The French Revolution
advertisement

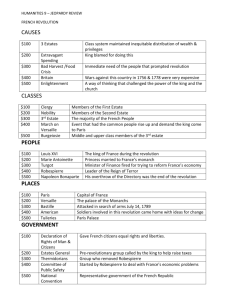
Causes Events Effects Vocabulary People Check Your Knowledge •Class system = Three Estates •Financial Crisis in Government • Frustration with the Monarchy • Social Unrest •Other Influences Return to Table of Contents First Estate Second Estate Roman Catholic Clergy Higher Clergy-bishops, abbots Lower Clergy-local priests Nobility Third Estate Peasants, Artisans, and Bourgeoisie Third Estate Land Ownership Second Estate Percentage of Population First Estate Return to Causes List 0 20 40 60 80 100 •Cost of living increased but wages did not •Government debt from aiding US in American Revolution •Banks refused to loan money to the government Return to Causes list •Louis XVI •Ascends the throne at age 19 •Marriage-alliance with Austria •Inexperienced- needed advice often •Marie Antoinette • Austrian Princess • Out of Touch with reality •She represented everything the people hated about the monarchy Return to Causes list Group Complaint Third Estate Unfair social structure No effective voice in government Want monarchy to return to Paris Second Estate Did not want to pay taxes Wanted more political power First Estate Higher clergy did not want to pay taxes Lower clergy resented luxurious lifestyle of Higher Clergy Return to Causes list • Enlightenment thinking •Success of American Revolution •Desire to end Absolute Monarchy •Crop Failure Return to Causes list • • • • • Meeting of the Estates General Tennis Court Oath Fall of the Bastille Declaration of Rights Reign of Terror Return to Table of Contents • Members representing all three Estates • Goal of approving taxes of 1st and 2nd Estates Return to Event s List • Walk out of the Estates General •Protest the locking out of the Third Estate •Created the National Assembly- Representative government •Promise of a new Constitution for France Return to Event s List • Prison symbolized the injustice of the monarchy • Mob attacks on July 14, 1789 • Get weapons to defend the National Assembly • First battle of the French Revolution Return to Event s List • Nobles feared attack by peasants • Rumors spread of Nobles hiring robbers to kill peasants • Peasants preemptively strike • Drive out landlords and destroy feudal records Return to Event s List • Inspired by American Declaration of Independence • Incorporated Enlightenment ideas from •Jean Jacques Rousseau •John Locke •Baron de Montesquieu •Called for Divide Freedom of Speech Return to Event s List Freedom of Religion Freedom of Assembly Natural Power Freedom of Rights Popular Press Between Limited Sovereignty Equal Government Branches • Louis XVI rejects Declaration • Women respond by • Storming the castle • Escorting the king and queen back to Paris Return to Event s List • Committee of Public Safety controlled the government • Strike fear in the hearts of people to prevent disloyalty • Anyone suspected of disloyalty were executed • Terror ends with the execution of Robespierre Return to Event s List •War with Austria •Conscription compulsory military service, •Execution of Louisalso XVIknown and Marie Antoinette as the draft. •Creation Introduction of Committeeof of the Public Safety for executions Guillotine •Reign of Terror More humane Agency created to • Creation of the Directory Political crisis that occurred as the Jacobins Equality in death direct the effort •Coup d’état and Girondists foughtwar to gain the .support of seizure of power orinsudden •Rise of NapoleonquickThe the growing mobs Paris. People who ran wanted executive council that theradical changeby in France. overthrow of government leaders a government after the creation of They represented theaworking General Moderates who who felt led that French the revolution victory had over Austria. small group. They second used drastic and violent measures to new constitution in 1795. class gone far enough after the execution of the a coup d’état. He gained power inprevent France through strike fear to people from questioning King, They wanted to protect the wealthy class thea revolution. Itmiddle created bicameral legislature. Return to Effects List It ended when Robespierre was beheaded. •National Assembly 1789-1791 (Tennis Court Oath) • Legislative Assembly 1791-1793 (First French Republic) • National Convention1793-1794 (Reign of Terror) •Directory 1794-1799 (Loss of rights gained by revolution) •Emperor Napoleon 1799-1813 (Coup d’état) Radical Left Liberal Moderates ( Due Conservatives Reactionaries •Restoration Monarchy 1815-1848 to Congress of