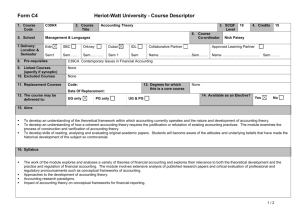
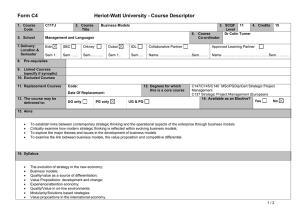
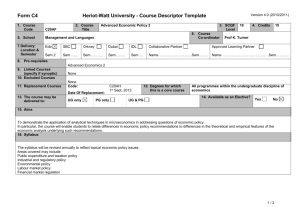
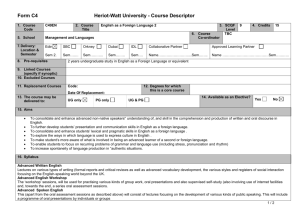
SEM - University of Windsor
advertisement

SEM University of Laval, 2008 Strategic Enrolment Management at the University of Laval Setting the Context: Core Concepts © Smith, 2008 1 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Presenter Clayton Smith, Ed.D. Vice-Provost, Students & Registrar University of Windsor, Ontario, Canada Telephone: 519.253.3000 ext. 3879 Email: csmith@uwindsor.ca © Smith, 2008 2 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Workshop Goals Establish a common understanding of SEM Present recent trends, best practices & emerging Canadian SEM issues Review key components of a SEM Plan Ensure lots of discussion and sharing of challenges & best practices © Smith, 2008 3 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Materials SEM Core Concepts PowerPoint presentation SEM Audit Article on Canadian vs. U.S. SEM SEM Plan Web Sites Bibliography © Smith, 2008 4 SEM University of Laval, 2008 What is SEM? Enrollment management is an organizational concept and a systematic set of activities designed to enable educational institutions to exert more influence over their student enrollments. Organized by strategic planning and supported by institutional research, enrollment management activities concern student college choice, transition to college, student attrition and retention, and student outcomes. These processes are studied to guide institutional practices in the areas of new student recruitment and financial aid, student support services, curriculum development and other academic areas that affect enrollments, student persistence and student outcomes from college. - Don Hossler, 1990 © Smith, 2008 5 SEM University of Laval, 2008 A Few Other Definitions SEM is a comprehensive process designed to help an institution achieve and maintain optimum enrolment, where optimum is defined within the academic context of the institution. -Michael Dolence (1993) Strategic enrolment management is a concept and process that enables the fulfillment of institutional mission and students’ educational goals. -Bob Bontrager (2004) © Smith, 2008 6 SEM University of Laval, 2008 A bit about SEM… © Smith, 2008 7 SEM University of Laval, 2008 SEM Started in the U.S. Started in the late 1970’s at Boston College • As a result of declining traditional student enrolments Early focus on attracting new students (e.g., returning adults, women, minorities, lowincome) Expanded to all types of PSE institutions (e.g., public, private, 2-year, 4-year, grad) © Smith, 2008 8 SEM University of Laval, 2008 SEM Started in the U.S. (Cont’d) Grew to include student success • First-Year Experience programs • Increased levels of student engagement Increasing emphasis on connecting with institutional financial management Now the concern of the senior leadership team – presidents, provost, deans © Smith, 2008 9 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Emergence of SEM in Canada Slower emergence of SEM in Canada Driven by funding cuts, lack of revenue, heavier reliance on tuition, changing demographics Many Canadian institutions have now adopted SEM in name, practice or both • We’re attending webinars, workshops & conferences • Some of us are working with consultants © Smith, 2008 10 SEM University of Laval, 2008 © Smith, 2008 11 SEM University of Laval, 2008 A Few Core Concepts © Smith, 2008 12 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Prospects The Classic Admissions Funnel Inquiries Applicants Admits Matrics © Smith, 2008 13 SEM University of Laval, 2008 • Traditional Enrollment Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Orientation Classroom Experience Co-curricular Support Student’s University Career Admission Financial Support © Smith, 2008 Academic Support Retention 14 SEM University of Laval, 2008 • The SEM Perspective Recruitment/ Marketing Orientation Classroom Experience Co-curricular Support Student’s University Career Admission Financial Support Academic Support © Smith, 2008 Retention 15 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The Enrolment Funnel is Different for Different Students Student Type: •Aboriginal Students •New Canadians •International Students •First Generation Students •Northern Canadians •Rural Students •Students with Disabilities •Dislocated Workers •Francophone Students •Sole Support Mothers •Low-income Students •Visible Minority Students •High-Achieving Students © Smith, 2008 16 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The Concept of Optimum Enrolment Ethnicity Physical Capacity Undergrad/ Grad Majors Institutional Mission Academic Profiles Special Skills Residency Program Capacity © Smith, 2008 17 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Creating a Data-Driven Enrolment Plan The Enrolment Data Agenda Alumni Research Placement Data Graduate Rates Retention Data Student Surveys Enrolment Strategies Active Alumni Graduated Engaged, Satisfied Retained Financial Aid Analysis Alumni engagement Graduation/ Career Development First Year Exp. & Retention Programs Enrolled Yield Yield Data Admission Statistics Competitive Analysis Market Research Deposited Applied/Admitted Recruitment Prospective Students Marketing © Smith, 2008 18 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Institutional Mission & Enrolment Goals Are Determined By: Current competitive status Programs offered Range of influence Niche Aspirational status