136.UNIT 5 UNIVERSE study guide
advertisement

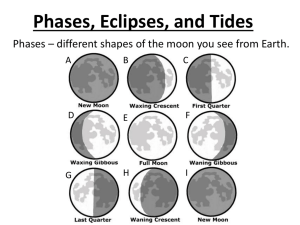
UNIT 5 Earth/Moon/Sun Study Guide 1. The Sun – see Star Carousel The Sun has a total of __________ layers. The Sun does not have a ___________________ surface. Nuclear fusion occurs here at temperatures of 15 million oC. ____________________ The energy produced at the Sun’s core transfers through this very dense layer of gasses as electromagnetic radiation. ________________ The outermost layer of the Sun’s interior. Hot gasses rise from the interior, cool, and sink back forming a cycle. _________________ The first layer of the Sun’s atmosphere and the layer that we see. It is considered the Sun’s surface. ____________________ The middle layer of the Sun’s atmosphere, the “color layer.” ____________________ The outer layer of the Sun’s atmosphere ___________________ is visible only through a solar eclipse. The _______________ radiates out from the Sun here. Areas of cooler gasses on the Sun’s surface are called ________________; when groups of these are connected, they form a ____________________. ____________________ can erupt from the Sun’s surface, emitting large amounts of electromagnetic radiation. 2. Earth’s Rotation and Revolution The Earth moves through space in two ways; _______________ around its own axis, and _______________ or orbiting, around the sun. The Earth’s axis has a tilt of approximately _____________ degrees. Because the tilt of the axis does not change, the hemispheres can receive both _______________ and _______________ sunlight. The maximum sunlight is called the _______________ _____________. The minimum sunlight is called the _______________ _____________. Between the solstices, the hemispheres receive equal amounts of sunlight at the _______________ and _______________ equinoxes. The direct and indirect sunlight causes the _______________. The seasons are always _______________ between the southern and northern hemispheres. 3. Earth’s Moon – see Moon Carousel: formation, characteristics, phases (see also p.120 and p.121) Eclipses are rare because the moon’s orbit is tilted by ____________, causing the moon’s or Earth’s _______________ to miss each other. A solar eclipse occurs during a _______________ moon, when the moon blocks the sunlight from reaching the Earth and the moon’s shadow hits the Earth instead. The very darkest part of the moon’s shadow is called the ______________. Only people within this dark shadow see a _______________ _______________ eclipse. People within the lighter part of the moon’s shadow, the _______________ or the _______________ see a partial solar eclipse. _______________ lunar and solar eclipses are the most common, as the _______________, _______________, and _______________ are not quite in line. 4. Tides The sun and moon’s _______________ causes the tides. Tides occur roughly every __________ hours. The force of the _______________ gravity is basically responsible for the tides. Even though the sun is bigger, it is _______________ away. Spring tides are caused when the Earth, moon, and sun are in a direct line. This occurs during a _______________ and _______________ moon. High tides are _______________ than normal, and low tides are _______________ than normal. Neap tides are caused when the moon is at right angles to the Earth and sun. This occurs during a _______________ and _______________ moon. High tides are _______________ than normal, and low tides are _______________ than normal.