What is Truth ?
advertisement

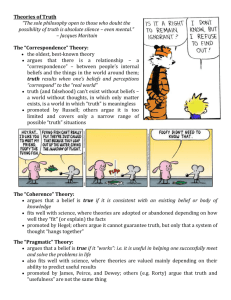
2+2=4 Your mother loves you. Death is a part of life. The sky is blue. Truth PowerPoint What do we mean when we say we “know” something? Ex. “I know my car is in the parking lot.” If P is any proposition, what requirements must we meet to claim P? a) We must believe that P is the case (knowledge implies belief, but belief does not imply knowledge-assumption b) We have evidence for justification or warrantability (sufficient reason for belief … how much is enough?) c) Knowledge requires truth! Knowledge is warrented, true belief. To understand knowledge, we must understand warrantability and truth. Modes of Warrantability Logical warrantability – laws of logic Semantic warrantability – analyzing the meaning of words Systemic warrantability – derive warranty from logical interdependence of all propositions in a deductive system Empirical warrantability – confirmatory relation to specific qualities of first person experience, sometimes conformation needed outside self Warrantability does not imply truth Warrantability = justification and evidence Warrantability comes in degrees, truth does not What is Truth? •Truth is closely connected to knowledge and belief •“The contemplation of truth and beauty is the proper object for which we were created” William Hazlett I. The Correspondence Theory of Truth Most popular theory of truth Plato, Aristotle & Aquinas Truth is an agreement between a proposition and a fact Bertrand Russell (1872-1970) states that there is a realm of facts that exists independent of us (e.g. Toronto is the capital of Ontario) … “the truth” of a belief depends on whether the belief corresponds to the independent fact Critiques of the Correspondence Theory Critics ask “what is a fact ?” Assumes that we know our experience of things and also facts about the world II. The Coherence Theory of Truth Adherents include Leibniz, Spinoza and Hegel A statement is true if it is consistent with other statements that we regard as true Brand Blanchard (18921989) said that “an agreement between judgments is best described not as a correspondence but as a coherence.” Geometry constructs an entire system of truths by building on a few basic axioms Critique of the Correspondence Theory Does not distinguish between consistent truth and consistent error A judgement may be true if it accords with other judgments, but what if other judgments are false? Result is a system of consistent error What does the first judgement cohere with? III. The Pragmatic Theory Pragmatism develops in the west …. William James (1842-1910) and John Dewey (1859-1952) …if something works it is true ! There is no absolute truth … truth is dynamic changing, subjective and relative See if the belief satisfies the whole of human nature over a long period of time A statement is true if people can use it to get the results that they need Critiques of the Pragmatic Theory of Truth Critics argue that truth depends on the fallible judgments of human communities … unacceptable If truth is not absolute but relative, who is to decide what is true and what is not? Cartoons on Truth The Instrumentalist View Related to the Pragmatic Theory of Truth Scientific Theories are true if they enable us to accurately predict what will happen ...they work ! No one believed that Copernicus’ theory was an accurate description of the solar system but it explained the motion of the celestial spheres The Realist View Related to the Correspondence Theory of Truth Scientific theories are true or false in so far as they describe what really exists The goal of science is to explain the world as it really is The scientist “discovers” the scientific truth The Conceptual Relativist View Related to the Coherence Theory of Truth and the work of Thomas Kuhn A true scientific theory coheres with the conceptual framework accepted by a community of scientists Our theories about reality influence what we think we are seeing when we observe reality reality ….we cannot independently know the real world