Driving Performance in the New Work Environment
advertisement

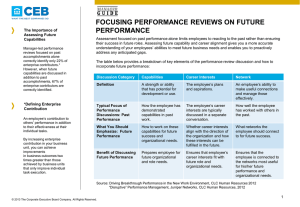
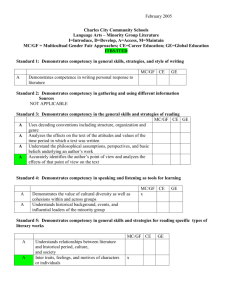
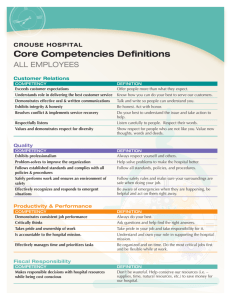
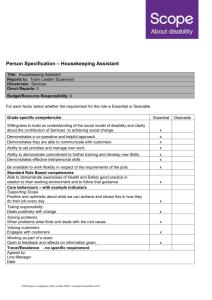
DRIVING BREAKTHROUGH PERFORMANCE IN THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT Gail Thakarar June 2014 AGENDA • Changes in the Labor Market • Driving Performance & Retention Through Employee Engagement • Driving Performance in the New Work environment CHANGES IN THE LABOR MARKET CHANGES IN THE LABOR MARKET • • • • Geographically Dispersed Workforces Higher Volume of Information More Matrixed Organization Structures Generational CHANGES IN THE LABOR MARKET WORKPLACE CHARACTERISTIC VETERANS 1922-1945 BABY BOOMERS 1946-1964 GENERATION X 1965-1980 GENERATION Y 1981-2000 Work Ethic Respect Authority, Hard work, Company first, Seniority Workaholics, Desire quality, Question authority Eliminate the task, Self reliant Want structure & direction, Skeptical What’s next, Multitasking, Tenacity, Entrepreneurial Work Is: An obligation An exciting adventure A difficult challenge, A contract A means to an end Leadership Style Directive, Command & control Quality Everyone is the same, Challenge others, Ask why Remains to be seen Communication Formal memo In person Direct, Immediate E-mail, Voicemail CHANGES IN THE LABOR MARKET WORKPLACE CHARACTERISTIC VETERANS 1922-1945 BABY BOOMERS 1946-1964 GENERATION X 1965-1980 GENERATION Y 1981-2000 Rewards & Feedback No news is good news. Satisfaction in a job well done Money. Title. Recognition. Give me something to put on the wall Sorry to interrupt but how am I doing? Freedom best reward Whenever I want it. Meaningful work Motivated By Being respected Being valued and needed Freedom and removal of rules Working with other bright people Work/Life Balance Keep them separate No balance ‘Live to work’ Balance ‘Work to Live’ Balance – It’s 5pm - I’ve got another gig Technology is: Hoover Dam The microwave What you can hold in your hand, PDA, cell Ethereal – intangible EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT WHAT IS EMPLOYEE ENGAGEMENT? •“The extent to which employees commit to something or someone in their organization, how hard they work, and how long they stay as a result of that commitment.”* •CLC research demonstrates that increased discretionary effort is a direct prediction of improved performance CLC survey of 50,000 employees found: •Engaged employees perform 20% better •87% less likely to leave the organization •1 in 10 employees are fully disengaged •No high-engagement or low-engagement groups •Engagement levels determined by company strategies and policies •Emotional engagement is 4 times more valuable than rational engagement *Defined by Corporate Leadership Council MOST EFFECTIVE LEVERS OF DISCRETIONARY EFFORT 20 MOST EFFECTIVE LEVERS OF EFFORT MANAGER IMPACT 1. Connection Between Work & Organization Strategy 2. Importance of Job to organization Success 3. Understanding of How to Complete Work Projects 4. Internal Communication 5. Demonstrates Strong Commitment to Diversity Yes 6. Demonstrates Honesty & Integrity Yes 7. Reputation of Integrity 8. Adapts to Changing Environments Yes 9. Clearly Articulates Organizational Goals Yes 10 Possesses Job Skills Yes MOST EFFECTIVE LEVERS OF DISCRETIONARY EFFORT 20 MOST EFFECTIVE LEVERS OF EFFORT MANAGER IMPACT 11. Sets Realistic Performance Expectations Yes 12. Puts the Right People in the Right Roles at the Right Time Yes 13. Helps Find Solutions to Problems Yes 14. Breaks Down Projects into Manageable Components Yes 15. Accepts responsibility for successes & failures Yes 16. Encourages & Manages Innovation Yes 17. Accurately Evaluates Employee Potential Yes 18. Respects Employees as Individuals Yes 19. Demonstrates Passion to Succeed Yes 20. Cares About Employees Yes MAXIMUM IMPACT ON DISCRETIONARY EFFORT Change in Discretionary Effort EMOTIONAL Source: CLC Employee Survey RATIONAL The impact of rational commitment is much smaller DRIVING BREAKTHROUGH PERFORMANCE IN THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT EXECUTIVE EXPECTATIONS Percentage of Executives 32% 59% 67% 33% Increase Stay the Same Decrease 15% 17% 26% Revenue Expectations 35% 16% Cost Pressures Headcount Source: Business Barometer Quarterly Report, CEB Finance Leadership Council, Q3 2012 Percentage of Employees PERCENTAGE OF EMPLOYEES EXPERIENCING AN INCREASE IN WORKLOAD IN THE PAST 3 YEARS Source: CEB, CLC, HR High Performance Survey, 2012 TO ACHIEVE PROFITABLE GROWTH • Understand the most important changes taking place in the new work environment and the implications for employee performance and productivity • Identify the necessary new skills and competencies for employees to be productive and