File
advertisement

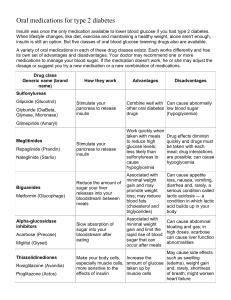
Kelsi Baron Hillary Colbry Katelyn Gaffney Cody Kryfka Stephanie Logan Megan Moore People eat food which digest into glucose which then causes the pancreas to release insulin to lower blood sugar levels In pregnancy, the placenta produces multiple hormones which impair the action of insulin in the mom causing the blood sugars to stay elevated. 90% of pregnant women develop GDM Between 24-28 weeks gestation a Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) will be completed ◦ Woman drinks a syrupy glucose solution ◦ Wait 1 hour ◦ Gets blood drawn Normal blood sugar level are <140 If >140, then a follow-up OGTT will be done ◦ Fast over night ◦ Drink a higher concentrated glucose solution ◦ Blood sugar levels are tested every hour for 3 hours 2 or more tests are higher than 140 then women is diagnosed with GDM Low blood sugars Excessive birth weight Type 2 diabetes later in life for mom & baby Pre-term birth Family history of diabetes During a pervious pregnancy A baby weighing more than 9 pounds Being overweight Race Diet could limit or remove the need for medication interventions Carbohydrates have the biggest impact on blood sugar levels DO… ◦ Healthy portions ◦ Fruits, vegetables, whole grains ◦ Foods high in fiber, low in fat/calories AVOID/LIMIT ◦ Sweets ◦ Refined Carbohydrates ◦ Eating Carbohydrates at breakfast/morning Necessary during and after pregnancy ◦ “Lowers blood sugar by stimulating your body to move glucose into your cells where it’s used for energy”(Mayo, 2014) ◦ Increases sensitivity to insulin ◦ Decreases possibility of later onset Type 2 diabetes Moderate activity OR build up slowly ◦ Cycling, walking, swimming, housework, gardening If diet and exercise are not enough ◦ 10-20% of women with GDM need insulin Oral and/or Insulin ◦ Common Oral Medication Glyburide: stimulates pancreas-does not cross the placenta in significant amount Metformin: decreases amount of glucose the liver makes-crosses placenta in small amounts ◦ Insulin Requires more check ups with obstetrician-weekly or twice weekly Non-stress test, ultrasound, kick counts, biophysical profile(combination non-stress test /ultrasound) Focus on maintaining normal blood glucose levels: Diet and Exercise Insulin injection techniques if necessary Monitoring anxiety and feelings of mother Effective communication Providing normal pregnancy care Stress management Postpartum care Reinforcement and review accurate information Demonstration of specific skills Teaching support persons skills and information on GDM Knowledge of effects of GDM if poorly managed Explain the need for frequent check-ups and tests Deficient Knowledge in management of gestational diabetes Imbalanced nutrition less than body requirements After Birth Complications Risks ◦ Macrosomia ◦ Hypoglycemia Mayo Clinic. (2014). Gestational diabetes. Mayo Clinic. Retrieved from http://www.mayoclinic.org/diseasesconditions/gestational-diabetes/basics/definition/con20014854 Baby Center. (2014). The best kinds of exercise for pregnancy. Baby Center. Retrieved from http://www.babycenter.com/0_the-best-kinds-of-exercisefor-pregnancy_7880.bc