Personality Theories 1. Psychodynamic Sigmund Freud
advertisement

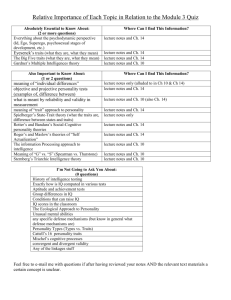
What is Personality? An individual’s typical patterns of thinking, feeling, and acting Theories: Psychoanalytic Humanistic Social-Cognitive Trait Sigmund Freud and Psychoanalysis childhood sexual development, and unconscious motivations (Id), influence adult personality Unconscious mind – sex and aggression Core tendency: maximize instinctual gratification, while minimizing punishment and guilt Personality Structure Structure of the mind Id, Ego, Superego Levels of awareness Conscious, preconscious, unconscious • • • • • • • • Defense mechanisms Repression Projection Displacement Reaction formation Regression Denial Sublimation Carl Jung 1875-1961 Analytical Psychology personal and collective unconscious (archetypes) snake symbolism in Australian aboriginal bark painting, Egyptian tomb painting, 15th century European painting Jung: Archetypes: innate universal psychic dispositions from which the basic themes of human life emerge – a set of keys we all inherit to understand life and create culture mother, father, man, woman, etc Joseph Campbell, mythologist, identified Jung’s archetypes in all of the myths and religions of the world George Lucas read Campbell’s books and translated the archetypal characters into his Star Wars films. Luke (hero) – must sacrifice to save tribe, culture Leia (princess) – must be rescued by hero; reward Darth Vadar (evil) – dark side of human nature tries to lure hero Wookie (threatening animal) – danger of nature Hans Solo (joker) – humor soothes us poking fun at ourselves keeps us honest Obi-wan Kenobi (wise sage) – wisdom of elders R2D2, C3PO (technology can turn on us) Jung - Other instincts are just as important as sex, aggression Anima (feminine side of males) Animus (masculine side of females) Similar to Asian concept of Yin/Yang Personal and Collective Unconscious Personal – your own “dark side”; repressed emotions and ideas (like Freud) Collective – the dark side of humanity; deeper unconscious, where archetypes live; ingrained in human nature Easily explains why “7 deadly sins” (pride, greed, envy, anger, lust, gluttony, sloth) are common ideas in all cultures (these sins were not Jung’s idea) Behavioral & Social-Cognitive Theories Personality traits are learned habits, shaped by an interaction between the individual’s actions, cognitive expectations for responses, and actual feedback from others Julian Rotter: Internal vs External Locus of Control – master of my fate, or not? Related to achievement and learned helplessness Humanistic Perspective Abraham Maslow (1908-1970) studied selfactualization processes of productive and healthy people (e.g., Lincoln) Carl Rogers (1902-1987) self-actualization congruence between real and ideal self unconditional vs conditional positive regard genuineness acceptance empathy self-concept The Trait Perspective Much more "observable" and rational approach to personality Grounded in empirical research Goal is to describe more than explain personality Supports notion that characteristics are strongly influenced by genes Raymond Cattell – Source vs Surface traits - p. 399 Moody Anxious Rigid Sober Pessimistic Reserved Unsociable Quiet UNSTABLE Touchy Restless Aggressive Excitable Changeable Impulsive Optimistic Active melancholic choleric INTROVERTED EXTRAVERTED phlegmatic sanguine Passive Careful Thoughtful Peaceful Controlled Reliable Even-tempered Calm Sociable Outgoing Talkative Responsive Easygoing Lively Carefree Leadership STABLE Trait a disposition to think, feel, and act a certain way Personality Inventory Hans and Sybil Eysenck use two primary personality factors as axes for describing personality variation • The BIG 5 Theory of Personality • Traits are independent of one another Big Five – Domains (5) and Facets (6 each domain) Openness to experience Fantasy Aesthetics Feelings Actions Ideas Values Conscientiousness Competence Order Dutifulness Achievement Striving Self-Discipline Deliberation Extraversion Warmth Gregariousness Assertiveness Activity Excitement Seeking Positive Emotion Agreeableness Trust Straightforwardness Altruism Compliance Modesty Tendermindedness Neuroticism Anxiety Hostility Depression Self-Consciousness Impulsiveness Vulnerability to Stress Recent research shows that some species of animals demonstrate reliable personality traits similar to the Big 5 factors Traits not reliably measured until 8 yrs Traits very stable from age 30 + Degree of traits very similar across cultures N,E,O decline. A,C increase Assessment Interviews Halo effect Projective Tests Rorschach Inkblot Test Thematic Apperception Test Reliability, Validity Behavioral Assessment Personality Inventories NEO FFI Myers-Briggs MMPI Geert Hofstede – Cultural Traits • Individualism – Collectivism (Western vs Asian) • Power Distance (Middle East vs Western) • Masculinity – Femininity (Ireland, U.S. vs Sweden, Chile) • Uncertainty Avoidance (South American vs Asian, U.S.) • Long-term – Short-term orientation (China, Hindu vs U.S.)