Health Care Delivery System in USA
advertisement

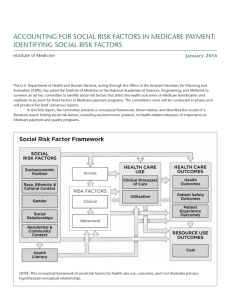
Health System in USA VIKASH R KESHRI Moderator Dr. P. R. Deshmukh Outline of Presentation: • • • • • Introduction Organizational structure Health Care Delivery System in US Components of US health System Major Stakeholders in the Health Care System in US • Health Financing: • Private Health Insurance • Government Health Insurance: Medicare Medicaid SCHIP • Public Health System • Health Care Reform 2010 in USA Introduction: • Complexity of Health System in USA • Relies on a combination of governmental action, market forces, and voluntary charitable initiatives to deliver health services. Government Market force Charitable trust Organizational Structure: Health Care Delivery System in USA: • The health care delivery system in USA is in piecemeal. • Overall the system goes like this: Physician’s Office (Self-employed physician): Contractual agreement is made between group of individual and physician office Payment mode : can be direct or by reimbursement Hospitals: large number of primary care is also provided by the hospitals only Payment mode: Direct or by reimbursement only. Components of US Health Care delivery System: Health care providers Federal Hospital Hospitals Ambulatory Care Provider Non – Federal Hospital Community Hospital Non profit For profit Mental and substance abuse care State – local government Pharmacy service providers Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs): • Unique feature of US health system. • Within the private system in US only. • Staff Model: Physicians work for HMOs. • Group Model: HMO contract with separate physicians group to provide its service. • Pre- paid group practice (PPGP). • IPA: Individual Practice Association. Major Stakeholders: Major stakeholders Health care purchaser Health care providers Other supplier, policy makers/ regulator, consumers Table.1: Health Care Expenditure pattern (2010): Total health care expenditure 100 Health Consumption Expenditure 93.7 Hospital services 30.5 Professional Services 27.1 Other health residential care 4.9 Home Care 2.7 Nursing Care and continuing care 5.5 Medical Product 13.2 Govt. Admn. 1.2 Govt. Health Insurance 5.4 Govt. public health 3.1 Investment: 6.3 Research 1.8 Structure and equipment 4.5 Figure: Personal Health Care Expenditure by type of expenditure (2009). Health Care Workforce: Table.2: Number of physician and Dentist per 10,000 populations (2010) Human Resource Number per 10,000 Active physician 27.4 Physician in patient care 25.4 Dentist 6 Health-Care Purchasers: Health Care Purchaser Private Health Insurance Employer supported Self supported Government Health Insurance Medicare Medicaid SCHIP VA Flow Chart: Over view of health financing Medicare: Three basic categories of beneficiaries: • Individuals age 65 and older, • Individuals who are permanently and completely disabled, and • Individuals with end-stage renal disease. Four major components: PART - A PART - B PART - C PART - D PART- A Coverage: Coverage under part- A is mandatory for all eligible beneficiary: • Short-stay hospital inpatient services, • Skilled nursing facilities, • Home health services, and • Hospice care. Financing for part- A: • Medicare Trust Fund: financed by employer and employee payroll tax. • Out of pocket deductible for hospital care. • Fixed amount for an episode of care. PART - B • Covers physician care and other outpatient services. • Optional benefit • Beneficiaries are responsible for paying a monthly premium. • Exposed to significant out-of-pocket costs, including deductibles, copayments, and costs for non-covered services. Part C: • covers an array of managed care plans an alternative to the traditional Medicare program. • Medicare +Choice program. Part – D: • Coverage for outpatient prescription drugs. • As part of the Medicare Modernization Act of 2003 and • Effective during 2006. Table.3: Medicare coverage for age 65 yrs. and above. Medicare Age > 65 yrs. : Medicare Medicaid 22.1 % 8.8% Employee insured plan 32.7 % Medigap 21.5 % Medicare free for service 14.9% total population covered by 47.1 million Medicare Free for all coverage 35,360 Medicaid: • Single largest health-care program in the country. • Jointly financed and administered by the federal government and individual state governments. • Beneficiary: Poor, Elderly, Disabled, Children, Pregnant Women and Parents of young children Minimum services covered: • Inpatient and outpatient medical care, • Physician services, • Laboratory and imaging services, • Family planning services, • Mental health services, • Early childhood diagnostic screening and treatment services, and • Selected long-term care services including nursing home care and home health care. Medicaid cont… Optional services: • Rehabilitation care, • Dental care, and • Home and • Community-based long-term care services. Table.3: Medicaid coverage on the basis of eligibility in year 2009 Total beneficiaries 56.0 Million Aged 65 or above 6.5% Blind or disabled 14.0% Adult in the family of 22.6% dependent children Children < 21 years 48.4% Others 8.55% Overall Medicaid coverage: Figure: Health insurance coverage among children < 18 years of age. SCHIP: State Children’s Health Insurance Program • Started in 1997. • For