Working with Data in Windows
and Descriptive Statistics
HRP223 – Topic 2
October 5th, 2011
Copyright © 1999-2011 Leland Stanford Junior University. All rights reserved.
Warning: This presentation is protected by copyright law and international treaties.
Unauthorized reproduction of this presentation, or any portion of it, may result in
severe civil and criminal penalties and will be prosecuted to maximum extent possible
under the law.
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
Sources of Data
• Small data sets (aka Toy data)
– You may be able to type in the data directly into a SAS code file
with EG like in The Little SAS Book for EG.
• Excel
– For small amounts of HIPAA safe data you can use Excel with
validation.
• Text files with columns of numbers and text
– Exports created by databases frequently provide a text file full
of data and a program for loading it into SAS (like REDCap).
– Data from the CDC Wonder database
• SAS
– Native SAS datasets created by somebody else.
Types of Files
Suffix
File Type
.pdf
Adobe portable document format
.zip
Archives full of compressed data
.xls
Excel prior to 2007
.xlsx
Excel 2007 and later
.csv
Comma separated values (text which Excel likes)
.txt
Text files (letters number and punctuation without formats
.sas
SAS code files
.egp
Enterprise Guide projects
.sas7bdat
SAS data files
.htm or .html
Web pages
.css
Cascading style sheets for web pages
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
SAS and EG files
• .sas files are text files full of instructions that a
programmer can easily write and/or edit.
• .egp files are not.
What is an EGP file?
• EGP files are actually zip archives (with a .egp
suffix instead of .zip) which contain XML text
and other text files.
Searching
• Because the contents of .egp files are
compressed, the built in Windows file finder
will not be able to find files by searching for
keywords inside the projects.
• This affects me when I can’t remember the file
name for a project and to find it I want to
search for key words in the code (like the
principal investigator’s name or the name of
the source data file).
Searching Inside .egp files
• File Locator Pro can search inside the egp files:
– Tools menu > Configuration …
Click here
Add egp here.
Without the .
Files in Enterprise Guide
• Alternatively, you can save SAS code files outside
of the EG project.
• Most people create EG projects that reference data
files that live outside of EG.
– SAS datasets
– Excel files
– Text files full of data
Native Excel
format
Converted to
SAS format
How SAS EG works
Data (.xls,
.sas7bdat, etc)
SAS
SAS EG
Saved
output
Shortcuts
• Windows
indicates a
“shortcut” to a
file that lives
elsewhere with
an arrow in the
bottom left
corner of an icon.
• EG uses the same
symbol to denote
a shortcut to a
file outside of the
project.
What is in an EGP file?
• An EG project file ( a file with an .egp suffix)
contains information and instructions but it
will also have links to a lot of external files.
Shortcut to a
file NOT in the
project.
This is
part of
the
project
Shortcut to a
file NOT in the
project.
EG and Code
• Most of the time you will point and click to
build an analysis but you can write and store
your “code” instructions to SAS inside of the
EG project or you can create a short cut to the
code file which lives outside of EG.
Right click and choose New > Program
Look at the process flow
No shortcut icon
External SAS files
• You can easily save a code file outside of the
project by choosing Save Program As… from
the File menu or clicking the Save or Save As …
from the program tab (when the code is
open).
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
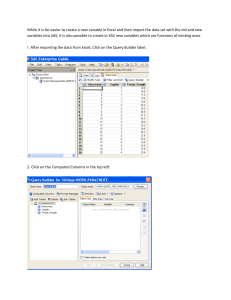
Where are SAS data sets Stored?
• While SAS can refer to files using their Windows
path, it is easier to type a short name instead of a
long path.
• SAS calls the short names “libraries”.
• EG automatically knows about a couple of places
where data can be stored.
– It creates a temporary work folder whenever EG
starts.
– It creates a permanent sasuser folder when EG is
installed.
• The locations for data are called libraries.
Where are those folders?
Look at the servers list and expand
out the tree to show:
Servers - Local - Libraries - WORK
Right click on WORK and choose
Properties.
If the Server List display is not
showing use view menu.
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
Importing the Easy Way
• The most bulletproof way for importing with
EG 4.3 is to use the import wizard and save
into the Work library.
Always
check this
on.
Double check
that it guesses
the right Type,
especially for
dates.
By default you don’t
see the library or path
to the Excel file.
Check this on
Libraries
• Prior to the version of EG that shipped with
SAS 9.3, the default behavior was for EG to
save all data into the same folder/library,
sasuser. This is a very bad idea.
– Naïve students would end up with every SAS data
set in one folder.
– Anybody using SAS can access that folder, so there
are significant HIPAA issues.
• You can right click on a file and pick Properties
to see where it is stored.
Change the Default File Location
• If you are working with an old SAS install,
change the default file location to the work
library. Do this once per machine.
Click 1st
Click 2x
Permanent Store
• I suggest that you save your data into the
temporary work library by default.
• If you have a huge file which you only want to
import once, or if you want to keep a
permanent copy of a SAS data file, you will
want to set up a permanent library.
