How are light microscopes and Electron
advertisement

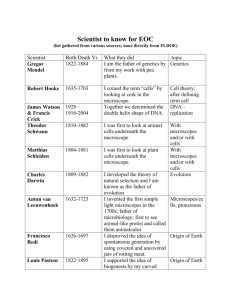
What measurement system do most Scientists use? How are light microscopes and Electron microscopes similar? How are they different? Ladder Method 1 2 KILO 1000 Units HECTO 100 Units 3 DEKA 10 Units DECI 0.1 Unit Meters Liters Grams How do you use the “ladder” method? 1st – Determine your starting point. 2nd – Count the “jumps” to your ending point. 3rd – Move the decimal the same number of jumps in the same direction. CENTI 0.01 Unit MILLI 0.001 Unit 4 km = _________ m Starting Point Ending Point How many jumps does it take? 4. __. __. __. = 4000 m 1 2 3 Conversion Practice Try these conversions using the ladder method. 1000 mg = _______ g 1 L = _______ mL 160 cm = _______ mm 14 km = _______ m 109 g = _______ kg 250 m = _______ km Compare using <, >, or =. 56 cm 6m 7g 698 mg Length Length is the distance between two points. The SI base unit for length is the meter. We use rulers or meter sticks to find the length of objects. Analyzing Biological Data Scientists collect data to find out whether certain factors change or remain the same. Often, the simplest way to do that is to record the data in a table and then make a graph Computers help scientists to gather, analyze, and present large quantities of data. Analyses of data are used to make predictions about complex phenomena. Microscopes Microscopes are devices that produce magnified images of structures that are too small to see with the unaided eye. Scientists today use Two kinds of microscopes: Light Electron A light microscope, also called an optical microscope, is an instrument to observe small objects using visible light and lenses. Onion Peel Stained animal cheek cell The electron microscope is a type of microscope that uses a beam of electrons to create an image of the specimen Dust mite House Fly In order for a microscope to be useful, there must be two important properties---- magnification and resolution Magnification is the ability to make things larger than they are Resolution-the sharpness of an image What’s my power? To calculate the power of magnification, multiply the power of the ocular lens by the power of the objective. 6 steps of how to view a specimen under a microscope: 1. Turn on the light 2. Lower the stage to minimum and click low objective in 3. Slide over light hole 4. Focus slide/course adjustment 5. Click on high lens 6. Focus with fine adjustment Compound light microscopes • allow light to pass through the specimen • use two lenses to form an image. • Light microscopes make it possible to study dead organisms and their parts • to observe some small organisms and cells while they are still alive. Laboratory Techniques • biologists place a single cell into a dish • contains a nutrient solution. The cell is able to reproduce so that a group of cells, called a cell culture, develops from the single original cell. Mosquito Cell Culture Cell cultures can be used to: •test cell responses under controlled conditions •study interactions between cells •select specific cells for further study Centrifuge • Cells are broken into pieces in a special blender. • The broken cell bits are added to a liquid and placed in a tube. • The tube is inserted into a centrifuge that spins, causing the cell parts to separate, with the most dense parts settling near the bottom of the tube. • A biologist can then remove the specific part of the cell to be studied by selecting the appropriate layer.