I. Channel Performance
advertisement

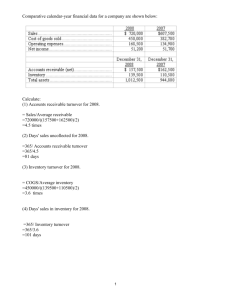
Chapter 14 Evaluating Channel Performance Major Topics for Ch. 14 •What is Channel Performance?* •Scope and Frequency of Performance Evaluations* • Channel Performance Audit •Key Criteria for Performance Audit* •Applying Evaluation Criteria •Recommending Corrective Actions •Extra Topic: Micro Channel Performance* 14 What is Channel Performance?* 14 I. Channel Performance: The extent to which the channel members meet the desired channel goals. II. Dimensions of (Macro) Channel Performance a) Efficiency: Productivity; Profitability b) Effectiveness: Stimulation of New Demand (ex: online channel); Customer Satisfaction (ex: Walk in clinic) c) Equity: Easy Access and Opportunity Ex) U.S. versus Japan; L.A. and Indian Reservation 14 Scope & Frequency of Channel Performance Evaluations Depend on* 1. Degree of the manufacturer’s control over channel members 2. Relative importance of channel members 3. Nature of the product 4. Number of channel members (channel intensity) 1. Degree of Control Control that a producer, manufacturer, or franchisor has over members is based on strong contractual agreements Channel manager can demand a great deal of information on member operations 14 Manufacturer lacks strong market acceptance for its products & strong channel control based on contractual commitments Manufacturer can exert little control over channel members 2. Importance of Channel Members Evaluation of channel members is more comprehensive for manufacturers who sell all of their output through intermediaries Why? Because the firm’s success in the market is directly dependent on the channel members’ performance 14 3. Nature of the Product The more complex the product, the broader the scope of evaluation + For products of very high unit value, the gain or loss of a single order is important to the manufacturer 14 4. Number of Channel Members Manufacturers who use intensive distribution Channel member evaluation may be cursory Manufacturers who use highly selective distribution Channel member evaluation is comprehensive 14 Performance Evaluation versus Monitoring Performance Evaluation Day-to-Day Monitoring Overall performance reviews that give management a complete & objective analysis of distributor operations Appraisals that assist management in maintaining current operating control of distributors’ efforts 14 Channel Performance Audit Three Phases of Channel Performance Audit 1. Developing evaluation criteria Channel goals 2. Periodically evaluating the performance against the criteria 3. Recommending corrective actions 14 I. Key Criteria for Channel Performance Audit* 14 • Sales performance of channel members • Inventory maintenance of channel members* • Selling/Service capabilities of channel members* • Attitudes of channel members • Competition faced by channel members* • General growth prospects of channel members* 14 1. Sales Performance Criteria channel manager should use to evaluate sales data: 1. 3. Comparisons of the channel member’s current sales to historical sales Comparisons of the channel member’s sales with predetermined quotas 2. Cross comparisons of a member’s sales with those of other members 2. Inventory Maintenance Key Criteria for evaluating member inventory performance: 1. Total level of channel member’s inventory 2. Shelf or floor space devoted to inventory 3. Shelf or floor space relative to competitors’ inventory 4. Breakdown by particular products in units & dollars 5. Comparison of figures with channel members’ estimated purchases of related & competitive lines 6. Condition of inventory & inventory facilities 7. Amount of old stock & efforts made to move it 8. Adequacy of channel member’s inventory control & record-keeping system 14 14 3. Selling Capabilities Ex) CISCO Manufacturer who obtains sales records for channel members’ salespeople should examine the following factors: 1. 