Weaknesses Historical status Strengths …with consideration to institutional differentiation! © Smith, 2008 19 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Establishing clear goals for the number & types of students needed to fulfil the institutional mission Promoting student academic success by improving access, transition, retention, & graduation Promoting institutional success by enabling effective strategic & financial planning © Smith, 2008 20 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The Purposes of SEM are Achieved by… Creating a data-rich environment to inform decisions & evaluate strategies Improving process, organizational & financial efficiency & outcomes Establishing top quality student-centred service Strengthening communications & collaboration among departments across the campus to support the enrolment program -Bontrager (2004) © Smith, 2008 21 SEM University of Laval, 2008 © Smith, 2008 22 SEM University of Laval, 2008 No One Way “Myths about enrolment management are abundant, yet one truism has emerged…there is no single way to implement enrollment management.” -Jim Black (2004) © Smith, 2008 23 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Determine your niche, focus on it, and deliver on it as well as you possibly can . . . …the very essence of SEM © Smith, 2008 24 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Enrolment Goals: The Classic Conundrum All may want better students Administration may want more students Faculty usually want fewer students Access vs. Quality -Adapted from Henderson (2005) © Smith, 2008 25 SEM University of Laval, 2008 What SEM is Not A quick fix Solely an organizational structure An enhanced admission & marketing operation A financial drain on the institutional budget An administrative function separate from the academic mission of the institution © Smith, 2008 26 SEM University of Laval, 2008 A Few Ways to Look at SEM © Smith, 2008 27 SEM University of Laval, 2008 “Capacity Development Loop” + + “Delivery Loop” Programs & Courses Offered + Courses Taught + or + Programs & Courses Developed & Approved + Demand for Programs & Courses Courses Enrolled Reasons For Not Continuing + + + + Tuition & Other Sources Of Revenue Gov’t Grants & External Funding Student Retention + Student Attrition Programs & Courses Completed Students Graduated, Transferred, Hired = Gov’t Approval For Credit Programs + + + + + + Source: P. Seto, 2008 © Smith, 2008 28 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Enrolment Management System Student Characteristics Environmental Factors Member of underserved student group Student enrolment behaviour Beliefs & values Demographic trends Academic preparation Competition Motivation to learn Educational aspirations Public Accountability (loan default rate, graduation, Accessibility, retention) Self-discipline Adaptability Interpersonal skills Peer involvement Ability to pay Study habits Family & peer Support Student geographic draw Institutional Goals Quantitative Goals Qualitative Goals Diversity Goals Institutional Objectives Student headcount Admission average Transfer GPA Visible minorities, Aboriginal, international Federal & provincial polices Desired Outcomes •Marketing •Recruitment •Admission •Financial aid/pricing •Orientation •Residence •Athletics •First Year •Experience •Advising •Supplemental instruction •Service learning •Learning communities •Academic support •Peer support •Teaching & learning approaches •Student engagement •SEM organization •Data mining Persistence Goals Retention rates, Student Satisfaction, graduation rates Capacity Goals Classroom capacity, adequate sections, Class size Net Revenue Goals Financial aid discount rate, international © Smith, 2008 enrolment Economic Trends Off-campus employment availability Institutional Strategies Awareness Enduring Effect Institutional Loyalty Enduring Behaviour Institutional Image Interest Commitment Enrolment Persistence Satisfaction Education Relationship Source: Adapted from Kuh et al , 2007; Black, 2003 29 SEM University of Laval, 2008 © Smith, 2008 30 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Major SEM Components Accessibility Enrolment Marketing Accountability Organization Admission Policies Planning Financial Aid Recruitment Geographic Draw Retention © Smith, 2008 31 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Emerging SEM Issues in Canada © Smith, 2008 32 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Educational System Blending/overlap of college & university roles, offerings Pressure for more seamless pathways, collaborative programs Re-conceptualization of post-secondary education, move to differentiation Expanding capacity (Ontario, B.C., Alberta) © Smith, 2008 33 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Educational System (Cont'd) Emergence of accreditation bodies (quality councils) Private institutions (e.g. Quest, Meritus) Out-of-country universities establishing campuses in Canada • e.g. Australia’s Charles Stuart U in Burlington; Fairleigh Dickinson U in B.C. © Smith, 2008 34 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Fiscal Pressures Decreased government funding Targeted funding with more strings attached Heavier reliance on tuition, revenues Increasing costs (food, energy, construction) Deferred maintenance, crumbling buildings & infrastructure Fixed costs are high & difficult to reduce (e.g., faculty & staff levels, salaries) Maintaining/expanding enrolment becomes necessary from a financial perspective © Smith, 2008 35 