3. OR Simplex
advertisement

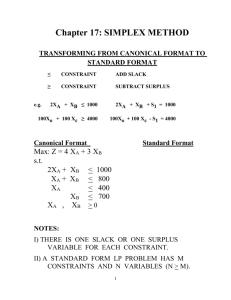
Operational Research Linear Programming With Simplex Method Minggu 2 Part 1 Introduction George Dantzig (1947) This is an iterative procedure that leads to the optimal solution in a finite number of steps. Begin with a basic feasible solution and then moves from one basic solution to the next until an optimal basic feasible solution is found. Definisi Metode simplex adalah metode optimasi pemrograman linear dengan cara evaluasi sederetan titik-titik ekstrim sehingga nilai objektif dari suatu titik ekstrim lebih baik atau sama dengan nilai objektif suatu titik ekstrim yang dievaluasi sebelumnya Contoh soal Suatu perusahaan skateboard akan memproduksi 2 jenis produk yaitu skateboard deluxe dan professional. Proses produksi terdiri dari 2 tahap yaitu proses perakitan dan proses penyesuaian. Waktu yang tersedia untuk proses perakitan adl 50 jam sedangkan utk proses penyesuaian adl 60 jam. Jumlah unit rakitan roda yang tersedia hanya 1200 unit. Setiap produk deluxe membutuhkan 1 unit rakitan roda, 2 menit proses perakitan, dan 1 menit proses penyesuaian. Setiap produk professional membutuhkan 1 unit rakitan roda, 3 menit proses perakitan, dan 4 menit proses penyesuaian. Jika dijual, keuntungan setiap produk deluxe dan professional berturut-turut adl $3 dan $4. Tentukan kombinasi produksi yang optimal! Case x1 = number of deluxe product x2 = number of professional product Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2 (profit) subject to x1 + x2 1200 2x1 + 3x2 3000 x1 + 4x2 3600 with x1 , x2 0 The Initial Simplex Tableau 1. Each constraint must be converted to an equation 2. In every equation there must be a variable that is basic in that equation. 3. The Right Hand Side (RHS) of every equation must be nonnegative constant. Converting constraints into equations Maximize Z = 3x1 + 4x2 + 0S1+ 0S2 + 0S3 subject to x1 + x 2 + S1 = 1200 2x1 + 3x2 + S2 = 3000 x1 + 4x2 + S3 = 3600 with x1, x2, S1, S2, S3 0 ..contd cj = objective function coefficient for variable j bi = right-hand-side value for constraint i aij = coefficient of variable j in constant i c row : a row of objective function coefficients b column : a column of RHS values of the constraint equations A matrix : a matrix with m rows and n columns of the coefficients of the variables in the constraint equations. ..contd The input parameters for general linear programming model c1 a11 a21 c2 a12 a22 : : am1 am2 ... ... ... ::: ... cn a1n a2n : amn b1 b2 : bm Initial Simplex Tableau cb 0 0 0 cj 3 4 0 0 0 BASIS x2 1 3 4 S1 1 0 0 S2 0 1 0 S3 0 0 1 Solution S1 S2 S3 x1 1 2 1 Zj 0 0 0 0 0 0 cj - Zj 3 4 0 0 0 1200 3000 3600 In every equation there must be a variable that is basic in that equation If S1, S2, and S3 are basic, x1 and x2 must be nonbasic. Therefore, the constraints are simply (1)(0) + (1) (0) + (1) S1 + (0) S2 + (0) S3 = 1200 (2)(0) + (3) (0) + (0) S1 + (1) S2 + (0) S3 = 3000 (1)(0) + (4) (0) + (0) S1 + (0) S2 + (1) S3 = 3600 Or S1 S2 S3 = 1200 = 3000 = 3600 Choosing the pivot column Rule : for maximization problem, the nonbasic variable with the largest cj-Zj value for all cj-Zj 0 is the pivot variable. The variable that is nonbasic and becomes a basic variable is often called the entering variable. Choosing the pivot row If the jth the pivot column, compute all ratios bi/aij, where aij > 0. Select the variable basic in the row with the minimum ratio to leave the basis. The row with the minimum ratio is the pivot row Initial Simplex Tableau cj 3 4 0 0 0 cb BASIS x1 x2 S1 S2 S3 0 0 0 S1 S2 S3 1 2 1 1 3 4 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 Zj 0 0 0 0 0 cj - Zj 3 4 0 0 0 Solution Ratios 1200 1200/1 = 1200 3000 3000/3 = 1000 3600 3600/4 = 900 0 The pivot operation and the optimal solution Suppose the jth is the pivot column and the kth is the pivot row, then the element akj is the pivot element. The pivot operation consists of m elementary row operations organized as follows: 1. Divide the pivot row (ak , bk) by the pivot element akj. Call the result (ak , bk). 