From Discrete Mathematics to AI applications: A progression path for

From Discrete Mathematics to AI applications:
A progression path for an undergraduate program in math
Abdul Huq
Middle East College of Information Technology, Sultanate of
Oman huq@mecit.edu.om
and
Narayanan T. Ramachandran
Middle East College of Information Technology, Sultanate of
Oman narayanan@mecit.edu.om
1
Approaches to AI
Can be approached in different ways..
AI as a branch of Computer Science
AI’s strong links with Math
May be thought of as Applied Math
Clarification of Theoretical issues
2
AI and Math
The term AI has its roots in Math
Dominant role played by Mathematicians in the establishment of CS disciplines: Introduced by John McCarthy,Prof. of Math, Dartmouth
College
There are Math departments with AI Groups
Use of technology in traditionally strong
Mathematical subjects
3
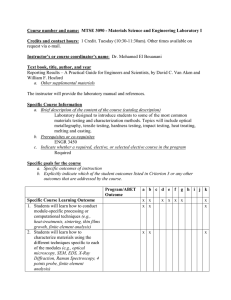
Proposed approach
Math
Modules
Computer
Science
Modules
Discrete Math and Logic
Formal
Specification
Automata &
Formal Lang.
4
Three essential aspects
fundamental concepts of AI computational language concepts that support AI and applications of AI
5
Component mapping with essential aspects
fundamental concepts of AI computational language concepts that support AI and applications of AI
Discrete Math and Logic
Automata & Formal Lang.
Formal Specification
Prolog
Expert
System
Natural
Lang.
Proces sing
Automatic
Theorem
Proving
Robotics
6
Discrete Math
Data Structures
Discrete Structures
- Sets
- Sequences
- Relations
7
Logic
Propositional Logic
Predicate Logic
Logics of higher order
Fuzzy Logic
Useful in Knowledge Representation
There are researchers who consider logic as the most important factor in developing strategic, fundamental advances
8
VDM
A formal specification language
Specifies what needs to be done rather than how it is to be done
Based on predicate logic
Useful in program development and proving correctness of programs
9
Prolog
Based on predicate logic
A logic programming language
Automatic Theorem Proving
Developed into a general purpose programming language for AI applications
10
Key Features
Ensure a firm understanding of the basic tools and techniques that are required for AI applications
Instill knowledge in a spectrum of related subjects
Encourage Creativity in the process of developing solutions to a variety of problems
Provide opportunities to convert complex scenarios into various solvable parts and identify a solution from a list of known options
Increase ability to search for solutions
Develop computational skills that are needed in the industry
Develop the ability to reason logically, analytically and critically
Ensure that there is clear understanding of the role of AI specialists
Provide the necessary skills to appreciate different AI concepts, their use and rationale
11
Categories of modules
•
Fundamentals
•
Computation
• Applications
• General Education
• Additional Modules
•
Projects
12
Categories of modules : Fundamentals
Graph Theory
Combinatorics
Discrete Math
Logic
Operating Systems
Operations Research
Introduction to AI
13
Categories of modules :
Computation
Data Structures
Algorithms
Formal Specification
Prolog
Theory of computation
14
Categories of modules :
Applications
Pattern Recognition
Expert Systems
Natural Language Processing
Automatic Theorem Proving
Robotics
Machine Intelligence
Human Computer Interaction
15
Categories of modules :
General Education
English
Biology
Philosophy
Pyschology
16
Additional Modules
Calculus
Mathe. Statistics
Numerical Methods
Hardware Networking
Systems Software
Computer Architecture
DBMS
Physics
Computer vision
Fuzzy set &fuzzy logic
17
Structure of the programme
Four year/8 semester
15 weeks/sem
No. of modules??
Credit points??
Exit points??
18
Pedagogy
Group work
Task based
Effort based
Individual effort
Self study
Blend of theory and practice
Exposure to real life problems
19
Learning outcomes of the programme
On completion of the programme, student will be able to:
Formulate AI problems Mathematically
Apply standard Mathematical methods
Write code to implement solution procedures
Search for information in tackling advanced problems
20