– A library reference is just a fancy way of specifying
what folder SAS should use to save the .sas7bdat
data files.
Fix the Registry (Once) then Make a
Library
• First fix the problematic registry entries that are
described in my instructions on installing SAS.
– If you do not do this, if you have mixtures of characters
and number values in a column from Excel, programs
reading the data (including SAS) can drop the cells that
have character data without warning.
• Using Windows, make a folder
c:\blah\libraryDemo to hold the data set.
• Using SAS, make a library to point to the folder
where your data should be stored.
Tell SAS that there is
a folder which can
hold data by
creating a library.
This only makes SAS
aware of the folder.
It does not
automatically put
stuff into the folder.
It’s just a folder!
• When the library is created it is just a pointer to a
preexisting folder. That folder can contain anything.
• When you want to use the folder you need to explicitly tell
EG to store data in the folder.
• First rename your input the node and draw an arrow to
indicate where the library is used. These changes are
mostly just aesthetic.
2nd add a line to the flowchart connecting the library
to the import. It just looks good.
1st rename the node to match the library name
Now it looks
good but the
import is still into
work.
Find your library
here.
Notice it is in the library.
You can see it in
Windows.
A “design feature” is that
you have to Refresh the
library to see the freshly
added file.
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
Playing with Data
• Once the data is imported you can add code
“nodes” to the flowchart or use the graphical
user interface to tweak the data and do
Quick and easy
analyses.
subset and sorting
Complex changes
Select all variables for
the new dataset
Push Validate to see
the SQL code.
Notice the
tabs in the
output.
Notice Analysis.css hidden in the
voodoo. It has the appearance
scheme (color, bold, etc.)
Convert From a Character to a Number
• Remember that page I told you to bookmark
in OnlineDoc?
Hold the control key
and type f to bring
up the find box.
2nd
3rd Click New
4th Click Advanced
expression
5th Click Next
Convert to a 4 digit number with
the input function:
input( t1.score , 4. )
Before
After
Context sensitive
menus help you
describe the data
you are browsing.
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
Descriptive Statistics
Turn on Higher Quality Graphics
Tools > Options > Tasks > Custom Code
This is SAS code that can be cut
and pasted into a .SAS file and
run outside of EG.
I like this color
scheme.
Fixing the title is too advanced for now but it is trivial to
cut it in Illustrator or to mask it in PowerPoint.
Clean the Project
2nd Right click and rename.
3rd Right click and link it to the code
1st Right click and rename it.
In this lecture…
• How SAS works in Windows
– SAS vs EG files
– Libraries vs. Folders
•
•
•
•
Importing Data
Subsets and creating new variables
Describing Data
Making better summary tables
Table 1
• Table 1 in a manuscript describes data
grouped by something, typically a treatment.
– Frequency count by gender
– Means for age
Drowning…. is bad
• SCUBA divers practically never drown.
• Can I find any patterns in who dies?
• Load the fakeDrowningData Excel file. It is
real data based on the CDC’s mortality data
from 1999-2007:
wonder.cdc.gov/controller/datarequest/D53
The actual ages are sampled from the age bins
the CDC gives and the SCUBA rate is
simulated.
For each treatment table 1 always has…
• For continuous data, a measure of central
tendency and variability.
• Number of people
• Mean and standard deviation
• Median, min, max, 25th and 75th percentiles
• For categorical data
– Frequency counts, percentages
Too Many Nodes
Continuous
You can request lots of tables. Typically people
do one node per variable.
.M (dot M)
Add ageFixed
Now there is a useful dataset
Now the analysis is
running on the wrong
data.
Select the new
input data and
modify the node to
run on the new
variable.
The new
variable
The minimum is not -1.
N is not the number of
observations.
Notice the bug… it lost the 5 year bins.
Right click the node and reset it.
Categorical:
several
variables cross
tabulated
Outcome
Exposure
Notice the
table
request
Typically I want
row not column
percentages.
Watch the code change
as you click.
Women don’t drown while
diving and there is no
evidence of a SCUBA effect
You can rinse and repeat
building this table but then you
need to copy and paste a LOT
for your paper.
Bug with Reports
• If your table has missing data you may get an
Unable to read SAS Report file error. Use the
Tools > Options menu to turn on the procedure
titles in the output.
Categorical
and
continuous…
pretty tables.
I am going to want to count people. The
easiest way to do this is to add a new
column. Every person should have the value
1 then I can count or sum that variable.
I am going to write a program to do this…
Add a programming node to the project by
right clicking on the process flow and
choosing new program.
Make a new dataset called
analysisFinal
Base the new dataset on
everything in the analysis
dataset.
What library will the new dataset live in?
Is the variable one character or numeric?
Make a new variable call it
one and have it contain
the number one.
Describe> Summary
Tables…
Rename and link the
program…
Add Race then State.
This is too confusing
with row and column
percentages.
It is too advanced for now but you can do
fancy formatting like using colors for big or
impossible values/patterns.
You can save this as HTML and open it in
Excel to do final touches.