General Medicine Conditions NMHS
advertisement

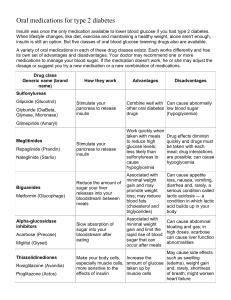
100+ strains Most common communicable disease Upper respiratory infection Self-limiting…lasts 5-10 days regardless of tx Acute infectious respiratory viral disease Types: • Type A: assoc w/ worldwide epidemics (most common) • Type B: geographic epidemics • Type C: mild flu Recovery in about 7-10 days Fever, chills, headache, myalgia, loss of appetite Avoid aspirin in children – Reye’s syndrome Acute infection caused by Ebstein-Barr virus Typically found in young adults • Mild when it occurs in young children • Older adults are typically immune Transmitted by respiratory secretions Sx: • Fever, sore throat, swollen lymph nodes, malaise, hepatomegaly, splenomegaly(50-70% have enlarged spleen) Infection usually ensures permanent immunity • You carry virus, but typically don’t get symptoms when virus occasionally becomes active (you can give it to others when active & asymptomatic) 90% of acute bronchitis = viral infection of the lungs Lasts 1-3wks • Typically doesn’t need tx unless you have severe or persistent sx Sy: SOB, chest pain/tightness, fatigue, muscle aches Sx: Possible fever, difficulty breathing, coughing (possibly w/ mucus) Lung infection caused by bacteria or virus Sx: • Chest pain, spitting up blood, fever, difficulty breathing, coughing up yellow/greenish sputum Tx: • Antibiotics for bacteria (sometimes viral to prevent complications) • Most can be treated at home with lots of rest • It often clears up in 2 to 3 weeks Constriction of air passages in the lungs Causes: cold, smoke, allergic reaction/allergies, exercise Sy: Tightness in the chest, SOB Sx: Trouble breathing, increased RR, wheezing, bluish skin, increased pulse, tingling? Tx: Inhaler, monitor, calm the athlete down, EMS? Inflammation of the coverings around brain & spinal cord Usually caused by a bacterial or viral infection • Viral: most common, usually not as serious Can cause prolonged fever & seizures • Bacterial: not as common, but very serious Can cause brain damage & death Typically seen in children, teens, and young adults Contagious – passed via coughing, sneezing, & close contact Sx: • • • • A stiff & painful neck, especially w/ neck flexion Fever Headache Seizures Causes: • Excessive loss of blood (can be seen w/ menstrual cycles) • Deficient intake of iron • Poor absorption of iron Sx: • Weakness/Feeling tired • Feeling grumpy • Headaches • Difficulty concentrating • Light-headedness • Difficulty breathing Physical findings or changes in behavior that occur after an episode of abnormal electrical activity in the brain Often used interchangeably w/ "convulsions" • Convulsions are uncontrollable body • shaking/contracting & relaxing of muscles There are many types of seizures…not all have convulsions Remain calm Cushion fall Clear area Loosen restrictive clothing Place soft cloth between teeth Allow patient to awaken normally Do not restrain patient during seizure Call 911 if: • • • • • • First seizure Lasts more than 2 to 5 min The person remains unconscious More then one seizure Caused by head injury or has diabetes Atypical seizure for them Due to rapid breathing, levels of carbon dioxide are low (compared to O2) in bloodstream Body responds to lower CO2 by constricting blood vessels in brain Sx: • • • • Lightheaded, headache Rapid heartbeat & RR Numbness or tingling in hands, feet, or mouth Shaking/seizures Tx: Slow respiratory rate • Breath in through nose & out through mouth • Inhale/exhale through one nostril w/ the other pinched and mouth closed • Breath into a paper or plastic bag Severe allergic reaction Sy: Chest tightness, difficulty breathing, dizziness Sx:Wheezing, swollen tongue/lips/throat, bluish skin, hives, nausea, vomiting, confusion Tx: Epi-pen, monitor, activate EMS Prevention: Know athletes’ Hx Stones may form in any part of UT, most occur in kidney Dissolved urine salts begin to solidify May increase in size & result in obstruction Intense radiating pain from kidney area to groin Tx: US waves, ureteroscopic removal, allow to pass on own UTI or Kidney Infection • Caused by bacteria Obstruction or ‘holding it’ paves way for infection due to stagnation of urine