Understanding by Design: A Rigorous Approach
advertisement

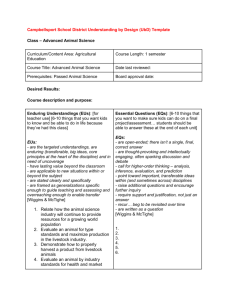
Understanding By Design To Increase Rigor Adapted from the work of J. McTighe and G. Wiggins Introduction . Dr. Theresa Melenas -Instructional Coach/ Asst. Principal Mrs. Amanda Horne - Instructional Coach SESSION “I CAN” STATEMENTS I can articulate to others the rationale behind UbD I can explain the three stages of UbD I can write an outline of UbD using all three stages Why UbD? • To overcome the prevalence of “Aimless Activity” and “Superficial Coverage” • To increase rigor • To support deeper understanding of the standards (K,U,D) • To ensure alignment between objectives, assessment and instruction What UbD is 1.Starting with the end in mind 2.Reaching a higher level of understanding with students 3.Planning units more deliberately 4.Assessing true understandings and not just lower levels of learning What UbD is NOT • A step by step program, it only provides a framework • Meant to compete with SIOP, Differentiated Instruction, 21st century skills, but work in conjunction • A daily lesson plan Three stages of backward design 1. Identify desired results 2. Determine acceptable evidence 3. Plan learning experiences & instruction 7 STAGE 1 Identify desired results 8 Stage 1 – Desired results Stage 1 – Desired Results Content Standard (s): G Provide a framework for curriculum design; generalizations that define parameters about what students are expected to know and be able to do Understanding (s): Essential Question (s): EU Students will understand that… Insight into the generalization; what students will walk away with Knowledge: Student will know … K Inquiry used to explore the generalization to enable students to earn the understanding EQ Skills: Students will be able to … Specific priorities about what students are expected to know and be able to do S Stage 1- Identify Desired Results Key Questions • What should students know, understand, and be able to do? • What is the ultimate transfer we seek as a result of this unit? • What enduring understandings are desired? • What essential questions will be explored indepth and provide focus to all learning? Design Standard for ENDURING UNDERSTANDINGS Enduring, based on transferable, big ideas at the heart of the discipline Need to be “uncovered”, not merely stated Transcends individual lessons Starts with the stem: “The student will understand that…. What we want students to Know (Facts) Vocabulary Terminology Definitions Key factual information Formulas Critical details Important events and people Sequence and timelines What we want students to be able to DO: (Skills) Basic skills – decoding, computation Communication skills – listening, speaking, writing Thinking skills – compare, infer, analyze, interpret Research, inquiry, investigation skills Study skills – notetaking, fill out charts Interpersonal, group skills Essential Questions should be… Arguable - and important to argue about At the heart of the subject Recurring - in professional work, adult life, as well as in classroom inquiry Raising more questions for learners – provoking and sustaining engaged inquiry Centered around important conceptual or philosophical issues A tool for organizing purpose; for making student learning meaningful and connected Essential Question or not? • Essential Question: • What causes a species to become extinct? • Topical Essential Question: • What caused dinosaurs to become extinct? • Guiding Question: • What is an omnivore? • What was the largest species of dinosaur? Four Corners Corner 1- Essential Question Corner 2- Topic Essential Question Corner 3- Guiding Question Corner 4- Unsure Science What are the parts of a cell? Guiding question How does an organism’s structure enable it to survive? Essential question Social Studies What factors cause today’s global migrations? Topical Question Why do people move? Essential Question Math In what situations should I use meters, kilometers or centimeters? Topical Question When and why should we estimate? Essential Question Which is more 10 kilometers or 10 meters? Explain. Guiding question Design Standards for KNOWLEDGE AND SKILLS • Includes Knowledge & Skills (inquiry, literacy and/or numeracy) • Start with the stem: “To understand, students will need to……” or “Students will be able to…” • Verbs reflect higher order thinking (Blooms taxonomy) • Typically only one verb per objective STAGE 2 Determine Acceptable Evidence Stage 2—Determine Assessment Evidence Key Questions: • How will we know if students have achieved the desired results? • What will we accept as evidence of student understanding and their ability to use (transfer) their learning in new situations? • How will we evaluate student performance in fair and consistent ways? Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence Performance Task (s) T Other Evidence OE Stage 2: Determine Acceptable Evidence a. Through what performance tasks(s) will students demonstrate understanding, knowledge, and skill? b. Through what prompts/academic problems or test/quiz items will students demonstrate understanding, as well as more discrete knowledge, and skill? c Through what unprompted evidence (e.g., observations, work samples, etc.) will students demonstrate understanding, knowledge, and skill? d. How will students reflect upon, and self-assess their learning? Three-ring Audit Process Assessments Traditional quizzes or tests Worth Being Familiar With Important to Know and Do Authentic performance tasks and projects Constructed or selected responses Enduring Understanding Wiggins, G. and McTighe, J. (1998). Understanding by Design. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development STAGE 3 Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction Stage 3—Plan Learning Experiences and Instruction Key Questions: • How will we support learners as they come to understand important ideas and processes? • How will we prepare them to autonomously transfer their learning? • What enabling knowledge and skills will students need to perform effectively and achieve desired results? • What activities, sequence, and resources are best suited to accomplish our goals? W.H.E.R.E.T.O. W Where are we going? What is expected? H How will we hook the students? E How will we equip students for expected performances? R How will we rethink or revise? E How will students self-evaluate and reflect their learning? T How will we tailor learning to varied needs, interests, and learning styles O How will we organize the sequence of learning? Wiggins, G. and McTighe, J. (1998). Understanding by Design. Alexandria, VA: Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development Applying Differentiation McTighe and Tomlinson • Stage 1 – Desired Results Established Goals, Understandings and Essential Questions – Should not be differentiated Knowledge and Skill – May be differentiated • Stage 2 – Assessment Evidence May be differentiated • Stage 3 – Learning Plan Should be differentiated Tying it all together • Deeper understanding of standards • Ability to determine Understandings and what is expectable evidence of understanding • Increased rigor based on more than just knowledge and skills • More time devoted to planning- not an expectation to plan in isolation QUESTIONS?