Meaning, nature and relevance of insurance
advertisement

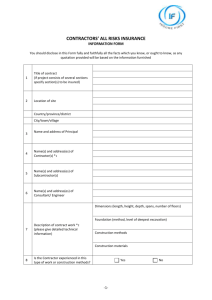
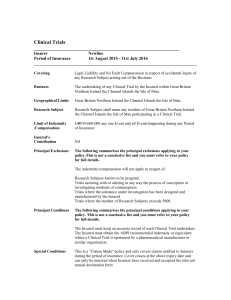
INTRODUCTION We are exposed to many risks in our day to day life. Nobody can predict what may happen in the next moment. There may be an accident, calamity, theft, loss due to certain other cause etc. Similarly, there are always risks in business. Everybody feels like shifting the risk to some agency which can compensate in case of loss or damage. MEANING OF RISK: Risk is expressed differently by people. To some, it is the chance or possibility of loss, to others, it may be uncertain situations. The word ‘risk’ has been defined as follows: “Risk is a condition in which there is a possibility of an adverse deviation from a desired outcome that is expected or hoped for”. DEFINITION OF INSURANCE CONTRACTUAL DEFINITION: In the words of E.W. Patterson, “Insurance is a contract by whichg one party, for a consideration, called premium, assumes a particualr risk of the other party and promises to pay to him or his nominee a certain or ascertainable sum of amount on a specified contingency.” IMPORTANT TERMS USED IN INSURANCE RISK PERIL CONTINGENCY COMPENSATION INSURANCE POLICY INSURER INSURED PREMIUM INSURANCE TERMS INSURED AMOUNT NATURE & SCOPE OF INSURANCE 1. sharing of risk 2. Cooperative instrument 3. Evaluation of risk 4. Payment is linked to contingency 5. Contract 6. Consideration Continued…… 7. Good Faith 8. Contract of Indemnity 9. Insurable Interest 10. The Amount 11. Large no. of insured persons 12. It is not gambling and charity FUNCTIONS OF INSURANCE PRIMARY FUNCTIONS SECONDARY FUNCTIONS OTHER FUNCTIONS PRIMARY FUNCTIONS Providing Cover for Risk Distribution of Loss Provides Security SECONDARY FUNCTIONS Provides Funds for Development Helps in Increasing Efficiency Provides Certainty Sharing of Risk Helping Businessmen Helpful in Reducing Losses Proper Assessment of Projects a) Marine Insurance b) Fire Insurance GENERAL INSURANCE c) Social Insurance d) Liability Insurance KINDS OF INSURANCE e) Other insurance LIFE INSURANCE a) Double Insurance b) Reinsurance c)Over Insurance OTHERS d) Under Insurance CHARACTERISTICS OF INSURANCE ASSURANCE AND INSURANCE BASIS OF DIFFERENCE ASSURANCE INSURANCE 1. Scope This word is used only in Life Insurance contract. Hence the scope is limited. The word is used to describe all other types of insurance. Hence the scope is wider 2. Renewal of Policy Requirement of renewal of policy is only if policy lapse as lifer insurance contract is a continuing contracts. Indemnity insurance is only for maximum one year. It lapses automatically after one year. It can e renewed every year. 3. Certainty of event The happening of event is certain but time is uncertain The event is not certain. It may happen or not. 4. Insured Sum Insurance policies can be taken for any amount or any number Policy amount is equal to the market value of property because the amount of indemnity cannot be more than the actual value of property 5. Certainty of payment of claim Payment of claim is certain. It may be either on maturity of the policy or on the death of the assured Payment of claim is not certain. It is paid only in case of loss of the asset insured 6. Element of Investment There is element of investment in assurance as payment of sum assured is certain either on death or on maturity of the policy. There is no element of investment as certainty of payment depends upon the happening of element. 7. Amount of claim Insurance company makes the payment of policy amount in full on the maturity or on death Amount of claim cannot be more than actual loss or amount of asset in any case 8. Principle of Indemnity Principle of Indemnity is not applicable in case of assurance. Sum assured is paid in full extent of amount insured irrespective of any profit or loss Principle of Indemnity is applicable. The basis of insurance contracts is the principle of indemnity. 9. Assurance Insurance companies assure the insured to compensate in case of maturity of policy or death Insurance companies only promises to compensate in case of actual loss 10. Time of Insurable interest It is proved at the time of Contract. It is not necessarily be present at the time of payment of claim Insurable Interest must e present at the time of loss in case of marine insurance. RELEVANCE OF INSURANCE RELEVANCE TO AN INDIVIDUAL RELEVANCE TO BUSINESS RELEVANCE TO SOCIETY 1. Insurance provides security, safety 2. Insurance affords peace of mind 3. Insurance protects mortgaged property 4. Insurance eliminates dependency 5. It encourages savings 6. Profitable investment 7. It fulfils needs of person 1. Uncertainty of business losses is reduced 2. Business efficiency is increased 3. Keyman indemnification 4. Enhancement of credit 5. Business continuation 6. Welfare of employees 1. Wealth of the society is protected 2. Economic growth of the country 3. Reduction in inflation