determine how best to quickly build them across the workforce, and • Adjust management approaches and target technology investments to better enable high performance UNDERSTAND THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT • Frequent Organizational Change – more and frequent – greater financial uncertainty – organizational downsizing • Interdependent Work – cross-function or departmental work groups – matrix reporting relationships – Geographically dispersed workforce – Team-based work • Knowledge Work – New information technology – More non routine work – Greater information availability NEW COMPETENCIES: DRIVERS OF PERFORMANCE HIGH PERFORMER CHARACTERISTICS NEW COMPETENCIES – DRIVERS OF PERFORMANCE Adapt to Change Organizational Awareness (3) Self-Awareness (5) Proactivity (6) Learning Agility (9) Work Collaboratively Teamwork (2) Influence (7) Technical Expertise (10) Apply Judgment Prioritization (1) Problem Solving (4) Decision Making (8) Source: CEB - High Performance Survey TECHNOLOGY INVESTMENTS Target Technology Investments to the Evolving Needs of Knowledge Workers & Collaborative teams • Build back from employee needs, not just broad business needs • Identify and use early adopters to redefine technology needs • Fix data accessibility and usability • Create collaboration platforms to make immediate , inthe-moment interactions easy • Provide a wider array of analytic application Business Unit Performance Against Profit Goals EMPLOYEE PERFORMANCE SCORES CANNOT PREDICT BUSINESS UNIT PERFORMANCE Business Unit-Specific Average Employee Performance Score Source: CEB, CLC, HR High Performance Survey, 2012 MODEL OF HIGH PERFORMANCE Individual Task Performance An employee’s effectiveness at achieving his / her individual tasks and assignments + Network Performance An employee’s effectiveness at improving other’s performance and using other’s contributions to improve his or her own performance = Enterprise Contribution An employee’s effectiveness at his / her individual tasks, contribution to others’ performance, and use of others’ contributions to improve his / her own performance Business Unit Outcomes • Profit • Revenue THE ENTIRE WORKFORCE MUST DISPLAY ENTERPRISE CONTRIBUTION Percentile Change in Profit High Individual Task and Network Performance (High Enterprise Contribution) High Individual Task Performance Alone Percentage of Employees Source: CEB, CLC, HR High Performance Survey, 2012 FOUR IMPLICATIONS FOR COMPETENCY MODEL DESIGN Problem Solving Organizational Awareness Teamwork Prioritization From: 1 Prioritizes Tasks: Prioritizes activities to fulfill job description and manager directs work 2 Builds Connections: Increases the number of, and maintains strong, personal relationships 3 Knows Formal Organization: Understands business basics and the formal structure and mechanics of the organization 4 Receptive to Change: Displays openness and willingness to change behavior in response to new situations To: Prioritizes Contributions: Prioritizes activities based on organizational goals and self-directs work Understands Peers’ Motivations: Coordinates one’s work and performance with that of others to achieve mutual outcomes Understands Organizational Context: Understands the informal structures and decision-making processes of the organization Initiates Change: Identifies problems or opportunities for changes and implements solutions when appropriate TO DRIVE BREAKTHROUGH PERFORMANCE IN THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT • Design jobs and roles that provide: – Clear guidelines for network responsibilities, not just individual responsibilities – Boost manager effectiveness at facilitating and advising not filtering – Design roles to facilitate critical relationships, not tasks TO DRIVE BREAKTHROUGH PERFORMANCE IN THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT • Improve Critical Competencies: – Update competency models to reflect fundamental changes in how employees’ prioritize their contributions, work with others, understand the organization and initiate change – Tailor core competency models for critical employee segments – Incorporate customer input to improve the relevance and impact of competency models – Consider the needs of specific business lines and customize the relative importance of behaviors for each specific group TO DRIVE BREAKTHROUGH PERFORMANCE IN THE NEW WORK ENVIRONMENT • Performance Management Systems – Update current performance management approaches to better align with changes in the nature of work – Orient talent investments toward improving individual task and network performance – Focus on shifting all employees, not just a handful of ‘A-players’ to higher enterprise contribution to achieve breakthrough performance QUESTIONS?