Vienna) Minor •Second Republic •1848-1852 • Extreme French • Some • Keep the • Return to changes political Change but status quo Absolute •Second Emperor Napoleon III 1852-1870 (Coup d’état) • Girondists change not as Monarchy •Third Republic 1871-1940 (Ends with rewriting • Sans- French extreme • Émigrés Culottes Constitution) • Jacobins • Maximilien Robespierre • Jean-Paul Marat Return to Effects List Vocabulary • • • • • • • • Absolute Monarchy-Political system in which a monarch holds supreme, unlimited power granted by divine right (god given) Bourgeoisie- Members of the Middle Class including doctors, lawyers, merchants and business managers. They made up the largest part of the Third Estate Committee of Public Safety- Agency created to direct the war effort. Conscription- compulsory military service, also known as the draft. Coup d’état- quick seizure of power or sudden overthrow of government leaders by a small group. Directory- The executive council that ran the government after the creation of a second new constitution in 1795. It created a bicameral legislature. They authorized the use of the army to put down the uprising of the sans-culottes and royalists. Estate- One of three distinct social classes in France during the 1700s that determined a person’s legal rights and status Émigrés- Nobles who fled France but wanted to return France to an Absolute Monarchy. They tried to raise armies to put down the Revolution. Return to Table of Contents More Vocabulary • • • • • • • Girondists- Moderates who felt that the revolution had gone far enough after the execution of the King, They wanted to protect the wealthy middle class form radical attacks. They often felt that the Jacobins encouraged mob rule and called for too many executions. Higher Clergy- Bishops and Abbots (members of the noble families) Jacobins- People who wanted radical change in France. They supported the sansculottes. Often felt that Girondists were royalists. Lower Clergy- Parish priests, (usually members of peasant or bourgeoisie families) National Assembly- Legislative body created in France by members of the three estates who walked out of the Estates General to protest the decision to bar the third estate from the meeting. Reign of Terror- Political crisis that occurred as the Jacobins and Girondists fought to gain the support of the growing mobs in Paris. It ended when Robespierre was beheaded. They used drastic and violent measures to strike fear to prevent people from questioning the revolution. Sans-Culottes Paris shopkeepers, artisans and workers who saw themselves as heroes and heroines of the Revolution and demanded respect from the upper classes. They supported the Jacobins. They got name because they would no longer wear the short-pants that previously denoted their station in life. Return to Table of Contents People • • • • • Antoinette, Marie - Queen of France when the French Revolution began. She was from Austria. Her opulent lifestyle angered many of her people who were starving. She was executed during the French Revolution, accused of conspiring with Austria to put down French rebellion. Bonaparte, Napoleon- General who led French victory over Austria. He gained power in France through a coup d’état. Louis XVI- King of France when the French Revolution began. At age 19, he married Marie Antoinette to strengthen his throne. Although he was inexperienced, he recognized the growing financial crisis in France. He was executed during the French Revolution. Marat, Jean-Paul- Jacobin leader and member of the Mountain. He published articles to support the cause of the Revolution. He was later stabbed to death by Charlotte Corday. She believed the revolution would end with his death. It did not, and she was sent to the guillotine. Robespierre, Maximilien- Jacobin leader and member of the Mountain. Saw himself as a defender of the Revolution. He ruled the Committee of Public Safety. After overstepping his power, he was himself sent to the guillotine by those he had charged to be traitors to the revolution. Return to Table of Contents If the first estate made up one percent of the population and the second estate made up two percent of the population, what percent of the population made up the third estate? A. 95% B. 97% C. 98% Return to Table of Contents If the First estate owned 10% of the land and the Second estate owned 25 % of the land, what percent of land was owned by the Third Estate? A. 85% B. 75% C. 65% Return to Table of Contents CORRECT Return to Next Question CORRECT Return to Slide Show