EQIP Organic Transitional Funds and CSP for Organic Production
advertisement

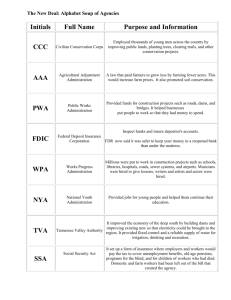
Where to get more information Lauren Smith, District Conservationist, NRCS Pictures and materials borrowed from Lauren Cartwright, NRCS History of NRCS Hugh Hammond Bennett became aware of the threat posed by the erosion of soils as a surveyor for the USDA Bureau of Soil Bennett launched public crusade about the soil erosion crisis in 1928 President Franklin D. Roosevelt in 1932 made conservation of soil and water resources a national priority in the New Deal administration The National Industrial Recovery Act (Public Law 7367) passed in June 1933 included funds to fight soil erosion Funds created the Soil Erosion Service (SES) established in the Department of Interior and appointed Hugh Hammond Bennett Chief in September 1933 History of NRCS On April 27, 1935 Congress passed Public Law 7446 which established the Soil Conservation Service (SCS) 1994, SCS’s name was changed to the Natural Resources Conservation Service Soil Human Air Water Plants Animals ENERGY Since 1935 Technical Assistance Opportunities Financial Assistance Opportunities Since 1935 Technical Assistance Opportunities Since 1935 Financial Assistance Opportunities Environmental Quality Incentives Program Conservation Stewardship Program This is just an example of the most prevalent financial assistance programs and initiatives available nationally through NRCS. Depending on your location there may be other regional or state initiatives. Graphic from: Building Soils for Better Crops: Sustainable Soil Management by Magdoff and Ven Es (2009) Sustainability Historically Underserved (HU) Limited Resource Farmer (LRF) • Gross Farm Sales Determination: In each of the last two years, was your direct or indirect Gross Farm Sales less than or equal to $172,800 (for Johnson/Massac & Pope Counties) per year? Gross Farm Sales is defined as: Gross Income entered on IRS Form 1040, Schedule F, in the Farm Income Section. For FY 2013 Programs, the Gross Farm Sales level should be less than the 2010 and 2011 Farm Sales. • Adjusted Gross Income Determination: In each of the last two years, was your Total Household Income less than the JOHNSON/MASSAC/POPE County "County/Area Value" of $23,050? Total Household Income is defined as Adjusted Gross Income for all members in your household or the amount you entered on IRS Form 1040, Adjusted Gross Income Section. See IRS Web Site for more information on the IRS form. For FY 2013 Programs, this should be compared with your Adjusted Gross Income for 2010 and 2011. County/Area Value is calculated as the higher of the National Poverty level or 50% of the County/Area Median Household Income. Historically Underserved (HU) Beginning Farmer (BF) • A Beginning Farmer or Rancher means an individual or entity who: • Has not operated a farm or ranch, or who has operated a farm or ranch for not more than 10 consecutive years. This requirement applies to all members of an entity, • Will materially and substantially participate in the operation of the farm or ranch. In the case of a contract with an individual, individually or with the immediate family, material and substantial participation requires that the individual provide substantial day-to-day labor and management of the farm or ranch, consistent with the practices in the county or State where the farm is located In the case of a contract with an entity, all members must materially and substantially participate in the operation of the farm or ranch. Material and substantial participation requires that each of the members provide some amount of the management, or labor and management necessary for day-to-day activities, such that if each of the members did not provide these inputs, operation of the farm or ranch would be seriously impaired. Historically Underserved (HU) Socially Disadvantaged Farmer (SDF) • According to Section 2501(e)(2) of the Food, Agriculture, Conservation, and Trade Act of 1990 (7 USC 2279(e)(2)), a Socially disadvantaged farmer or rancher (SDA) is defined as a farmer or rancher who is a member of a “Socially Disadvantaged Group". Therefore a "Socially Disadvantaged Farmer or Rancher" is defined as: • Socially disadvantaged group- a group whose members have been subjected to racial or ethnic prejudice because of their identity as members of a group without regard to their individual qualities. The definition that applies to Titles I, V, and VI includes members of a group subject to gender prejudice, while the definition that applies to Titles II, IX, XII, and XV does not. Title XIV and the Education and Risk Management Assistance provision in Title XII do not make specific reference to the statutory definition of socially disadvantaged farmer or rancher. • Socially disadvantaged Farmer or Rancher- a farmer or rancher who has been subjected to racial or ethnic prejudices because of their identity as a member of a group without regard to their individual qualities. This term means a farmer or rancher who is a member of a socially disadvantaged group. Specifically, a group whose members have been subjected to racial or ethnic prejudice because of their identity as members of a group without regard to their individual qualities. Those groups include African Americans, American Indians or Alaskan natives, Hispanics, and Asians or Pacific Islanders. Payment Rates EQIP • Payment rates for HU Producers are 15-20% above the traditional payment rate for all practices. • Funds allocated to separate fund pools Application competes in regular fund pool and HU fund pool CSP • Funds allocated to separate fund pools Application competes in regular fund pool and HU fund pool NRCS – Natural Resources