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Enrolment Planning Demographic “bubble” about to burst • Will increase in educational participation rate & immigration make up for it? Impact of economy → a “wild card” Not just first-year numbers, but total enrolment….right through the funnel © Smith, 2008 36 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Impact of Online Learning Double digit growth in recent years Distinctions between on-line and bricks & mortar institutions blurring Moving from the fringes to the centre Why? • Focus on high demand programs with strong career orientations • More convenient & flexible delivery mechanisms • Increasing price of oil (transportation costs) Impacts enrolment & service planning & provision © Smith, 2008 37 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Data Concern over lack of common data set Questioning whether we’re collecting & sharing the “right” data Use of KPI’s • A tool for assessment of strategies, tactics & outcomes but…. • Also used as a basis for funding (& ranking) institutions © Smith, 2008 38 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Recruitment Escalating competition has resulted in seeking of new markets (geographic, post-secondary, “mature”, under-served populations) Concern with access (& persistence) of “1st generation” & “low-income” students Desire for increased flexibility (scheduling, course offerings, mode of instructional delivery) Focus on parental expectations & pressures • Gen-X parents involved in children’s college search, selection & career choices © Smith, 2008 39 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Impact of E-Recruitment Development of the “stealth” marketplace • Proliferation of secret shoppers • Resistant to traditional marketing People get information directly from each other, not from institutions • Growth of WOM, “viral” marketing, social networking • We no longer control our own messages © Smith, 2008 40 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Impact of E-Recruitment Importance of developing relationships through online (& offline) communications CRM systems, Web portals & enhanced Web sites • Information “just in time” • Personalized & customized communication - Example: Customized print-on-demand viewbooks Expectation of 24/7 e-services On-line recruitment fairs © Smith, 2008 41 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Admissions Change in philosophy from gatekeeper to facilitating enrolment • Self-admission (UBC); self-reporting of grades Centralized application centres Some universities beginning to advocate entrance testing due to a concern over grade inflation at the high school level © Smith, 2008 42 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Admissions (Cont'd) Holistic admissions assessment Pressure for more transfer pathways & collaborative agreements Dual enrolment programs Reserving spaces for under-represented groups © Smith, 2008 43 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Financial Aid Use as a SEM strategy to boost enrolment Rising fees & higher student debt load 59% of undergraduates graduate with debt (2007) Biggest failure of student financial aid system has been its inability to close gap in access to postsecondary education for low-income youth © Smith, 2008 44 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Financial Aid (Cont’d) Affordability seen as an accessibility issue • Low-income students think they can’t afford tuition & rule themselves out before graduating from HS Need for financial aid workshops for families when students in middle & high school to build expectations for attending PSE On-campus work-study programs Need to simplify financial aid & make it more transparent © Smith, 2008 45 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Financial Aid (Cont'd) Growing use of merit aid • Disproportionately awarded to higher income students • Now being questioned, shift to more use of needs-based aid Targeted aid/scholarships to Aboriginal students (B.C.; U of Winnipeg) Increase in athletics scholarships (Ontario) Slated closure of Canada Millennium Scholarship Foundation in 2009 © Smith, 2008 46 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Student Service Antiquated policies, procedures, programs, delivery methods & organizational culture that developed during period of student abundance continue to function Lack of a strong “culture of service” • Students seen as interrupting more important activities • Need for more e-service programs & support Bicameral governance structures & collegial decision-making processes make it difficult to respond quickly © Smith, 2008 47 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Student Success Recognition of link between recruitment & retention Students drop out because of dissatisfaction with their program, financial concerns, & career indecision (CMSF, 2008) Bridging & transition programs Need to reach out to parents, families & communities • Parent listservs, web-based resources Focus on the student experience, student engagement, service learning • uCalgary: e-portfolio to recognize volunteerism & extra- curricular activities © Smith, 2008 48 SEM University of Laval, 2008 How Do You Know You Are Doing SEM Well? © Smith, 2008 49 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #1 - Assessments Inputs into the strategic planning process • Key performance indicators • Enrolment management calendar • Student and faculty needs and priorities © Smith, 2008 50 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #2 - Comprehensiveness A strong linkage with academic programs An institution-wide recruitment and retention program An operations orientation © Smith, 2008 51 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #3 – Definitions A common set of definitions and classification systems including: • An adequate recruitment structure • A complete retention classification system • A comprehensive list of operational responsibilities © Smith, 2008 52 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #4 – Documentation Recording of: • The process • Changes in the process • Any assessments determined © Smith, 2008 53 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #5 – Evaluation The process by which an institution learns how much of what it set out to do was accomplished and how well it was done © Smith, 2008 54 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #6 – Key Performance Indicators A detailed list of measurements the institution considers key to monitoring and evaluating enrolment management strategies © Smith, 2008 55 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #7 – Leadership A clear and concisely written charge establishing the enrolment management program, which: • Initiates a formal strategic planning process • States in unambiguous terms who is responsible • Articulates a commitment to make decisions • Expresses a commitment to implement the program once designed © Smith, 2008 56 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #8 – Participation & Integration Participation of senior administration, academic governance, academic administration, faculty and the persons responsible for strategy and tactic implementation © Smith, 2008 57 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #9 – Resources Effective resource allocation systems which: • Utilize consensus building • Link enrolment management objectives directly with manager performance evaluations © Smith, 2008 58 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #10 – Strategies Straight-forward, easy to understand, and workable strategies which fit the resources of the institution © Smith, 2008 59 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #11 – Systems Integration of support systems Accurate, secure and available data Access to the right tools to ensure that tasks are accomplished accurately and in the proper sequence © Smith, 2008 60 SEM University of Laval, 2008 #12 – Timing A master enrolment management calendar which shows: • How decisions are made • Who makes them • On what basis they are made © Smith, 2008 61 SEM University of Laval, 2008 (2004) Research Finds Participation & Integration to be the most Important Factor in Sustaining Long-term SEM Success Change of R value = 0.417 Statistically significant at the 0.05 level -Smith, 1997 © Smith, 2008 62 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The SEM Plan: A Great Place to Start © Smith, 2008 63 SEM University of Laval, 2008 When you don’t know where you’re going, any road will take you there. - Cheshire Cat, Alice in Wonderland © Smith, 2008 64 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The enrolment plan serves as the road map for achieving specific institutional goals, typically connected to student body size, enrolment mix, and revenue, while also providing specific indicators on the effectiveness of the learning environment. - Janet Ward, 2005 © Smith, 2008 65 SEM University of Laval, 2008 © Smith, 2008 66 SEM University of Laval, 2008 © Smith, 2008 67 SEM University of Laval, 2008 SEM Planning Model Meeting Goals Typical starting point Tactics Strategies DATA Enrolment Infrastructure Structure, Staffing, Skills, Systems, Service Clear Mission & Goals © Smith, 2008 68 SEM University of Laval, 2008 SEM Planning Model Meeting Goals Tactics Strategies DATA Enrolment Infrastructure Structure, Staffing, Skills, Systems, Service Starting point for long-term success Clear Mission & Goals © Smith, 2008 69 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The SEM Plan- Components 1. Define relationship to the College’s strategic plan 2. Produce an environmental scan 3. Collect data: informs everything (goal-setting, tactics/strategies, assessment) Enrolment: totals, demographics, 5-year trends, etc. Promotion & marketing Admissions & entry process Image & reputation Retention Market surveys, competitor analysis Financial aid Course offerings: capacity, scheduling, waitlists Budget: income streams, expenditures © Smith, 2008 70 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The SEM Plan- Components (Cont’d) 4. Identify key enrollment-related issues 5. Identify how to respond to those issues 6. Set goals: enrolment targets, program mix, program delivery, income targets, services © Smith, 2008 71 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The SEM Plan- Components (Cont’d) 7. Suggest strategies Recruitment Marketing Program mix Policies and procedures Retention Financial aid 8. Establish accountability Who does what and when? © Smith, 2008 72 SEM University of Laval, 2008 The SEM Plan- Components (Cont’d) 9. Include measurements/ key performance indicators (KPIs) Most goals should be measurable Know your baseline data, and measure against it 10. Be sure the process is on-going: Follow-up on assessment of the KPIs Update often – this is not a long range plan...it is a strategic plan. Be strategic! Ensure continuous communication with campus © Smith, 2008 73 SEM University of Laval, 2008 SEM Audit © Smith, 2008 74 SEM University of Laval, 2008 Q&A Thank you! © Smith, 2008 75