low-income children not eligible for the traditional Medicaid program. • Uninsured children who reside in families with incomes below 200% of the FPL or whose family has an income 50% higher than the state’s Medicaid eligibility threshold. • Jointly financed and administered by the federal government and individual state governments. Veteran’s Administrations: • Federally administered program for veterans of the military. • Health care is delivered in government-owned VA hospitals and clinics. Private Health Insurance: Employer-sponsored insurance: • Principle mode • Part of the benefits package for employees. Administration: • Private companies, both for-profit (e.g. Aetna, Cigna) and nonfor-profit (e.g. Blue Cross/Blue Shield). Self-Insured Company: • Pay for all health care costs incurred by employees directly (general motors). Private non-group (individual market): • Population that is self-employed or retired. USA: Public Health System: Public Health’s Three Core Functions: (as defined by IOM) • Assurance • Policy Development • Assessment The Ten Essential Services: • Based on the three core principles, ten essential services has been defined: Source: Wallace RB, Kohatsu N. editors. Maxcy- Rosenue – Last: Public Health and Preventive Medicine. 15th ed. New York; The Mac – Graw hill Company: 2008. P1217- 50. Unique feature of US public health system: Council on Linkages between Public Health Practice and Academia: • public health practice “de-coupled” from its academic base. • to facilitate additional activities that would enhance the practice/academic connection Organizations under the Public Health System: The current operational arms of the PHS include: • National Institutes of Health (NIH), • Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), • Health Resources and Services Administration (HRSA), • Indian Health Service (IHS), • Food and Drug Administration (FDA), • Agency for Toxic Substances and Disease Registry (ATSDR) (administered by the CDC), and Substance Abuse and Mental Health Administration (SAMHA) The state public health role: • Assessment of the health needs in the state based on statewide data collection: • Assurance of an adequate statutory base for health activities in the state • Establishment of statewide health objectives, delegating power to locals as appropriate and holding them accountable • Assurance of appropriate organized statewide effort to develop and maintain essential, personal, educational, and environmental health services; • Provision of access to necessary services; and solution of problems inimical to health • Guarantee of a minimum set of essential health services • Support of local service capacity. Health Care Reform: 2010 (Obama Care) • Long history of Reform in US. • The 2010 health reform basically enactment of 2 laws: Patient protection and Affordable care bill (PPACA) 2010. Health care and Education reconciliation act of 2010 • Key features of these laws are: Pt.’s Rights and Protection: 1. SBC: Summary of benefit and coverage: 2. Consumer Assistance Programme: • File complaints and appeals. • Enroll in health coverage • Get educated about your rights and responsibilities. Key features of 2010 Reforms cont.…… • Appealing Health Plan Decisions • Preventive Care • Patient's Bill of Rights: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. Coverage to Americans with Pre-existing Conditions: Protects consumer’s Choice of Doctors: Keeps Young Adults Covered: Ends Lifetime Limits on Coverage: Ends Pre-Existing Condition Exclusions for Children under 19: Ends Arbitrary Withdrawals of Insurance Coverage. Reviews Premium Increases: Helps Get the Most from Your Premium Dollars: Restricts Annual Dollar Limits on Coverage: Removes Insurance Company Barriers to Emergency Services: Key features cont.…. • Doctor Choice & ER Access: • Grandfathered Health Plans Insurance Choices: • • • • • Pre- Existing condition insurance plan (PCIP): Young Adult Coverage: Affordable insurance exchange: CO – OP insurance plans: Preventive and other services for > 65 years under Medicare and also covers donut hole. • Medicare Drug Discounts: to cover the donut hole Health System: US ---- INDIA • Multiple players. • Different Providers. • Private Pre- dominance. • Private Insurance • Private service providers References: • • • • • • Wallace RB, Kohatsu N. editors. Maxcy- Rosenue – Last: Public Health and Preventive Medicine. 15th ed. New York; The Mac – Graw hill Company: 2008. P1217- 50. Detel R. Holland WW. McEwen J. Ommen J. editors. Oxford Textbook of Public Health. 3rd edition. New York; Oxford University Press. US Department of Health and Human Services, Centre for Disease Control, National Centre for Health Statistics. Health – United States 2011: With Special Feature on Socioeconomic Status and Health. Hyattsville, MD. 2012. Chua KP. Overview of American Health System. Available from URL: http://www.amsa.org/AMSA/Libraries/Committee_Docs/HealthCareSystemOv erview.sflb.ashx National Center for Health Statistics, USA. Health, United States, 2011: With special feature on socio-Economic status and health. Hyattsville, MD. 2012. U. S. Department of health and human services. Key Features of law. Available from URL: http://www.healthcare.gov/law/resources/authorities/health-reform-andhhs.html