Simple Invertebrate Review
advertisement

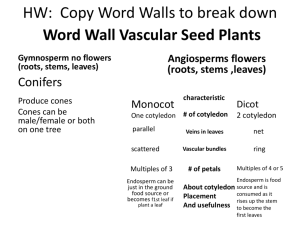
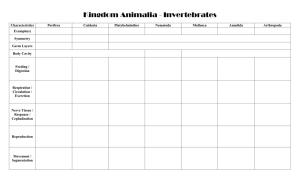
Word Bank homeostasis hermaphrodite bilateral symmetry vertebrates invertebrates radial symmetry Animals without a backbone invertebrates larva Word Bank homeostasis hermaphrodite bilateral symmetry vertebrates invertebrates radial symmetry Body parts arranged in a circle like spokes of a wheel radial symmetry larva Word Bank homeostasis hermaphrodite bilateral symmetry vertebrates invertebrates radial symmetry Maintaining stable internal conditions homeostasis larva Word Bank homeostasis hermaphrodite bilateral symmetry vertebrates invertebrates radial symmetry An individual animal that produces both sperm and eggs hermaphrodite larva Word Bank homeostasis hermaphrodite bilateral symmetry vertebrates invertebrates radial symmetry Immature form of an animal (different from adult) larva larva Which is NOT a characteristic of animals? A. heterotrophic B. reproduction C. movement D. autotrophic Sponges show this type of symmetry. A. asymmetry B. bilateral symmetry C. radial symmetry D. spherical symmetry The underside or belly of an animal that has bilateral symmetry is called A. anterior B. posterior C. ventral D. dorsal For organizations of animals, which choice is listed from simplest to most complex? A. cell, organ, organ system, tissue B. organ, organ system, tissue, cell C. cell, tissue, organ, organ system D. cell, tissue, organ system, organ What type of cell in sponges is responsible for water flow and capturing food particles? A. spike cells B. collar cells C. jelly-like cells D. pores The bodies of many sponges contain sharp structures called A. jelly-like cells B. pores C. collar cells D. spikes Which of the following statements is true for sponges? A. Sponges reproduce sexually through budding. B. Jelly-like cells produce haploid sperm and egg cells for sexual reproduction C. The larva of a sponge forms before fertilization. D. Sponges reproduce through sexual reproduction only Members of the phylum Cnidaria are able to reproduce through A. asexual reproduction only B. binary fission only C. sexual reproduction only D. both asexual and sexual reproduction What body type best describes a hydra? A. larva B. medusa C. polyp D. sponge An example of a cnidarian that is actually a colony of individual organisms is a A. Sea anemone B. Portuguese Man-of War C. hydra D. jellyfish Corals spend their adult lives as A. medusas B. larvae C. polyps D. cnidocytes Worms reproduce asexually through A. gamete formation B. budding C. regeneration D. binary fission Tapeworms have hooks and suckers for attachment that are A. anterior B. posterior C. dorsal D. ventral An animal such as a planarian that does not live in or on another organism is said to be A. parasitic B. free-living C. autotrophic D. infectious Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Filter feeders Porifera Nematoda Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Platyhelminthes Cnidaria Nematoda Digestive system with two separate openings Nematoda Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Tentacles armed with stinging cells Cnidaria Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Platyhelminthes Cnidaria Nematoda Flattened bodies Platyhelminthes Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Polyp and medusa body types Cnidaria Match the description with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda “pore bearing” animals that are covered with tiny holes Porifera Match the organism with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda coral Cnidaria Match the organism with the correct phylum Porifera Platyhelminthes Cnidaria Nematoda roundworm Nematoda Match the organism with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda fluke Platyhelminthes Match the organism with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda planarian Platyhelminthes Match the organism with the correct phylum Porifera Cnidaria Platyhelminthes Nematoda Basket sponge Porifera