral in the teaching-learning process It encourages research teachers have foresight to think deeply about the lesson maximize learning opportunities LP’s don’t always have to be detailed Planning can be an internal process A GOOD LESSON PLAN IS – Apparent Serves as a Guide Flexible Clear & Understandable Well-documented It becomes a historic document of the class which can aid in performance evaluation, student assessment and curriculum development. THANK YOU!!!