Chapter 1 Lesson 3
advertisement

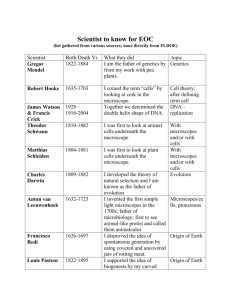
Exploring life CHAPTER 1 LESSON 3 THE DEVELOPMENT OF THE MICROSCOPE Allowed people to see details of an object that they could not see before Robert Hooke- in the 1600’s used a microscope to look at cork He was the first scientist to name cells because they resemble “prison cells” He was looking at the remains of the cell wall in the cork THE FIRST MICROSCOPES Anton van Leeuwenhoek- Dutch merchant Late 1600’s Made improvements to the existing microscopes Microscopes could not magnify up to 270 time the original size CHARACTERISTICS OF MICROSCOPES Magnification of the microscope Magnification makes the object look bigger Resolution of a microscope How clearly you can see the object has to do with the resolution of the microscope TYPES OF MICROSCOPES Two major types based on the source of illumination Light Electron Electron Light LIGHT MICROSCOPES Uses a light source or mirrors to enlarge an object Some light microscopes have a single lens The microscope we use is a compound microscope Two lenses 1. In the ocular 2. In the objective To find the magnification you MULTIPLY the ocular value by the objective Example: Ocular 4 X Objective 10 X So total magnification is 4 x 10 or 40 X RESOLUTION OF LIGHT MICROSCOPES 0.2 micrometers or two millionths of a meter Dyes maybe used to help visualize parts of the cell ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Use a magnetic field to focus a beam of electrons through an object Can magnify up to 100,000 times or more (light can only magnify up to 1500 times) The resolution is 0.2 nanometers or two billionths of a meter TEM SEM TWO TYPES OF ELECTRON MICROSCOPES Transmission electron microscopes (TEMs) Study extremely small structures in cells Specimen needs to be in plastic and then thinly sliced Only dead specimens can be used Scanning electron microscopes (SEMs) Study the objects surface Electrons bounce off the image and produce a 3 D image on the computer Can be a living specimen REAL WORLD USES OF MICROSCOPES Health care Laboratory to study specimens like blood Surgery like cataracts or brain surgery Determine if tissue sample has cancer or not Forensics Crime scenes- to determine body fluids and insect data Archeologists Study fossils and the material surrounding the fossil