Preoperative assessment in the Older Adult
advertisement

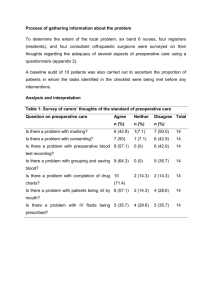
UMMS CRIT Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Erika Oleson, DO, MS Division of Geriatric Medicine University of Massachusetts Objectives By the end of this lecture, the participant should be able to identify and describe: • The purpose of preoperative assessment • How age-related physiologic changes influence perioperative care • Components of preoperative assessment • How to minimize perioperative risks UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Why do a Preoperative Assessment? • Identify specific patient related factors which may increase risk for complications • Identify procedural risks and how they can impact recovery • To recommend treatment plans to minimize complications during and after the procedure UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Key determinants of preoperative risk • Type of surgery (elective, urgent, emergent) • Functional status at baseline • Life expectancy • Co-morbid conditions • Expected outcomes and complications UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Physiological changes associated with aging • Diminished organ reserves • Decreased thermoregulation may increase risk of perioperative hypothermia • Cardiac and vascular stiffening may complicate fluid management • Decreased hepatic blood flow and number of functional nephrons may alter metabolism and clearance of several medications • Sarcopenia may prolong functional recovery • Altered sensory perception may increase risk of postoperative delirium UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Perioperative complications in the geriatric patient • Cardiac events • Infection • Delirium • Pressure ulcers • Functional decline • Malnutrition • Inadequate pain control • Deep vein thrombosis UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Components of preoperative assessment • Detailed review of clinical history and physical examination • Functional/Physical activity assessment • Cognitive evaluation • Nutritional assessment • Social support • Goals of Care • Advance directives UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Functional/Physical Activity Assessment Metabolic Equivalents 1 Examples Watching television Eating, dressing, cooking, using toilet Walking 1-2 blocks at 2-3 miles per hour Light housework 4 Climbing flight of stairs Walking on ground level at 4 mph Running a short distance Doing heavy chores (eg scrubbing floors, lifting furniture) >10 Playing moderately strenuous sports (eg golf, dance, bowling) Playing strenuous sports (eg tennis, basketball) Holt NF Perioperative Cardiac Risk Assessment Am Fam Physician 2012; 85(3):239-246 Fleisher LA, Beckman JA, Borwn KA, et al. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation and care for noncardiac surgery J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50 (17) UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation ASA Scores American Society of Anesthesiologists (ASA) score: Class I: normal healthy patient for elective surgery Class II: patient with mild systemic disease Class III: patient with severe systemic disease that limits activity but is not incapacitating Class IV: patient with incapacitating systemic disease that is constant threat to life Class V: moribund patient who is not expected to survive 24hrs with or without surgery UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Cognitive Assessment • Evaluate baseline cognitive function (Mini-cog, MOCA, MMSE, etc.) • Dementia and history of delirium increase the risk of postoperative delirium • Post-operative delirium associated with predisposing risk factors: – Age ≥ 70, cognitive impairment, limited physical function, history of alcohol abuse, abnormal serum sodium, potassium or glucose, and intraoperative blood loss • Confusion Assessment Method (CAM) is a useful screening tool for delirium UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Nutritional Assessment Instant Nutritional Assessment • No malnourishment Serum albumin >=3.5g/dl and TLC >=1,500 cells/mm3 Severe malnourishment Serum albumin <3.5g/dl and TLC < 1,500 cells/mm3 Hypoalbuminemia (<3.5mg/dl) increases risk of: - Systemic sepsis and pneumonia - Superficial and deep wound infection - Poor wound healing - Pulmonary edema and failure to wean from ventilation - All-cause mortality rate - Increased hospital length of stay and readmission rates Gibbs J, Cull W, Henderson W, Daley J, Hur K, Khuri SF. Preoperative serum albumin level as a predictor of operative mortality and morbidity: results from the National VA Surgical Risk Study. Arch Surg. 1999;134:36-42. Corti M. Serum albumin level and physical disability as predictors of mortality in older persons. JAMA 1994; 272:1036-1042 Gastroenterol Clin North Am. 2007; 36:1-22 UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Strategies to Minimize Risk: Pre-operatively • Manage hypertension - Peri-operative β-blockers for major surgery, if not contraindicated • Manage diabetes appropriately • Treat reversible factors (anemia, infection, electrolyte imbalance etc.) • Avoid prolonged periods without nutrition • Pre-operative testing, based on clinical predictors and type of surgery UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Assessing Cardiac Risk in Non-cardiac Surgery Emergency Surgery? Yes Proceed to Surgery Yes Cancel or postpone surgery; correct acute cardiac conditions Yes Proceed to surgery Yes Proceed to surgery No Are of major risk factors present? No Is procedure low risk? No Is patient able to do light housework, climb a flight of steps, walk up a hill, or run a short distance? No or unknown Assess for clinical risk factors: Hx of ischemic heart disease, prior or compensated heart failure, history of cerbrovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, renal insufficiency ≥3 risk factors High risk surgery Intermediate risk surgery Strongly consider stress testing if it will change management; if not, proceed to surgery with perioperative B-blockade 1 or 2 risk factors 0 risk factors Proceed to surgery with perioperative B-blockade; consider stress testing if it will change management Proceed to surgery Fleisher LA, Beckman JA, Borwn KA, et al. ACC/AHA 2007 guidelines on perioperative cardiovascular evaluation and care for noncardiac surgery J Am Coll Cardiol. 2007; 50 (17) UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Strategies to Minimize Risk: Postoperatively • Manage hypertension and monitor volume status • Control blood sugars appropriately in your diabetic pts • Adequate analgesia, avoid prn orders for patients with cognitive impairment • Early mobilization/Avoid prolonged bed rest • DVT prophylaxis • Avoid/Remove catheters if possible • Regularly review medications • Address nutritional needs • Communicate with proxy/family UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation Summary • Elderly patients have decreased reserves in multiple organ systems which increases their risk for several perioperative complications • Preoperative assessment should be individualized, comprehensive, and multidisciplinary • Comprehensive perioperative management minimizes complications in older patients, especially those with chronic medical problems and functional impairments UMMS CRIT 2012 Module I: Preoperative Assessment in the Older Adult Advancing Geriatrics Education (AGE) A UMMS initiative funded by the Donald W. Reynolds Foundation