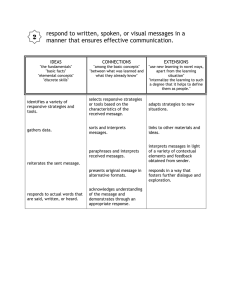
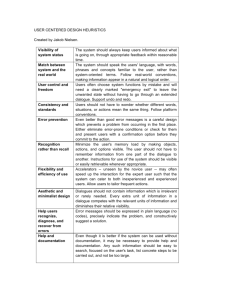
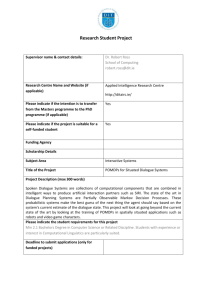
Speech Processing and Brain Signatures of speech, particularly in
advertisement

SPEECH PROCESSING AND BRAIN S I G N A T U R E S O F S P E E C H , PA R T I C U L A R LY I N D I S T I N G U I S H I N G T R U E / FA L S E O R Y E S / N O RESPONSES Speech processing can refer either to a device that receives and interprets speech then performing a command in response or a machine that interprets brain wave signals related to thoughts of speech then performing a command. The brain quickly interprets speech; this includes understanding a statement based on semantics, grammar, and intonation (Buzo ). Goal is to create a machine that can do the same and allow LIS patients to communicate effectively. There’s little difference between the psychophysiological responses and brain signatures of an objectively true statement and those of a delusional (subjectively true) statement. (Langleben ) The brain shows increased activity to noises that have pitches or are decibels outside that of everyday speech. (Zatorre ) Through the processing of brain signatures through BMI (or BCI) to a speech synthesizer, individuals in a locked-in state can form speech and potentially engage in verbal conversation. (Guenther ) To create these communication devices, the first step is to create binary communication devices though the processing of Yes/No thinking. This is done by first semantic classical conditioning cortically evoked responses to the meaning of a word or sentence CITATIONS Besserve & Co. , “Extraction of functional information from ongoing brain electrical activity”, Tubingen, Germany. Buzo & Co., “Word Error Rate Improvement and Complexity Reduction in Automatic Speech Recognition”, 2011 Speech Technology and Human Computer Dialogue. Guenther & Co., "Brain-machine interfaces for real-time speech synthesis”, 2011 Annual International Conference of IEEE. Henig, R., “Looking for the Lie”, New York Times. Langleben & Co., “True lies: delusions and lie-detection technology”, Neuroethics Publications Center for Neuroscience & Society. Mozsary & Co., “Comparison of feature extraction methods for speech recognition in noise-free and in traffic noise environment”, 2011 . Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue. Ruf & Co., “Semantic Classical Conditioning and Brain-Computer Interface Control: Encoding of Affirmative and Negative Thinking”. Schipor & Co., “Towards a multimodal emotion recognition framework to be integrated in a Computer Based Speech Therapy System”, 2011, Speech Technology and Human-Computer Dialogue. Sundaram & Co., “Experiments in context-independent recognition of non-lexical ‘yes’ or ‘no’ responses”, 2011, Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing. Zatorre & Co., “Lateralization of phonetic and pitch discrimination in speech processing”