2. For every other row (ai , bi), replace that row by (a , b) + (-aij)(ak , bk). In other words, multiply the revised pivot row by the negative of the aijth element and add it to the row under consideration. …pivot operation Step 1 : (1/4 4/4 0/4 0/4, 3600/4) Step 2* (modify row 2 by multiplying the revised pivot row by -3 adding it to row 2) (-0.75 -3 0 0 -0.75, -2700) +( 2 3 0 1 0 , 3000) ( 1.25 0 0 1 -0.75, 300) Step 2* (modify row 1 by multiplying the revised pivot row by -1 adding it to row 1) (-0.25 -1 0 0 -0.25, -900) +( 1 1 1 0 0 , 1200) ( 0.75 0 1 0 -0.25, 300) Second Simplex Tableau cb 0 0 4 cj 3 4 0 0 0 BASIS x2 0 0 1 S1 1 0 0 S2 0 1 0 S3 -0.25 -0.75 0.25 Solution S1 S2 x2 x1 0.75 1.25 0.25 Zj 1 4 0 0 1 3600 cj - Zj 2 0 0 0 -1 300 300 900 ..where Z1 = (0)(0.75) + (0)(1.25) + (4)(0.25) = 1 Z2 = (0)(0) + (0)(0) + (4)(1) =4 Z3 = (0)(1) + (0)(0) + (4)(0) =0 Z4 = (0)(0) + (0)(1) + (4)(0) =0 Z5 = (0)(-0.25)+ (0)(-0.75)+ (4)(0.25) = 1 and the objective value is (0)(300) + (0)(300) + 4(900) = 3600 Second Iteration Simplex Tableau cj 3 4 0 0 0 cb BASIS x1 x2 S1 S2 S3 Solution Ratios 0 0 4 S1 S2 x2 0.75 1.25 0.25 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 -0.25 -0.75 0.25 300 300 900 300/0.75 = 400 300/1.25 = 240 900/0.25 = 3600 Zj 1 4 0 0 1 3600 cj - Zj 2 0 0 0 -1 Third Iteration Simplex Tableau cj 3 4 0 0 0 cb BASIS x1 x2 S1 S2 S3 Solution 0 3 4 S1 x1 x2 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 -0.6 0.8 -0.2 0.2 -0.6 0.4 120 240 840 Zj 3 4 0 1.6 -0.2 4080 cj - Zj 0 0 0 -1.6 0.2 Ratios 120/0.2 = 600 ----840/0.4 = 2100 Fourth Simplex Tableau cb 0 3 4 cj 3 4 0 0 0 BASIS x2 0 0 1 S1 5 3 -2 S2 -3 -1 1 S3 1 0 0 Solution S1 x1 x2 x1 0 1 0 Zj 3 4 1 1 0 4200 cj - Zj 0 0 -1 -1 0 600 600 600 Optimal Condition for Linear Programming The optimal solution to a linear programming problem with a maximization objective has been found when cj – Zj 0 for all variable columns in the simplex tableau. Kesimpulan Solusi optimal didapatkan dengan nilai skateboard deluxe (X1)= 600; skateboard professional (X2)=600 dan keuntungan yang didapatkan adalah $4200 Review metode Simplex Mengubah bentuk batasan model pertidaksamaan menjadi persamaan. Membentuk tabel awal untuk solusi fisibel dasar pada titik origin dan menghitung nilai-nilai baris zj dan cj-zj Menentukan pivot column dengan cara memilih kolom yang memiliki nilai positif tertinggi pada baris cj-zj Menentukan pivot row dengan cara membagi nilainilai pada kolom solusi dengan nilai-nilai pada pivot column dan memilih baris dengan hasil bagi non negatif terkecil. Review… Menghitung nilai pivot row yang baru menggunakan formula: nilai pivot row tabel lama dibagi dengan pivot elemen. Menghitung nilai pivot yang lain menggunakan formula: nilai baris tabel lama – (koef.pivot column yang berhubungan dikali dengan nilai pivot row yang berhubungan) Menghitung baris-baris zj dan cj-zj yang baru. Lakukan iterasi sampai nilai cj-zj adalah nol atau negatif. Diperolehlah solusi optimal. Contoh soal: Selesaikan model program linear berikut ini menggunakan metode simplex! Maksimumkan Z= 4x1+5x2 Constrains: x1+2x2 ≤10 6x1+6x2 ≤36 x1 ≤4 X1,x2 ≥0