Conservation Service FSA – Farm Service Agency EQIP – Environmental Quality Incentives Program CSP – Conservation Stewardship Program GRP – Grassland Reserve Program WRP – Wetland Reserve Program How to participate in NRCS Programs EQIP Programmatic Overview CSP Programmatic Overview How to Participate Basic Eligibility Requirements (EQIP and CSP): FSA Farm Number Highly Erodible Land (HEL) Wetland Conservation Provisions Adjusted Gross Income (AGI) Proceed to your county NRCS office to sign an application, then go to the county FSA office to begin this process Environmental Quality Incentives Program Develops and implements contracts with agricultural producers to implement conservation practices to address natural resource problems. Payments are made to producers once conservation practices are completed according to NRCS requirements Nutrient Management Rotational Grazing Systems Alley Cropping Windbreak/Shelterbelt Hedgerow Planting Stripcropping Contour Buffers Pollinator Habitat Riparian Forest Buffer Filter Strip Terrace Cover Crop Pest Management Grassed Waterway Brush Management Field Border Seasonal High Tunnel Conservation Crop Rotation Environmental Quality Incentives Program …And Much More! Environmental Quality Incentives Program Regular EQIP and EQIP National Initiatives… Funding is competitive Applications are ranked based upon national, state and local criteria – developed annually EQIP National Initiatives & Regular EQIP General Fund – Statewide funding pools, participants compete statewide Regular EQIP Grazing & Forestland Funds – County funding pools, participants compete within a county (land use pools) Environmental Quality Incentives Program Deadlines: FY14 EQIP Application cutoff Funding cutoff Obligation cutoff Janurary 17 March 14 April 11 March 21 May 18 June 6 April 11 May 30 June 27 Continuous sign up Environmental Quality Incentives Program Eligibility for EQIP Persons engaged in livestock or agricultural production Land: cropland, pastureland, private non-industrial forestland EQIP Payment Rates Conservation Practice Practice Lifespan (years) Unit Practice Code Regular Payment Amount HU Payment Amount Description Brush Management 10 Acre 314 $310.85 $373.01 Biological control with grazing animals (goats) Conservation Crop Rotation 1 Acre 328 $76.60 $77.38 Add small grain to rotation Cover Crop 1 Acre 340 $37.13 $44.55 Species Mix Field Border 10 Acre 386 $580.58 $618.88 Pollinator Habitat Grassed Waterway 10 Acre 412 $3511.58 $4136.09 36’ top width with checks Integrated Pest Management 1 Acre 595 $7.35 $8.82 Basic IPM with 1RC Nutrient Management 1 Acre 590 $10.81 $12.97 Basic NM Seasonal High Tunnel for Crops 4 Sq Ft 789 $2.74 $3.29 SHT Windbreak Establishment 15 Ft 380 $0.33 $0.35 1 row – bare-root seedling planting stock Environmental Quality Incentives Program Conservation Stewardship Program Conservation Stewardship Program encourages maintenance of existing conservation activities and adoption of additional conservation activities – called enhancements Five Year Contracts, annual per acre payments for maintaining existing conservation activities and implementing new activities (enhancements) Examples of Enhancements Plant: Habitat development for beneficial insects for pest management Water Quality: Integrated Pest Management for Organic Farming Energy: Locally grown and marketed farm products Soil Quality: Use of Cover Crop Mixes Water Quantity: Mulching for moisture conservation Soil Erosion: Continuous No Till Intensive Management of Rotational Grazing Conservation Stewardship Program Applicants are ranked using an interactive tool – Conservation Measurement Tool Tool generates points based upon existing level of stewardship and new enhancement activities. Annual payment based upon points. National Average $18/ac maximum FY14 Application Deadlline: February 7 Continuous sign up Evaluate applications Fund Applications Obligate Contracts March 20 March 21 May 9 Conservation Stewardship Program CSP Eligibility Land: cropland, grassland, prairie land, improved pastureland, nonindustrial private forestland Applicants: Must be the operator of record on FSA farm records Conservation Stewardship Program CSP Resources NRCS- CSP website: Programmatic information www.nrcs.usda.gov/programs/new_csp/csp.html Enhancements www.nrcs.usda.gov/wps/portal/nrcs/main/national/programs/financial/csp/ Farmers’ Guide to the Conservation Stewardship Program http://sustainableagriculture.net/wpcontent/uploads/2008/08/CSP_FarmersGuide_final_September_2009.pdf Since 1935 www.nrcs.usda.gov www.iL.nrcs.usda.gov Phone Book Government Listings Federal – US Government Services USDA – US Dept of Agriculture Natural Resources Conservation Service Call and make an appointment to visit with your local NRCS conservationist! Since 1935 Equal Opportunity The U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA) prohibits discrimination in all its programs and activities on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, and where applicable, sex, marital status, familial status, parental status, religion, sexual orientation, genetic information, political beliefs, reprisal, or because all or a part of an individual's income is derived from any public assistance program. (Not all prohibited bases apply to all programs.) Persons with disabilities who require alternative means for communication of program information (Braille, large print, audiotape, etc.) should contact USDA's TARGET Center at (202) 720-2600 (voice and TDD). To file a complaint of discrimination write to USDA, Director, Office of Civil Rights, 1400 Independence Avenue, S.W., Washington, D.C. 20250-9410 or call (800) 795-3272 (voice) or (202) 720-6382 (TDD). Helping People Help the Land 35