Unit Nine: The Nationalist Era
advertisement

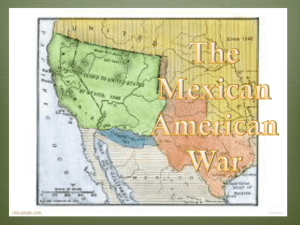
Unit Eleven: Manifest Destiny Mexican – American War The Election of 1840 • The Election of 1840 was between Democrat Martin Van Buren and Whig William Henry Harrison. • The main issue of the campaign was the Panic of 1837 with the Whigs calling Van Buren “Martin Van Ruin”, in return the Democrats called Harrison a yokel who only needed a log cabin and hard cider. • The Whigs used this to create the Log Cabin Campaign to make Harrison seem as one of the people. (They used log cabins as rally points and passed out Hard Cider (apple liquor) to the people with the slogan “Tippecanoe and Tyler too”. The strategy worked and Harrison won. Log Cabin Campaign Click above to hear Tippecanoe and Tyler too Harrison VS. Van Buren Whose President? • A third party developed during the election called the Liberty Party (abolition/Antislavery) which nominated James G. Birney but received few votes. • When Harrison took the oath of office he was 68 years old and gave one of the longest inauguration speeches on a cold wet day catching a cold that resulted one month into his administration in him dying from pneumonia. • Harrison was the first President to die in office, which led to the question as to whom should now be President, since at this time the U.S. Constitution said nothing about it. I’m President • Debates in Congress, among Harrison’s Cabinet, and the Vice President raged, but Harrison’s Vice President John Tyler simply assumed the power and took over the responsibility of President. • Tyler was a democrat who switched to the Whigs because of his dislike for Jackson’s polices, was a state’s rights man, and extremely pro-slavery; which brought him at odds with the Whig Party. • The Whig Party ran by Henry Clay tried to pass legislation to create a third BUS, a higher tariff, and distribute surplus money to states, which Tyler disagreed with most of these actions. I’m President • At this point all of the Presidential Cabinet (but Webster) resigned and Tyler was “read out” (kicked out) of the Whig Party, at this point they called him “His Accidency”. (first President without a Party) • The biggest legislation passed by Tyler and Congress was the Pre-emption Act of 1841 that allowed people called Squatters/Preemptors (settle on public land) the ability to purchase public lands in the West directly from the government before it was surveyed. • This law encouraged people to move West to settle the land and expand the country. (was also seen as an attempt to expand slavery) Tyler Administration • Tyler also supported annexation of Texas, but the Senate rejected a bill allowing it. (The issue was over slavery) • In 1841-1842 Tyler had to deal with an event called the Dorr Rebellion led by Thomas Dorr in Rhode Island for universal suffrage which failed. • In 1843 the House of Representatives tried to bring the first charges of impeachment (to charge a public official of misconduct) against an acting President, it did not pass. • In the last year of his term, Tyler also was almost killed when the cannon on the USS Princeton blew up while firing. (two cabinet members were killed) Election of 1844 • In the Election of 1844 Tyler tried to run as a third party candidate called the National Democratic Tyler, but dropped out of the race and returned to his plantation renamed Sherwood Forest. • The Whigs chose to run Henry Clay even though had been defeated twice before for the job. • The Democrats chose to run the dark horse candidate (a person who is little known) James K. Polk over Martin Van Buren. Just Who is James K. Polk? • Two other third party candidates were James G. Birney of the Liberty Party and Joseph Smith Jr. a Mormon independent candidate who ran until he was assassinated in an Illinois prison. • The main issue that developed during the election was the annexation of Texas as a state. • Polk won the election of 1844 and in 1845 Texas became the 28th State, Florida was also added before Texas as the 27th State. Expansionism • James K. Polk was an expansionist, who wanted to expand the boarders of America from the coast to coast. • Polk stated in his inauguration address that he would serve only one term and that he would lower the tariff and settle all the land disputes in the West. • During the 1830s and 40s many Americans had moved into Western lands outside of the jurisdiction of the United States and wanted their settlements to become part of the U.S., which led to issues with Britain and Mexico over Oregon, California, Utah, and the new state of Texas. “Fifty-four Forty or Fight” • For many years the Oregon Country was a disputed land between Russia, Spain, United States, and Brittan. • In 1828 Brittan and the United States agreed to a co-ownership of the Oregon Country, but in the 1840s disputes developed over where the line between them was. • From 1844 to 1846 Americans ran the slogan “Fifty-Four Forty or Fight” meaning that they wanted all of the Oregon territory or war would be declared, Polk used this as a bluff to work out a deal, which split the Oregon Country along the 49th north latitude at its current location. California and New Mexico • Both Jackson and Tyler had tried to purchase California from Mexico. • In 1842 Commodore Thomas Jones actually had taken over the port city of Monterey raising the American flag, but found out America and Mexico were not war and gave it back with an apology. • In 1843 John C. Fremont had “explored” California and gave report on what he found making many expansionists want this area too especially with the growing issues over Texas. Texas Dispute • To handle the issue Polk sent John Slidell with a special envoy to Mexico City to purchase California and New Mexico and handle the border dispute with Jose Joaquin Herrera, but the Mexican President refused to meet with Slidell out of fear of revolution in Mexico due to anti-American sentiment. • Texas became a disputed land, when America annexed Texas as a state, the Mexican government refused to recognize the treaty and broke diplomatic relations with America. Texas Dispute • Also the boundary