ccc revised syllabus (subject adfs details)
advertisement

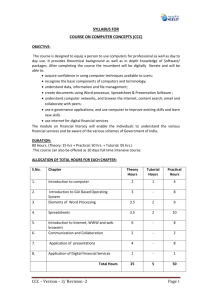
COURSE ON COMPUTER CONCEPT SUBJECT :-APPLICATION OF DIGITAL FINANCIAL SERVICES INTRODUCATION:Unbanked people are increasingly gaining access to financial services through digital channels. Banks, microfinance institutions, mobile operators, and other providers are using mobile phones and point-of-sale devices, along with networks of small-scale agents, to offer basic financial services at greater convenience and lower cost than traditional banking allows. Also referred to as branchless banking, these digital services offer great promise for better serving poor customers. Historically, the high cost of building and operating traditional bank branches has been a major obstacle for reaching poor customers with financial services. Brick-and-mortar branches are expensive for banks to maintain in far-flung communities, while traveling to urban areas is costly for many rural customers. Digital finance helps providers overcome these barriers: Agents equipped with mobile phones are the cheapest channel for processing small-value transactions for poor people at low cost and at scale. 8.1- WHY SAVINGS ARE NEEDED? Savings is the portion of income not spent on current expenditures. Because a person does not know what will happen in the future, money should be saved to pay for unexpected events or emergencies. An individual’s car may breakdown, their dishwasher could begin to leak, or a medical emergency could occur. Without savings, unexpected events can become large financial burdens. Therefore, savings helps an individual or family become financially secure. Money can also be saved to purchase expensive items that are too costly to buy with monthly income. Buying a new camera, purchasing an automobile, or paying for a vacation can all be accomplished by saving a portion of income. 1- EMERGENCIES:As much as we hope that emergencies won’t happen, we all know that they do. A family member can develop a health issue, you might need to make an emergency trip, you may have a car accident or breakdown, severe weather could flood your basement or crack your pipes, or you may have to fly to a loved one’s funeral. Any of these emergencies can be expensive, and we all know that we will likely encounter some sort of emergency from time to time. So why not be prepared rather than potentially become another victim of an emergency. 2- FUTURE NEEDS:If you intend to retire someday, you'll probably need savings and/or investments to take the place of the income you'll no longer get from your job. 3- LARGE EXPENSES:Large expenses sometimes surprise us by popping up at the most inopportune times. More often than not, however, you probably should have planned for these big expenses to pop up. A big home maintenance item, like replacing your roof or air conditioner, or an car repair can both be predicted in general terms. You know neither of these items will last forever and most people can predict the average life of these items. 8.2- DRAWBACKS OF KEEPING CASH AT HOME:- 8.3- WHY BANK IS NEEDED:The bank can send money on your behalf at your location. After all that money? Medium of exchange. Goods and services to those who produce them, changing the money. Modern man consumes a lot of services. For example, each month you may need to pay for: an apartment, telephone, intercom, garage, internet, mobile phone, etc. In this case, as long as you consume these services, you have a contract with those who provide these services, as well as these services are likely to organizations, each organization must have (must have at law) in which the account- a bank. So you stand to have to pay the organization and the organization has an account in a bank. You can pay in two ways to come to the accounting department of the organization whose services consume, and to withdraw cash from the cashier. Or, open an account in any bank (because you can send money from any bank in any) and pay the necessary organization of wire transfer directly from your bank account, they withdraw money from your account and the bank will be transferred to the bank account of the organization to which you gathered to pay. I think you are all clear? 8.4- BANKING PRODUCT:1- TYPE OF ACCOUNTS AND DEPOSIT:Savings Account Savings Account is meant for saving purposes. Any individual either single or jointly can open a savings account. Most of the salaried persons, pensioners and students use Savings Account. The advantage of having Savings Account is Banks pay interest for the savings. The saving account holder is allowed to withdraw money from the account as and when required. The rate of interest ranges between 4% to 6% per annum in India. There is no restriction on the number and amount of deposits. But withdrawals are subjected to certain restrictions. Some banks recommend to maintain a minimum amount to keep it functioning. Recurring Deposit Account Recurring deposit account or RD account is opened by those who want to save certain amount of money regularly for a certain period of time and earn a higher interest