Problem Set 4 Key
advertisement

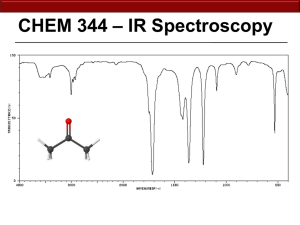
1. Mass Spectrometry O O 29 57 O 59 O 87 102 O A 154 B 139 strongest D C 111 125 weakest 1. Mass Spectrometry (cont’d) F OH O C6H13FO C 6 x 12.0000 H 13 x 1.0078 F 1 x 18.9984 O 1 x 15.9949 120.0950 O C5H12O3 C 5 x 12.0000 H 12 x 1.0078 O 3 x 15.9949 120.0780 O O C9H12 C 9 x 12.0000 H 12 x 1.0078 120.0940 C8H8O C 8 x 12.0000 H 8 x 1.0078 O 1 x 15.9949 120.0570 1. Mass Spectrometry (cont’d) 2 70 45 73 88 0 10 88 = Molecular ion 73 = M+ -15 (loss of methyl) 70 = M+ -18 (loss of water) 45 = M+ -43 (loss of propyl) 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 Loss of water indicates the compound is an alcohol. Alcohols also undergo αcleavage. Alcohol that can lose methyl and propyl via α -cleavage: OH OH or 2. Infrared Spectroscopy a. Which signal would be more intense in an IR spectrum, a C-O stretch or a C-N stretch? Why? Intensity of absorption is correlated to change in dipole moment with the vibration (stretch). The C-O bond is more polar and will thus experience a greater change in dipole moment during a stretching vibration, giving a more intense absorption. b. Which would give a stronger C=C stretch in an IR spectrum, 1-butene or 2-butene? Why? Intensity of absorption is correlated to change in dipole moment with the vibration (stretch). The 2-butene is symmetrical and will not experience a change in dipole moment during a stretching vibration. The 1-butene is not symmetrical about the C=C bond, and will this give a small change in dipole during stretching vibration and this the more intense absorption. c. Which would have a higher frequency absorption, an N-H bond or a P-H bond? Why? Absorption frequency is correlated to bond strength and atomic masses. Phosphorus is a larger atom than nitrogen, giving it a larger mass and weaker bonding via 3rd shell valence orbitals compared to nitrogen’s 2nd shell valence orbitals. Both of these factors cause the N-H bond to have a higher frequency absorption than the P-H bond. 2. Infrared Spectroscopy (continued) Cyclohexene - Presence of C=C at 1600 cm-1 - Absence of C=O around 1700 cm-1 - Absence of O-H around 3300 cm-1 Cyclohexenol OH - Presence of O-H at 3300 cm-1 - Absence of C=O around 1700 cm-1 - Absence of C=C around 1600 cm-1 Cyclohexanone - Presence of C=O at 1700 cm-1 - Absence of C=C around 1600 cm-1 - Absence of O-H around 3300 cm-1 O 3. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy O O O O OH O O 3. Ultraviolet Spectroscopy (cont.) 4 3 2 1 This would have the largest molar absorptivity (ε) and thus the most intense absorption 4. NMR Spectroscopy a. If an average carbon requires irradiation at 75 MHz to resonate in a 7.046 T magnetic field, what frequency will be required to resonate an average carbon in a 14.092 T magnetic field? ν = γB0 2π so doubling the magnetic field doubles the frequency needed to flip the same nucleus, therefore 150 MHz is needed. b. Use the following molecule to answer the following. a c b d Cl Which carbon is furthest downfield? _____d_____ Which carbon is furthest upfield? _____a_____ Which carbon resonates at the highest frequency? _____d_____ Which carbon resonates at the highest chemical shift? _____d_____ Which carbon resonates at the lowest chemical shift? _____a_____ Which carbon is the most shielded? _____a_____ Which carbon is the most deshielded? _____d_____ 4. NMR Spectroscopy (cont’d) O Br OCH3 O 3 5 5 6 5 Cl Cl 7 140 6 120 100 3 80 PPM 60 4 40 20 CH3 7 0 4. NMR Spectroscopy O Br OCH3 O 3 5 5 5 5 Cl Cl 7 8 s q 3 CH3 3 5 m (dq) m (7) t O F O O s d t d t Cl s m (dq) HO t t s q CH3 d t d 4. NMR Spectroscopy 3H 3H 2H 2H 3 2 PPM 1 O OCH3 0