TidesampEclipse2.3_CH2
advertisement

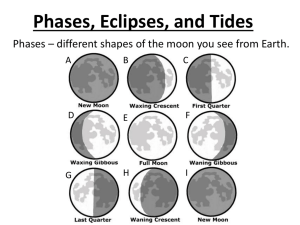
ECLIPSES SCIENCE STARTER: Draw a diagram to answer this question: Draw the position of the Moon, Sun, and Earth during a SOLAR ECLIPSE! Label EARTH, SUN, MOON! Set up page 22 in your ISN---ECLIPSES LOOK at my ISN if you are confused!!! The Tides: Lesson 2.3 Mrs. Gianelos Grade 8 Science • Tides caused by pull of Moon’s gravity on Earth • High tide – – Side facing Moon and side away from Moon – Every 12 hours, 25 ½ minutes • Low tide – – On sides of Earth What are tides? • They are the regular rising and falling of the ocean. • HIGH TIDE: the water moves way up the beach • LOW TIDE: you see lots of shore, since the water moves way out • There are 2 high tides and 2 low tides a day. The tides change every 6 hours. What causes the tides? Near Tide (Type of High Tide) Low Tide Opposite Tide (Type of High Tide) When and where? • The Earth rotates once every 24 hours which means that the places on the Earth where HIGH and LOW occur tides are always changing. The diagram below shows where HIGH and LOW tides will be 6 hours after the earlier diagram. C B D A What is a Spring Tide? • The Sun also has a gravitational effect on the sea. Although the Sun is larger than the Moon, it is further away from the Earth, which means that it has less effect on our tides. Twice a month, during the new moon and the full moon, the Moon and the Sun are in line with the Earth and so they pull together. This causes very high high tides and very low low tides called SPRING tides. What is a Neap Tide? • Twice a month, during the first and third (or last) quarters, the Sun and Moon are at right angles to each other, and so their pulls sort of cancel each other out, and are not as great. This causes much smaller tides. These are called NEAP tides. Solar and Lunar Eclipses Eclipse: The total or partial obscuring of one celestial body by another/ shadow makes the Sun or Moon seem to grow dark The obscuration can be either • One celestial body blocking the view to the other: – Solar eclipse---Moon blocking Earth’s view to the Sun • One celestial body is in the shadow of another: – Lunar eclipse--Moon is in the shadow of the Earth Lunar eclipse image from http://www.mreclipse.com Lunar Eclipses • Moon moves into Earth’s shadow – this shadow darkens the Moon • About 2-3 per year • Last up to 4 hours Solar Eclipses • Moon moves between Earth and Sun • Moon casts a shadow on part of the Earth • Total eclipses rare – only once every 360 years from one location! Solar eclipses • Solar eclipses occur when the shadow of the Moon falls on the surface of Earth – Only people in the shadow can see the eclipse. • Solar eclipses can be partial, annular, or total. • Solar eclipses can occur only at new moon. Click on the image to start animation What Causes Eclipse? • The Earth and Moon cast shadows. • When either passes through the other’s shadow, we have an eclipse. • Because the Sun is an extended bright object, there are two different regions of the shadow: – Penumbra is spreading cone of lighter shadow – Umbra is completely dark/ darkest part of shadow Click on the image to start animation Lunar eclipses • Lunar eclipses happens when the Moon passes through the shadow of the Earth – Everybody on the night side of Earth can see the lunar eclipse. • Lunar eclipses can be partial, penumbral, or total. • Lunar eclipses can occur only at full moon. Click on the image to start animation Solar Eclipse Forecast Solar eclipses from 2004 to 2030 Knowing the orbit of the Earth and the Moon, we can now calculate the time and path of solar eclipses with great accuracy. Back to Eclipse Path Eclipses: Summary • The parties involved: Sun, Moon, and Earth • Solar eclipse happens when the Moon is between the Earth and the Sun. • The size and distance of the Moon need to be just right for us to see total eclipse. • Lunar eclipse happens when Earth is between the Moon and the Sun. • Solar eclipses occur when the Moon passes directly between the Earth and the Sun.