rate. In RD account a fixed amount is deposited every month for a specified period and the total amount is repaid with interest at the end of the particular fixed period. The period of deposit is minimum six months and maximum ten years. The interest rates vary for different plans based on the amount one save and the period of time and also on banks. No withdrawals are allowed from the RD account. However, the bank may allow to close the account before the maturity period. These accounts can be opened in single or joint names. Banks are also providing the Nomination facility to the RD account holders. Fixed Deposit Account In Fixed Deposit Account (also known as FD Account), a particular sum of money is deposited in a bank for specific period of time. It’s one time deposit and one time take away (withdraw) account. The money deposited in this account cannot be withdrawn before the expiry of period. However, in case of need, the depositor can ask for closing the fixed deposit prematurely by paying a penalty. The penalty amount varies with banks. A high interest rate is paid on fixed deposits. The rate of interest paid for fixed deposit vary according to amount, period and also from bank to bank. Current Account Current account is mainly for business persons, firms, companies, public enterprises etc and is never used for the purpose of investment or savings. These deposits are the most liquid deposits and there are no limits for number of transactions or the amount of transactions in a day. While, there is no interest paid on amount held in the account, banks charges certain service charges, on such accounts. The current accounts do not have any fixed maturity as these are on continuous basis accounts. 2- TYPE OF LOAN AND OVERFRAFTS:Lending money is one of the two major activities of any Bank. Banks accept deposit from public for safe-keeping and pay interest to them. They then lend this money to earn interest on this money. In a way, the Banks act as intermediaries between the people who have the money to lend and those who have the need for money to carry out business transactions. The difference between the rate at which the interest is paid on deposits and is charged on loans, is called the "spread". Banks lend money in various forms and they lend for practically every activity. Let us first look at the lending activity from the point of view of security. Loans are given against or in exchange of the ownership (physical or constructive) of various type of tangible items. Some of the securities against which the Banks lend are : Commodities Debts Financial Instruments Real Estate Automobiles Consumer durable goods Documents of title Apart from the above categories, the Banks also lend to people on the basis of their perceived personal worth. Such loans are called clean and the Banks are understandably cagey about extending such loans. The credit card arms of the various Banks, however, fill up this void. Cash credit Account:This account is the primary method in which Banks lend money against the security of commodities and debt. It runs like a current account except that the money that can be withdrawn from this account is not restricted to the amount deposited in the account. Instead, the account holder is permitted to withdraw a certain sum called "limit" or "credit facility" in excess of the amount deposited in the account. Cash Credits are, in theory, payable on demand. These are, therefore, counter part of demand deposits of the Bank. Overdraft:The word overdraft means the act of overdrawing from a Bank account. In other words, the account holder withdraws more money from a Bank Account than has been deposited in it. How does this account then differ from a Cash Credit Account The difference is very subtle and relates to the operation of the account. In the case of Cash Credit, a proper limit is sanctioned which normally is a certain percentage of the value of the commodities/debts pledged by the account holder with the Bank. Overdraft, on the other hand, is allowed against a host of other securities including financial instruments like shares, units of mutual funds, surrender value of LIC policy and debentures etc. Some overdrafts are even granted against the perceived "worth" of an individual. Such overdrafts are called clean overdrafts. Bill Discounting:Bill discounting is a major activity with some of the smaller Banks. Under this type of lending, Bank takes the bill drawn by borrower on his(borrower's) customer and pay him immediately deducting some amount as discount/commission. The Bank then presents the Bill to the borrower's customer on the due date of the Bill and collect the total amount. If the bill is delayed, the borrower or his customer pay the Bank a pre-determined interest depending upon the terms of transaction. Term Loan:Term Loans are the counter parts of Fixed Deposits in the Bank. Banks lend money in this mode when the repayment is sought to be made in fixed, predetermined installments. This type of loan is normally given to the borrowers for acquiring long term assets i.e. assets which will benefit the borrower over a long period (exceeding at least one year). Purchases of plant and machinery, constructing building for factory, setting up new projects fall in this category. Financing for purchase of automobiles, consumer durables, real estate and creation of infra structure also falls in this category. 