Sx: pain w/ urination, increased urgency & frequency, fever & chills possible Tx: antibiotics Inflammation of the appendix Not sure what it does & we can live without it Medical emergency - requires prompt surgery to remove the appendix Will eventually burst, or perforate, spilling infectious materials into abdominal cavity In U.S. – affects 1:15, usually between 10-30 y/o Sx: Pain in LR abdomen, fever, loss of appetite, nausea or vomiting Protrusion of any organ or tissue through the wall of the cavity that contains it Sports Hernia: “Athletic Pubalgia” Typically no lump felt on exam, will worsen if not properly treated Tx: PT, Surgery? Strangulated Hernia: • Blood supply to hernia is cut off, can lead to necrosis/gangrene (tissue death) Direct blow to left side Mono may enlarge the spleen, making contact sports extremely risky Profuse internal bleeding Early stage: pain in upper left quadrant, tenderness, bruising Life threatening stage: Pain in left neck/shoulder, faintness, dizziness, pale skin, rapid pulse, vomiting, low BP, SOB, rigid abdominal muscles Blow to flank/mid back Early stage: Pain at site, bruising Advanced stage: faintness, dizziness, increased HR, bloody or cloudy urine, vomiting, rigid back muscles, pale and cool skin, frequent and burning urination Diabetes Mellitus (DM): • Most common pancreatic disorder • Type I • Type II • Gestational 7th leading cause of death in U.S. in 2006 23.6 million children & adults in US (7.8%) • Diagnosed: 17.9 million people • Undiagnosed: 5.7 million people • Pre-diabetes: 57 million people • New Cases: 1.6 million adults each year 22% of all people <20 y/o have diabetes • Recent estimates put this closer to 1/3 About 2 million adolescents aged 12-19 are considered pre-diabetic 20+ y/o: • 6.6% of non-Hispanic whites • 7.5% of Asian Americans • 11.8% of non-Hispanic blacks • 10.4% of Hispanics Heart disease and stroke • 2 to 4 x’s higher risk than adults w/o diabetes. High blood pressure • 75% of adults had BP > 130/80 or used meds Blindness • Leading cause of new cases of blindness among adults 20–74 y/o Kidney disease • Leading cause of kidney failure, accounting for 44% of new cases Amputation • >60% of non-traumatic lower-limb amputations occur in people with diabetes • From poor wound healing and poor circulation High cholesterol Erectile dysfunction $174 billion: Total costs of diagnosed diabetes in US Medical expenses were 2.3x’s higher than people s diabetes $218 billion: Factoring costs of undiagnosed diabetes, pre-diabetes, and gestational diabetes Body cannot effectively regulate blood glucose • Characterized by hyperglycemia Type 1: body’s failure to produce insulin due to autoimmune pathology (5-10%) Type 2: cell insulin resistance or failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin (90-95%) Gestational: glucose intolerance during pregnancy Pre-Diabetic: blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not high enough for a diagnosis Body converts food to glucose, if not used it is stored as glycogen in the liver & muscles Insulin produced in the pancreas, facilitates glucose transport in the cells for energy metabolism & storage “Autoimmune” – Juvenile body fights itself onset 5-10% of diabetes incidence Underweight or normal Low insulin levels FHx usually negative Usually diagnosed in children and young adults Previously known as juvenile diabetes Only 5% of people with diabetes have this form of the disease In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, a hormone that is needed to convert sugar, starches & other food into energy “Insulin resistant” Adult onset (typically) 90-95% of diabetes incidence Risk factors: • Overweight • Sedentary lifestyle • Poor diet • FHx Most common form of diabetes Previously known as ‘adult onset’ The body does not use insulin properly Initially the pancreas makes extra insulin to make up for it, but over time the body can’t make enough to keep your blood glucose at normal levels Fasting plasma glucose - p 8hr fast • Normal = 100 mg/dL • Pre-diabetic = 100-126 mg/dL • Diabetic = >126 mg/dL Casual plasma glucose • > 200 mg/dL Increased thirst Increased urination (polyuria) Unexplained weight loss Increased hunger Tingling in hands