CH 6 SPONGE adaptation and structure ppt
advertisement

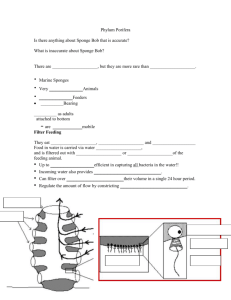
DESCRIBE 3 OBSERVATIONS ABOUT THE MARINE SPONGE • Hint : THE TEXTURE OF A SYNTHETIC SPONGE IS SIMILAR TO A MARINE SPONGE • WRITE OBSERVATIONS ON BOARD SPONGES INSTRUCTIONAL OBJECTIVES SPONGES MARINE SPONGES • SPONGES are 1. elastic 2. have many holes 3. all sponge parts look alike 4. adult sponge is sessile-doesn’t move • Sponges have several ADAPTATIONS that help them survive in the marine environment • Sponges are multicellular animals and are classified in kingdom animal and phylum porifera (pore bearing) • GUESS THE AIM??? AIM: HOW ARE SPONGES ADAPTED TO THEIR ENVIRONMENT? • Tell story about ancient sponges/divers-museum exhibit • ACTIVITY-LABEL WORKSHEET and DRAW ARROWS OF WATER FLOW • DRAW and LABEL COLLAR CELL/CHOANOCYTE SPONGE ANATOMY and WATER FLOW SPONGE REVIEW IN LESSON KEY QUESTIONS/VOCABULARY • HOW DO SPONGES INGEST FOOD? EXCRETE WASTES? DIGEST FOOD? BREATHE/RESPIRE? DEFEND ITSELF? REPRODUCE/GENDER TYPE? • VOCABULARY 1. amebocyte-undifferentiated cell • 2. CHOANOCYTE-collar cell • HOW DO COLLAR CELLS WORK? 1. flagella beat in unison creating current of water into ostia and through collar cells 2. collar captures food particles in water 3. food vacuole within cell digests food SPONGE STRUCTURE FUNCTION CHART structure ostia osculum Collar cells Ectoderm Endoderm spicules function CREATE STRUCTURE FUNCTION CHART Sponge Structure FUNCTION and explanation OSTIA(small pores) Ingestion-filter feed micro food particles out of water OSCULUM-located on top Excretion-eliminate waste COLLAR CELLS-located within central cavity(have flagella) Digestion-food vacuole with enzymes Filter feeding- flagella beating brings food in Ectoderm- outer cell layer Respiration-exchange of Oxygen and Carbon dioxide for energy Endoderm-inner cell layer spicules Structure and defense against predators HOW DO SPONGES REPRODUCE? • HOW DO I MAKE BABIES? HOW DO SPONGES REPRODUCE? • GENDER-HERMAPHRODITES-being both male and female. Can switch back and forth making eggs and sperm. Can change sex • Asexual-budding or regeneration, small piece breaks off and grows. Identical DNAexact clone. 1 parent • Sexual-2 parents. Sperm and egg form zygote, external fertilization and external development • How do sponges know when to release gametes simultaneously? Environmental cues like temperature, PH….. WHY ARE SPONGES CONSIDERED TO BE SIMPLE MULTICELLULAR ORGANISMS? WHY ARE SPONGES CONSIDERED TO BE SIMPLE, MULTICELLULAR ANIMALS? • The sponge is a simple animal because they have no organs(2 cell layers) which are the ectoderm and endoderm. The sponge lacks any specialization. • Comparatively most animals have organs which is third germ layer. SUMMARY • The sponge is a simple pore-bearing, filter feeding, multicellular organism that is composed of two layers of (mostly unspecialized cells). The sponge is classified in phylum porifera. SPONGE EXIT QUIZ • 1. T or F. Correct for full credit Sponges use collar cells for locomotion. • 2. Describe in detail how sponges ingest food? Include diet. • 3. Sponges excrete waste using its: A. Ostia B. choanocytes C. osculum D. spicules • 4. Why are sponges considered to be simple, multicellular animals?