3- FILLING UP TO CHEQUES, DEMAND DRAFTS:A demand draft is a document that allows you to withdraw money from another person's without needing a signature. The person that is withdrawing money will need to have routing and account numbers, in addition to the account holder's permission. Learn how to safely use a demand draft to easily transfer funds. Gather the necessary information. Before a demand draft can be created and deposited, the proper information will need to be acquired. This information will be used to fill out the demand draft itself and will be examined by the bank when it is deposited. See the following overview of the information that will be required: o o o If selling an item or service you will need to provide accurate details to your client about that item or service. You will need to obtain the account and routing numbers of the account belonging to the person paying. Consent by the person whose account will be debited to the transferral of funds by demand draft, written or verbal, must be obtained. Verbal consent should be recorded, while written consent might take the form of a faxed document with a signature and date. Give legally required information if selling a service or good. If you are working remotely with a client to sell them a service or good, it is a good idea to provide the proper information about either, as this can limit liability or promote customer relations. In addition, the financial institution accepting a demand draft might have consumer protection requirements before agreeing to transfer. Inform your client upfront about your sale by meeting the following criteria: o o o o The exact price and amount of items or services being sold. Additional information about the item or service regarding extra fees, deposits, certifications, limitations, etc. Any refund policy or no-refund policy. If any prizes for purchase are being offered, the exact details must be disclosed. These details include the chances of winning, costs of winning, or methods of entry with or without payment. o Any payment plan that is similar to a “free-trial offer,” which will require the buyer to take action to avoid future payments. Obtain information regarding your client's bank account. You will need to acquire the necessary pieces of information to successfully deposit the demand draft in your own bank account. Since a demand draft doesn't require a signature, providing accurate information is critical. o o You will need to obtain both the account number and routing number of the bank account being used to make the payment or payments. Routing and account numbers are found at the bottom of a check. The routing number appears first, at left, and consists of nine digits. The account number appears after the routing number, just to the right of it. Obtain consent. Although a demand draft doesn't require a signature, it does require some form of consent on the part of the person having money withdrawn from their account. Either written or spoken consent will suffice. o o o o Verbal consent is acceptable; however, you will need to have a recording of the consent. You may wish to record the entire conversation. If making a recording of verbal consent, make sure to include the date of the agreement, the amount being agreed upon, the name of the client, the number of payments, a telephone number where the client can call, and the date of authorization. [ Obtaining written consent can be the safest option. However, it may take more time as you wait for the written form of consent to arrive. Have the client write the date he agreed, the amount he agreed to pay, his name, number of payments, telephone number where the client can call, and the date of authorization. Written consent may be obtained in the form of a fax signed by both parties or avoided check sent by the client. 8.5- DOCUMENT FOR OPENING ACCOUNTS:1- KNOW YOUR CUSTOMER (KYC) :The objective of KYC guidelines is to prevent banks from being used, intentionally or unintentionally, by criminal elements for money laundering activities. Related procedures also enable banks to better understand their customers and their financial dealings. This helps them manage their risks prudently. Banks usually frame their KYC policies incorporating the following four key elements: Customer Policy; Customer Identification Procedures; Monitoring of Transactions; and Risk management. For the purposes of a KYC policy, a Customer/user may be defined as: a person or entity that maintains an account and/or has a business relationship with the bank; one on whose behalf the account is maintained (i.e. the beneficial owner); beneficiaries of transactions conducted by professional intermediaries such as stockbrokers, Chartered Accountants, or solicitors, as permitted under the law; or any person or entity connected with a financial transaction which can pose significant reputational or other risks to the bank, for example, a wire transfer or issue of a highvalue demand draft as a single transaction. 