between Texas and Mexico came under dispute with Texas and America recognizing the Rio Grande and the Mexicans recognizing Nueces River which was further north. • In response to these issues Polk sent General Zachary Taylor (old rough and ready) with 3,000 troops to encamp on the Rio Grande and wait until orders from him or Mexican aggression. • The Mexican government saw this as an act of aggression sent an army to encamp on the other side and wait for American aggression. (Mexican standoff) The Mexican- American War • While Taylor waited the call for volunteers went out, which many Americans joined to fight. (most were unruly, and Taylor instituted harsh punishment and training to bring the militias under control) • Taylor sent 70 scouts to overlook the area to see if the Mexican Army had crossed the Rio Grande, while looking into a hacienda the scouts were attacked known as the Thornton Affair. The Mexican- American War • Shortly after Polk asked for a declaration of war from Congress and the Mexican-American War began in 1846. (“American blood, on American soil) • The war from the beginning was split in popularity with the southern states in favor and the New England states against it calling it “Mr. Polk’s War” to expand the nation and slavery. • Congressmen Abraham Lincoln even offered the “spot resolution” in Congress asking if the spot Americans died was American soil or did they entice the Mexicans. The Mexican- American War • As war broke out John C. Fremont moved into California aiding a group of settlers led by William B. Ide who took the town of Sonoma and established the Republic of California in the called the Bear Flag Revolt. • The military strategy for the war was a three prong attack: 1.) March from Rio Grande and secure Northern Mexico, 2.) March from Fort Leavenworth (Kansas) and take New Mexico (Santa Fe), 3.) March from Santa Fe and take California. The Mexican- American War • Taylor marched south winning the Battle of Palo Alto, Battle of Resaca de la Palma, and the Battle of Monterrey the key to Northern Mexico. • During this time Santa Anna was allowed past General Winfield Scott’s Blockade and returned to Mexico to negotiate a peace treaty, but instead took back over Mexico. • After this Santa Anna met Taylor at the Battle of Buena Vista which the Americans won forcing Santa Anna to retreat back to Mexico City. The Mexican- American War • While Taylor marched south General Stephan W. Kearny marched toward Santa Fe taking the town and control of New Mexico (without a shot fired), at this time he split his forces in half to take California and the other to reinforce Taylor. • Kearny with a force of 300 men helped Commodore John D. Sloat take San Diego, Los Angles, and Monterey forcing the Mexican army out of Alta California. • With California, New Mexico, and Northern Mexico under control the focus was turned to Mexico City and Santa Anna. Who to Chose? • After the victory of Buena Vista Taylor received major press and became a popular war hero in America, fearing that he would use this to run as a Whig Presidential candidate, Polk chose to halt Taylor and allow General Winfield Scott “Ol Fuss and Feathers” finish the War. (Scott was a Democrat) • In 1847 General Winfield Scott made a naval amphibious landing taking the port city of Vera Cruz, then marched down the coast line finally in the Battle for Mexico City defeating Santa Anna ending the war. (He followed the same path Cortez had taken to conquer the Aztec) The Mexican-American War Zachery Taylor Winfield Scott Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo • The Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo ended the Mexican-American War which included these terms: 1.) Mexico gave up claim to Texas up to Rio Grande, 2.) U.S. got California and New Mexico, 3.) U.S. paid Mexico 15 million dollars, 4.) U.S. took over 3.5 million in debt Mexico owed U.S. citizens. (one and two are known as the Mexican Cession) • Even though some wanted to take all of Mexico and others did not like it because of the possibility of the expansion of slavery, the Senate ratified the Treaty in 1846. Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo Polk’s Legacy • When Polk left office in 1849 he left a legacy of expanding the American borders from Coast to Coast and carving out mostly the present borders of the U.S. • In 1848 Polk even tried to purchase Cuba for up to 40 million dollars from Spain, but they refused. • To round the Southwest in 1853 ambassador James Gadsden purchased the southern part of Arizona and New Mexico from Mexico for 10 million dollars known as the Gadsden Purchase. (completed the present borders) • For the Senate to ratify the purchase a proviso (amendment) was added by David Wilmot called the Wilmot Proviso that prohibited the expansion of slavery in any lands gained by the Mexican War. Poke’s Legacy California Gold Rush • Shortly after the Treaty of Guadalupe Hidalgo was signed John Sutter discovered gold at his lumber town called Sutter’s Mill in 1848. • News of the gold strike led massive numbers of usually young single men in 1849 (forty-niners) to make it rich off the California Gold Strike. (the people who actually got wealthy were the merchants and saloon owners (casino/bar)) • These men called prospectors panned for gold and then would use it to purchase things in the local Boomtown (town that sprang up quickly). • When a gold strike went bust the people moved making the town a ghost town because all the building were left intake. New Life in the West • The gold strike brought many people out west, even an influx of Chinese immigrants into California, even though many headed back East some stayed and settled. • Two of the biggest problems in the West were water rights and law and order. • In the West a law of prior appropriation was established giving water rights to the first person to discover it or to dig a well. (big business). • In Western boom towns law and order was established by groups of settlers known as vigilante committees (citizens taking the law into their own hands). GOLD!!!!!! San Francisco at the start of the Gold Rush 49er Sutter’s Mill Justice