Ed 745 BDA Lesson Planning
advertisement

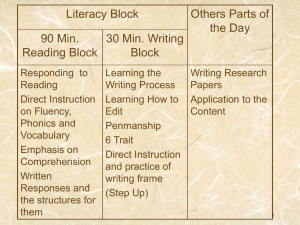
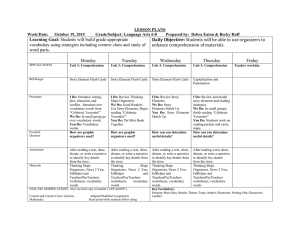
“Comprehension is the reason for reading. If readers can read the words but do not understand what they are reading, they are not really reading.” (Put Reading First, p. 48) Seven categories of strategies that provide evidence of efficacy in comprehension (NRP, 4-6) : 1. Comprehension Monitoring (metacognition) 2. Cooperative Learning (small groups) 3. Graphic & Semantic Organizers (show relationships) 4. Story Structure (who, what, where, when, why; plot, setting, characters, events) 5. Question Answering (QAR’s) 6. Question Generation (who, what, where, when, why, how) 7. Summarizing (main ideas) Levels of Comprehension Literal - Reading the lines • Getting information explicitly from the text Interpretive - Reading between the lines • Putting together information, perceiving relationships, and making inferences Applied - Reading beyond the lines • Using information to express opinions and form new ideas STRATEGIES TO IMPROVE READING COMPREHENSION Oral Reading Fluency Silent Reading • Repeated Readings • DRA • Assisted Reading • DRTA • Choral Reading • SSR/DEAR • Imitative Reading • ReQuest • Partner Reading • Reciprocal Teaching Oral Reading Fluency Silent Reading • Echo Reading • Guided Reading Procedure (GRP) • NIM • Anticipation Guides • Mumble Reading • QAR’s • Readers’ Theatre • KWL • 4-Way Reading • Graphic Organizers • Locational Reading • Semantic Mapping • Taped-Assisted Readings • Summarizing • Shared Reading B-D-A LESSON STRUCTURE Instructional Sequence Rationale Before Reading To establish purpose, activate background knowledge, sustain motivation, and provide direction During Reading To guide an active search for meaning After Reading To extend and elaborate ideas from the text Before-During-After Reading (B-D-A Lesson Structure) Before Reading: Set Goals Activate/build prior knowledge Establish any necessary background Arouse curiosity Motivate students to read Sample Strategies: K-W of KWL Anticipation Guide Cloze Procedure Brainstorm Vocabulary/Word Building Graphic Organizers Writing (Quick-Write) Book Talk Discussion Make Predictions (DRTA) Agree/Disagree Statements (Intra-Act) Questioning (QAR’s) S-Q of SQ3R During Reading: Facilitate Comprehension Focus attention on characters, issues, themes, or details Engage students in their reading Make Connection (T-S; T-T; T-W) Encourage reflection and personal responses Sample Strategies: Mapping; Webbing Reading Guide QtA Questioning/Predicting (DRTA) Reciprocal Teaching Discussion Note-Taking Response Journal/ Writing Log Compare/Contrast Charts After Reading: Provide closure Synthesize information Move beyond the book itself Critically analyze and evaluate Relate to personal experiences (T-S; T-T; T-W) Sample Strategies: Graphic Organizers (e.g., Relationship Web) Compare/Contrast Charts Cloze Procedure Writing (e.g., L of KWL) Analysis of literary style Drama Art Music Plays Poetry Multimedia Research Web Quests Student Inquiry Projects DR-TA (Directed Reading-Thinking Activity) 1. 2. 3. 4. Activating prior knowledge Predicting the content Reading Confirm or revise predictions “What do you think?” “Why do you think so?” “Can you prove it?” RECIPROCAL TEACHING • Predict • Question • Clarify • Summarize RECIPROCAL TEACHING • Predict • Question • Clarify • Summarize Comparison Chart (Nonfiction) -comparing different sources of information -comparing different opinions by different authors -charting “facts” for different versions of the same information Text Author Main Idea Supporting Details Difference of opinion ED 745 Dr. Schatmeyer Wright State University