2- PHOTO ID PROOF, ADDRESS PROOF 4- INDIAN CURRENCY : 8.6 The Rupee, or more specifically the Indian Rupee (symbol: ₹; ISO code: INR) (Unicode U+20B9) is the official currency of the Republic of India. The issuance of the currency is controlled by the Reserve Bank of India.[2] It is named after the silver coin, rupiya, first issued by Sultan Sher Shah Suri in the 16th century and later continued by the Mughal Empire. The modern rupee is theoretically subdivided into 100 paise (singular paisa), though as of 2011 only 50 paise coins are legal tender.[3][4] Banknotes in circulation come in denominations of ₹1, ₹2, ₹5, ₹10, ₹20, ₹50, ₹100, ₹500 and ₹1000. Rupee coins are available in denominations of ₹1, ₹2, ₹5, ₹10. The Indian rupee symbol '₹' (officially adopted in 2010) is derived from the Devanagari consonant (ra). The first series of coins with the rupee symbol was launched on 8 July 2011.[citation needed] The Reserve Bank manages currency in India and derives its role in currency management on the basis of the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934. BANKING SERVICE DELIVERY CHANNELS- I 1- BANK BRANCH AND ATM:A branch, banking center or financial center is a retail location where a bank, credit union, or other financial institution (and by extension, brokerage firms) offers a wide array of face-to-face and automated services to its customers. ATMs are scattered throughout cities, allowing customers easier access to their accounts. debit or credit card will be able to access most ATMs. Using a machine operated by your bank is usually free, but accessing funds through a unit owned by a competing bank will usually incur a small fee. 1. Debit Card An electronic card issued by a bank which allows bank clients ... 2. Service Charge A type of fee charged to cover services related to the primary ... 3. Activity Charge A fee charged to cover the servicing costs of an account. An ... Cash Card A cash card can be any card that you can insert into an ATM or ... 4. Deposit Slip A small written form that is sometimes used to deposit funds ... 5. Descriptive Statement A bank statement that lists deposits, withdrawals, fees, etc. ... 2- BANK MITRA WITH MICRO ATM:Micro-ATMs are biometric authentication enabled hand-held device. In order to make the ATMs viable at rural/semi-urban centers, low cost MicroATMs would be deployed at each of the Bank Mitra location. This would enable a person to instantly deposit or withdraw funds regardless of the bank associated with a particular Bank Mitra/Business Correspondent. This device will be based on a mobile phone connection and would be made available to every Bank Mitra/Business Correspondent. Customers would have to get their identity authenticated and withdraw or put money into their bank accounts. This money will come from the cash drawer of the Bank Mitra/Business Correspondent. Essentially, Bank Mitra will act as bank for the customers and all they need to do is verify the authenticity of customer using customer's UID. The basic transaction types to be supported by micro ATM are Deposit, Withdrawal, Fund transfer and Balance enquiry. Micro-ATM offers one of the most promising options for providing financial services to the unbanked population. Micro-ATMs would have various options of authentication like biometric, PIN based etc. and it would also be used as mobile ATMs to enable transactions near the door step of the customers. The MicroATMs offer an online interoperable, low-cost payments platform to everyone in the country. 3- POINT OF SALE:ATM Location is point of sales. BANKING SERVICE DELIVERY CHANNELS- II 1- INTERNET BANKING :Banking online or by phone allows you to make banking transactions such as transferring money, paying a bill, checking your balance or setting up a regular payment on your bank or building society’s secure website. Online banking is accessible via a computer or a mobile phone. Also known as internet banking. What would I use this for You can make a range of payments: such as paying utility, tax and credit cards; bills; make one-off payments to other individuals, small businesses or tradesmen; and make transfers to other bank accounts or savings accounts. How do I use it You will need to speak to your bank to get set up to use their phone or internet banking service. You will need the name, sort code and account details of the company/or person you want to pay. You will also be asked to provide a reference so that the person or company receiving the number knows what the payment is for. Online payments You will need to log on to your bank or building society’s internet banking service. Although different banks will structure their websites in different ways when making a payment you are likely to be asked to select the recipient from a list of previous payees (or recipients) or to input a new payee’s details (and there may be additional security checks before you can add a new recipient). You’ll then be asked to enter the amount you want to pay, and to re-verify that the amount is correct. Your payment will be confirmed. Phone payments Work in a similar way to internet banking and you will need to have registered to use the service. Your bank will have a designated phone banking number, and you will need to answer some security questions before you can check your balance or set up or make a payment. 