mitosis internet lesson
advertisement

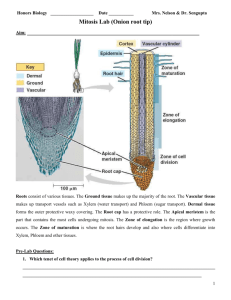
PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON http://teachers.olatheschools.com/apaepkeonw/ -INTRO TO ONION ROOT ACTIVITY -READ THROUGH before STARTING ACTIVITY -MITOSIS IN WHITE FISH & ONION ROOTS -DETAILED SKETCHES! (take your time) -use color when necessary [purple] -CELLS ALIVE -mitosis tutorial [play animation] -cell cycle [basic animation / checkpoints] -cell cam [cancer / bacteria ] -cell quiz -cell gallery check out MEIOSIS MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON RED PEN OUT PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON ONION ROOT TIP CLASSIFICATION 20 10 3 2 1 56 28 8 6 2 PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON MITOSIS IN WHITEFISH & ONION ROOT a- Why is the whitefish used to study mitosis? -CELLS RAPIDLY DIVIDE b- What are the four stages of mitosis? -PRO / META / ANA / TELO c- How long does it take for mitosis to complete? -SEVERAL HOURS d- Why will most of the cells you view be in interphase? -LONGEST STAGE -grow/develop [metabolism] -replicate DNA -prepare PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON MITOSIS IN WHITEFISH ANAPHASE METAPHASE PROPHASE TELOPHASE PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON MITOSIS IN ONION ROOT ANAPHASE METAPHASE PROPHASE INTERPHASE TELOPHASE LAB: OBSERVING MITOSIS/ONION ROOT -DETAILED SKETCHES! (take your time) -be NEAT: final copy READ DIRECTIONS WHEN LAB IS COMPLETED -you may OBSERVE other slides LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT PROBLEM/QUESTION: -Identify each stage of mitosis in a prepared slide of onion (allium) root tips. BACKGROUND: -In a growing plant root, the cells at the tip of the root are constantly dividing to allow the root to grow. Because each cell divides independently of the others, a root tip contains cells at different stages of the cell cycle. This makes a root tip an excellent tissue to study the stages of cell division. -Remember, interphase is not technically a part of Mitosis, but it is a part of the cell cycle and many of the cells you will be observing are in interphase. LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT PROCEDURE: 1-START with the microscope on LOW POWER OBJECTIVE / DIAPHRAM open to widest setting. 2-OBTAIN a prepared slide of an onion tip root. -Hold the slide up to the light to see the pointed ends of the root section. -This is the root tip where the cells were actively dividing. 3-PLACE the slide on the microscope stage with the root tips pointing AWAY from you. -Using the LOW-power objective to find a root tip and focus it with the COARSE adjust until clearly visible. -Just above the root “cap” is a region that contains many new small cells. -The larger cells of this region were in the process of dividing when the slide was made. -These are the cells you will be OBSERVING. -Center the image, the SWITCH TO HIGH POWER. LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT 4-OBSERVE the box-like cells that are arranged in rows. -Select one cell whose chromosomes are clearly visible. -If you need to change the focus when using the high power only use the FINE ADJUSTMENT. DATA: 5-SKETCH the cell that you selected in the circle below labeled A 6-SELECT (4) other cells whose internal appearances are DIFFERENT from each other and from sketch-A. 7-Looking along the rows of cells you SKETCHED, IDENTIFY what stage each cell is in. (see RESOURCE) LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT RESOURCE- Use the photos below as a guide to help IDENTIFY each stage of your sketches. CHROMATID CHROMATIN INTER PRO META ANA TELO PRELAB: MITOSIS INTERNET LESSON LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT 8-Use the data table to RECORD the number of cell that you OBSERVE in each of the stages. LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT CONCLUSION 1-What STAGE were the MAJORITY of the cells in? -INTERPHASE 2-What EVIDENCE shows that mitosis is a CONTINUOUS PROCESS, not a series of separate events? -stages FLOW / BLEND into each other LAB: MITOSIS ONION ROOT 3-SUMMARIZE what happens in each phase of MITOSIS: (use bullets) PROPHASE Mitosis begins- chromosomes CONDENSE [chromatid] Centrioles appear Spindle fibers form METAPHASE Chromatids attach to spindle fibers in MIDDLE ANAPHASE Chromatids separate- AWAY TELOPHASE 2 new nuclei form Mitosis ends 4-What is the end RESULT of mitosis AND why is it so IMPORTANT? - (result) NEW CELLS [identical daughter cells] - (important/function) REPAIR / REPLACE / GROW