The Circularity System
advertisement

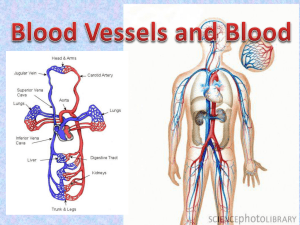
The Cardiovascular System The circularity system or cardiovascular system includes the heart, blood and blood vessels. The circularity system as four main functions, they include: Maintaining the body’s core temperature (homeostasis). Removing waste products from the cells (co2). Fighting infections. Transporting oxygen and nutrients to the cells. BLOOD Each person has approximately 4 – 5 litres of blood which take about 20 seconds to circulate the body at rest. Blood is made up of blood cells, the solid component (Hermatocrit 45%) and the blood plasma (final 55%). The blood cells include red cells, white cells and platelets. RED BLOOD CELLS give blood there red colour due to the haemoglobin content. Haemoglobin is essential in the transportation of oxygen from the lungs to the cells. Red blood cells are produced in the long bones marrow. WHITE BLOOD CELLS fight infection by absorbing and digesting disease causing organisms. White blood cells are produced in bone marrow of long bones, lymph tissue and the spleen. PLATELETS are produced in bone marrow and clot the blood to prevent excessive bleeding. BLOOD PLASMA is mostly made up of water (about 90%). It is the fluid that blood cells, nutrients and waste float in. Vessels The vessels that make up the circularity system include arteries, arterioles (smaller arteries), capillaries, venules (smaller veins) and veins. Arteries / Arterioles: carry blood away from the heart. With the exception of the pulmonary artery they carry oxygenated blood. Arteries have muscular walls and a pulse. The pressure in arteries is great. Veins / Venules: carry blood to the heart. With the exception of the pulmonary vein they all carry deoxygenated blood. Veins have thin elastic walls and valves that prevent the back flow of blood. Capillaries: link arterioles with venules. They are 1 cells thick which allows them to diffuse oxygen, carbon dioxide, nutrients and other waste. The Heart The heart is the size of your clenched fist and is made of cardiac muscle specific to the heart. The heart is comprised of two separate pumps. One to the lungs and the other to the rest of the body. The heart beats 60 – 80 times per minute at rest. It has four chambers, the left atrium, right atrium, left ventricle and right ventricle. http://www.smm.org/heart/heart/pumping.htm Superior vena cava Pulmonar y vein Inferior vena cava Bicuspid valve Heart rate Resting heart rate can vary from 45 – 85 beats per minute. Heart rate is affected by a number of factors, these include: Gender Age Body size Body Position Aerobic capacity Stress Anxiety Tension Excitement Level of food digestion Maximum Heart = 220 beats – Age What is yours? The blood exerting pressure against the artery walls as the heart contracts measures pulse. The amount of blood expelled in a beat is known as the stroke volume. Pulse can be measured most efficiently at the carotid artery (neck) of the radial artery (wrist). When taking your pulse, two fore fingers should be used, Never you thumb as it has its own weak pulse. Blood pressure Blood pressure is measured as systolic or diastolic. Systolic is the pressure of blood against the artery walls while the atria and ventricles contract. Diastolic is the pressure of the blood on the artery walls while the heart relaxes. Blood Pressure is the force exerted by blood against the blood vessel walls Cardiac output Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart each minute. Cardiac output (Q) = Heart rate (HR) x Stroke volume (SV) A-VO2 difference A-VO2 differences the amount of oxygen taken in and used by the tissues of a muscle. It is the difference in oxygen concentrations in the artery compared to the vein of a muscle. SUMMARY OF CHANGES DURING EXERCISE Factor Acute Chronic Heart rate (HR) Increase Decrease Stroke volume (SV) Increase Increase Cardiac output (Q) (Q) = (HR) x (SV) Increase increase A-VO2 difference Increase Slight increase Blood flow to working tissue, heart and lungs Increase Blood flow to non essential regions decrease