2- NATIONAL ELECTRONIC FUND TRANSFER (NEFT) :National Electronic Funds Transfer (NEFT) is a nation-wide payment system facilitating one-to-one funds transfer. Under this Scheme, individuals can electronically transfer funds from any bank branch to any individual having an account with any other bank branch in the country participating in the Scheme. Use NEFT service to transfer funds anywhere using the following modes: Internet Banking I Mobile 3- REAL TIME GROSS SETTLEMENT (RTGS) :The full form of RTGS is "Real Time Gross Settlement". RTGS can be defined as “as the continuous (real-time) settlement of funds transfers individually on an order by order basis (without netting") What do you mean by Real Time? What is the Meaning of Gross Settlement? Here the words 'Real Time' refers to the process of instructions that are executed at the time they are received, rather than at some later time. On the other hand "Gross Settlement" means the settlement of funds transfer instructions occurs individually (on an instruction by instruction basis). The settlement of funds actually takes place in the books of RBI and thus the payments are considered as final and irrevocable. 8.7 – INSURANCE:A promise of compensation for specific potential future losses in exchange for a periodic payment. Insurance is designed to protect the financial well-being of an individual, company or other entity in the case of unexpected loss. Some forms of insurance are required by law, while others are optional. Agreeing to the terms of an insurance policy creates a contract between the insured and the insurer. In exchange for payments from the insured (called premiums), the insurer agrees to pay the policy holder a sum of money upon the occurrence of a specific event. In most cases, the policy holder pays part of the loss (called the deductible), and the insurer pays the rest. Examples include car insurance, health insurance, disability insurance, life insurance, and business insurance. LIFE INSURANCE AND NON- LIFE INSURANCE:Life insurance is an insurance cover that gives out a certain amount to the insured or their nominated beneficiaries upon a certain event such as death of the individual who is insured. For our convenience and better understanding it won’t be wrong to state that Life Insurance is related to a human life. It’s basically a long term investment and requires periodic payments, either monthly or quarterly or annually. The risks that are covered by Life Insurance include – premature death, income during retirement, illness. The main products for the same consists of – whole life, endowment, term, medical and health, life annuity plan. Now, we move on to Non-Life Insurance which is covers things apart from the things covered in Life Insurance. It is basically an insurance policy to protect an individual against losses and damages other than those covered by Life insurance. The coverage period for most non-life insurance policies and plans is usually one year, whereby premiums are normally paid on a one time basis. The risks that are covered by non-life insurance is property loss (stolen car or burnt house), liability arising from damage caused by an individual to a third party, accidental death or injury. The main products of non-life insurance includes – motor insurance, fire/house owners/householders insurance, personal accident insurance, medical and health insurance and travel insurance. 8.8- VARIOUS SCHEMES IN INDIA:1- PRADHAN MANTRI JAN DHAN YOJANA (PMJDY):The Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana or more popularly known as PMJDY scheme is planning on revolutionizing the traditional banking system in India by providing the banking opportunity and insurance coverage to all including the poor. It is an initiative taken by the Prime Minister Narendra Modi who started this ambitious project to help the poor become more financially confident through this venture and allowing every citizen the right to have their own bank account and insurance coverage which was previously impossible for most of the population under poverty. The purpose of this scheme will definitely benefit the overall economy of the country and the scheme provides some lucrative benefits which should certainly be availed and considered. Here is listed some important benefits of the Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojna (PMJDY) scheme which would certainly inspire the country to a more prosperous future for all. Life insurance under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Under the PMJDY scheme the account holders will be given worth Rs.30000 insurance coverage if they comply with certain specification of the scheme which includes opening