3. Number of salespeople the channel member assigns to manufacturer’s product line Salesperson interest in manufacturer’s products 2. Technical knowledge and competence of channel member’s salespeople 4. Attitudes of Channel Members 4 Attitudes Not usually evaluated unless sales performance is unsatisfactory Negative ones often addressed after they have contributed to poor performance Should be evaluated independently of sales data 5. Competition 14 Channel manager should consider two types of competition: 1. 2. Competition from other Intermediaries (Inter-store) Competition from other product lines carried by the manufacturer’s own channel members (Within-Store) 14 6. General Growth Prospects Key issues for evaluating channel member growth prospects: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. Past performance Overall performance Expansion or improvement of organization Level of growth and qualification in personnel Management, age, health, or succession arrangements 6. Adaptability & overall capacity to meet market expansions 7. Member’s estimates of its own medium- & long-range outlooks 14 II. Applying Evaluation Criteria 1. Separate performance evaluations on one or more criteria Three Approaches 2. Multiple criteria combined informally to evaluate overall performance qualitatively 3. Multiple criteria combined formally to arrive at a quantitative index of overall performance 1. Separate Performance Evaluations Commonly used when the number of channel members is very large & when criteria are limited to no more than sales performance, inventory maintenance, & possible selling capabilities Cf) PQD in purchasing performance evaluation 14 2. Multiple Criteria Combined Informally Operational performance measures obtained Managerial judgment used to combine performance measures Qualitative judgment made about overall channel member performance 14 3. Multiple Criteria Combined Formally 5 Steps 1. Criteria & associated operational measures are decided on 2. Weights assigned to each of the criteria 3. Each member evaluated is rated on each of the criteria 4. Score on each criterion multiplied by weight for that criterion 5. Weighted criterion ratings summed to yield overall performance rating for each member 14 III. Recommending Corrective Actions Channel manager should attempt to find out why members have performed poorly Correction and enforcement 1. Develop concrete & practical approaches to actively seek information on member needs and problems 2. Programs of member support must be congruent* with member needs & problems 3. Constraints imposed by interorganizational setting of marketing channel must be understood 14 Dimensions of (Micro) Channel Member Performance* 14 a) Sales Performance b) Financial Performance* c) Reseller Competence d) Reseller Compliance e) Reseller Adaptation f) Reseller Growth g) End-Customer Satisfaction* Three Dimensions: Capability, Behavior, Outcome Measures of Channel Member Financial Performance 14 a) Strategic Profit Model* (a) Profit Margin (b) Asset Turnover (Turnover Ratio) (c) Return on Asset (d) Leverage Ratio (e) Return on Investment b) Economic Value Analysis : After-tax operating profit - total annual cost of capital (equity & debt) A TAXONOMY OF RETAILER TYPES* RETAILER TYPE MAIN FOCUS ON MARGIN OR TURNOVER? Margin BULKBREAKING SPATIAL CONVENIENCE WAITING & DELIVERY TIME VARIETY (BREADTH) ASSORTMENT (DEPTH) Yes Moderate Low wait time Broad Moderate/ Shallow Specialty store (e.g., The Gap) Margin Yes Moderate Low wait time Narrow Deep Mail Order/ Catalog (e.g., Lands' End) Margin Yes Extremely High Moderate/ High wait time Narrow Moderate Convenience store (e.g., 7Eleven) Both Yes Very High Low wait time Broad Shallow Category killer (e.g., Toys "R" Us) Turnover Yes Low Low wait time Narrow Deep Mass Merchandiser (e.g., Wal-Mart) Turnover Yes Low Moderate wait time (may be out of stock) Broad Shallow Hypermarket (e.g., Carrefour) Turnover Yes Low Moderate wait time Broad Moderate Warehouse Club (e.g., Sam's Club) Turnover No Low Moderate/high wait time (may be out of stock) Broad Shallow Department store (e.g., May Co.) The Strategic Profit Model Asset Turnover: Net sales/ Total Assets Profit Margin: Net Profit/ Net Sales Return on Assets: Net Profit/ Total Assets Leverage Ratio: Total Assets/ Net Worth Return On Investment: Net Profit/ Net Worth