and feet Blurry vision Glucose in the urine Type 1: Type 2: Diet Diet Exercise Exercise Insulin Oral Regular blood sugar monitoring anti-diabetic agents Regular blood sugar monitoring Insulin??? Pre-meal blood sugar: <100 mg/dL Post-meal blood sugar: <180mg/dL HbA1c value: <6-7% • Preferred test – less affected by daily glucose fluctuations • Avg glycemic control for 2-3 month period • Normal range is 4-6% Blood pressure <140/90 Pay special attention to Type I athletes during/after exercise Watch for sx’s of hypoglycemia • Confusion, irritation, pale?, sweating? Athlete will need to experiment w/ proper levels of insulin & food intake prior to and during exercise Athlete and ATC should have sugar source at all times Athlete may not be able to get sugar source before its too late, & then they will fight it Low blood sugar Mild: Hunger, irritability, weakness Moderate: Dilated pupils, sweating, strong and rapid pulse Severe: Confusion, convulsions, unconsciousness Treatment: Give athlete sugar, candy, fruit juice, or soda • If athlete does not recover w/in few minutes: Activate EMS, monitor High blood glucose levels Early stage: excessive thirst, dry mouth, nausea, sweet/fruity breath, excessive urination Advanced stage: Headaches, abdominal pain, dry/red/warm skin, weak/rapid pulse, heavy breathing, vomiting Treatment: Take insulin (if available), EMS?, monitor Smoking is leading cause of all types of lung cancers Breast and Testicular Cancer – Selfexams recommended Depositories for cellular debris Site of phagocytosis by macrophages, & lymphocytes (T-cells and B-cells) • Phagocytosis: digestion of bacteria & other materials During an infection: due to the number of bacteria destroyed – node often gets enlarged & tender Caused by bacteria that can lead to serious infections & infertility It can infect both men & women 1.4-2.86million cases/year Most common in young adults/teenagers – 1:15 sexually active females aged 14-19 have this disease It is easily treatable w/ antibiotics Sx: discharge, pain w/ urination Caused by Herpes Simplex Virus 2 776,000 new infections/year In U.S….16% 14 to 49y/o affected More common in women 1:5 vs 1:9 Sx: Blisters, painful sores…not always symptomatic • Can be spread while asymptomatic No cure If also infected w/ HPV – increased risk of cervical cancer 2-3x’s • 14 strains of HPV cause 90% of all cervical cancer Caused by bacteria that affects mucous membrane of genital & urinary tracts Treatable w/ antibiotics, but can cause infertility & death if left untreated In U.S. - 820,000 new cases/year ~570,000 of them were15-24 y/o Sx: discharge & pain w/ urinating Caused by bacteria that can cause lesions of CNS & CV system Treatable w/ antibiotics, but can cause long-term complications or death if not properly treated ~55,400 new cases/year Sx: Non-painful sore lasting 3-6wks…if not treated a rash will follow & in 10-30 yrs paralysis & death Acquired immune deficiency syndrome Caused by HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) • Infects helper T-cells w/ long incubation & replicates the virus • Slowly destroys immune system (T-cells) AIDS: during advanced stages of disease After immune system destroyed, opportunistic infections occur Cyst: fluid filled sac that can form anywhere on body When they form on the ovaries, they can cause pain & affect menstruation Under the age of 40, ovarian cancer is rare Most cysts are benign, asymptomatic & go away on their own in 1-3 months Disordered eating: Abnormal eating habits (i.e., crash diets, binge eating) or excessive exercise keeps the body from getting enough nutrition Amenorrhea: Poor nutrition, high-energy demands, physical and emotional stress, or low BF% can lead to hormonal changes that stop menstrual periods Premature osteoporosis (low bone density for age): Amenorrhea disrupts the body's bone-building processes and weakens the skeleton, making bones more likely to break Direct blow to groin area Sx’s: Pain, nausea Self-exam: • • • • • Swelling, discoloration, deformity, spasm Testicles draw up or twist Bloody or cloudy urine Vomiting Tenderness lasting >1hr Tx: Place in most comfortable position (knees to chest?), ice, refer to physician if serious sx’s present