an account by January 26, 2015 and having an accidental insurance coverage of over Rs. 200000. Loan benefits under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana The account holder can take loan benefit of up to Rs.5000 from the bank after six months from opening the account. Though the amount might seem insignificant for many but we have to realize the scheme is directed mostly towards people below the poverty line and who are struggling desperately to sustain their everyday living. The loan benefit can be a scintilla of hope for those people who could utilize the loan amount and invest it in a more profitable outcome, particularly in farming or other agricultural prospect. Mobile banking facilities under Pradhan Mantri Jan Dhan Yojana Though the technology of using smart phones to conduct our bank transactions is not novel anymore but the PMJDY scheme will allow its account holders to avail the same facilities of checking balance and transferring funds through a normal cell phone which is more affordable to the general economy. Hence PM Jan Dhan Yojana is indeed a prosperous venture and we certainly hope the Prime Minister and the mass economy are both benefited through this new venture. 8.9- SOCIAL SECURITY SCHEMES:1- PRADHAN MANTRI SURAKSHA BIMA YOJANA (PMSBY):Insurance is not a newer concept to India; however, its reach is still much limited. In spite of so many insurance companies operating in India with their products and services, there are a majority of people in rural areas, who are not at all covered under any kind of insurance. Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana is for them. These people are those who are mostly below the poverty line and insurance is an unaffordable service for them. PMSBY aims to reach such people with its benefited insurance schemes after the successful performance of Jan Dhan Yojana. Suraksha Bima Yojana Benefits The death benefits are up to 2 lakhs In case of irrecoverable and total loss of both hands, both eyes or sight or one leg or foot, the insurance cover would be up to 2 lakh In case of lost of one leg, hand, foot, eye or sight, the sum assured would be Rs 1 lakh 2- PRADHAN MANTRI JEEVAN JYOTI BIMA YOJANA (PMJJBY):One such scheme recently launched is Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY), that offers a renewable life insurance cover of Rs 2 lakh with just a mere premium of Rs 330. Any Indian resident within the age group of 18 to 50 years is eligible to avail the scheme, provided he or she has a saving bank account with which the scheme would be attached. 3- ATAL PENSION YOJANA (APY) :Named after the ex-prime minister of India, Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Atal Pension Yojana also known as APY Scheme was launched in continuation to the Jan Dhan Yojana Scheme to bring those employed in rural and unorganized sector under the ambit of Pension Schemes. The idea of the scheme is to provide a definite pension to all Indians. However, in order to get pension during your old age, you need to contribute accordingly. The more you can contribute the more pensions you would get during old age. The scheme is backed by Ministry of Finance, Government of India. The scheme would mostly touch those working under unorganized sector. Named after the ex-prime minister of India, Atal Bihari Vajpayee, Atal Pension Yojana also known as APY Scheme was launched in continuation to the Jan Dhan Yojana Scheme to bring those employed in rural and unorganized sector under the ambit of Pension Schemes. The idea of the scheme is to provide a definite pension to all Indians. However, in order to get pension during your old age, you need to contribute accordingly. The more you can contribute the more pensions you would get during old age. The scheme is backed by Ministry of Finance, Government of India. The scheme would mostly touch those working under unorganized sector. 4- PRADHAN MANTRI MUDRA YOJANA (PMMY) :Population engaged in small businesses always requires micro finance to facilitate their business and day to day business needs. PM Mudra Bank Yojana would help in facilitating micro credit up to Rs 10 lakh to such small business owners. PM Mudra Bank already has a corpus of more than Rs 70,000 CR and this amount would help in increasing the overall output and creating newer jobs. 8.9 – NATIONAL PENSION SCHEME:NPS is an easily accessible, low cost, tax efficient, flexible and portable retirement savings account. Under the NPS, the individual contributes to his retirement account and also his employer can also co contribute for the social security/welfare of the individual. NPS is designed on Defined contribution basis wherein the subscriber contributes to his account, there is no defined benefit that would be available at the time of exit from the system and the accumulated wealth depends on the contributions made and the income generated from investment of such wealth. The greater the value of the contributions made, the greater the investments achieved, the longer the term over which the fund accumulates and the lower the charges deducted, the larger would be the eventual benefit of the accumulated pension wealth likely to be. Who can Join NPS? Any citizen of India, whether resident or non resident, subject to the following conditions: Individuals who are aged between 18 –60 years as on the date of submission of his/her application to the POP/ POP SP. The citizens can join NPS either as individual uals or as an Employee -employer group(s) (corporate) subject to submission of all required information and Know your customer (KYC) documentation. After attaining 60 years of age, you will not be permitted to make further contributions to the NPS accounts. PUBLIC PROVIDENT FUND (PPF) SCHEME:The Public Provident Fund (PPF) Scheme, 1968 is a tax-free savings avenue that was introduced by the Ministry of Finance (MoF) in India in the year 1968. Interest earned on deposits in the PPF account are not taxable. Deposits made towards PPF accounts can be claimed as tax deductions. This makes the PPF Scheme one of the most tax efficient instruments in India. It was launched to encourage savings among Indians in general, especially to encourage them to create a retirement corpus. Public Provident Fund (PPF) Accounts People can deposit funds in PPF accounts (Public Provident Fund accounts) for a fixed period of time to earn returns on their savings. The current PPF interest ratethe financial year 2015 - 2016 is 8.7% p.a. Since this scheme was launched to encourage savings across income classes, minimum deposit requirements are very low and affordable. They are also tax-free accounts, easily accessible, safe (being backed by the government) and simple to understand, making them a popular investment avenue for a large majority of individuals in India. PPF accounts can be opened at any nationalized, authorized bank and authorized branches / post offices. PPF accounts can be opened at specific private banks as well. These accounts can be opened by filling out the required forms, submitting the relevant documents and depositing the minimum pay-in at such branches/offices that have been authorised for the same. Interest rates are set and announced by the government of India. Interest is calculated for a financial year according to the rate announced for the said year i.e. unlike bank FDs the rates are not fixed for the entire tenure of the holding. The maximum amount that can be deposited in the account is also subject to change. The period from April 1st - March 31st i.e. a financial year is considered to be a deposit year for a PPF account. E.g. for an account opened in November 2010 - 2011, Year 1 will be April 1st 2011 - March 31st 2012. 8.10- BANK ON YOUR MOBILE :1- MOBILE BANKING:Mobile banking is a service provided by a bank or other financial institution that allows its customers to conduct a range of financial transactions remotely using a mobile device such as a mobile phone or tablet, and using software, usually called an app, provided by the financial institution for the purpose. Mobile banking is usually available on a 24-hour basis. Some financial institutions have restrictions on which accounts may be accessed through mobile banking, as well as a limit on the amount that can be transacted. The types of financial transactions which a customer may transact through mobile banking include obtaining account balances and list of latest transactions, electronic bill payments, and funds transfers between a customer's or another's accounts. Some also enable copies of statements to be downloaded and sometimes printed at the customer's premises; and some banks charge a fee for mailing hardcopies of bank statements. 2- MOBILE WALLETS:Mobile wallets are essentially digital versions of traditional wallets that someone would carry in their pocket. While there are many variations, usually they can hold digital information about credit and debit cards for making payments, store coupons and loyalty programs, specific information about personal identity and more. Many companies are jumping into the mobile payments space— on both the paying and receiving sides of the transaction—and new innovators are continuously changing the industry. In the U.S., they include companies such as Google, Amazon, PayPal, Square, and Apple. Internationally, still more companies are developing and launching new technologies in this space. How does a mobile wallet work? A customer can utilize all of their stored information simply by opening an app on their phone, entering in a PIN, password or fingerprint and then selecting the information they need to access. The app then utilizes information transfer technology such as Near-Field Communications (NFC) to interact with a mobile wallet ready payment terminals. Mobile wallets store your credit or debit card securely. They may also store your loyalty cards, coupons, tickets, etc. They communicate with terminals using a variety of technologies. That's where you come in as a small business owner. Without a device that receives mobile wallet information, you won't be able to take advantage of this increasingly popular payment mechanism. 8.11- SUMMARYTHANKS FOR USE IT. (L.B. COMPUTER CENTRE SAMITI TEAM)