Application Software
advertisement

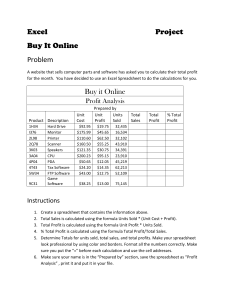
Applications Software Applications Software • Applications software is designed to perform specific tasks. • There are three main types of application software: • Applications packages • Tailor-made software • General purpose packages Applications Packages • Examples of applications packages include: • Word processing software – MS Word, WordPerfect • Spreadsheet software – MS Excel, Lotus 1-2-3 • Database software – MS Access Integrated Software • A common type of applications software found on home personal computers is integrated software. • This is a software package that includes a collection of application software that shares a common set of commands. Integrated Software • A typical integrated software package will include: • A word processor program • A spreadsheet program • A database program • A graphics manipulation program • Integrated software packages have advantages and disadvantages. Integrated Software Advantages: Disadvantages: • Easier to use • Tend to have weak areas (e.g. better at • Moving data word processing than between programs spreadsheets) within the package is easy • Data is not easily moved to programs • Cheaper than that are not part of the separate programs package • Cheap is not always best! Tailor-made Software (Bespoke) • Tailor-made software is very expensive because it is designed for a specific purpose. • It is software that is not available ‘off the shelf’ and is usually written or developed for large organisations (e.g. government, banks, insurance companies, manufacturers). General Purpose Software • General purpose software is not specific to a particular user (e.g. MS Word), and may be capable of development into tailor-made software (e.g. MS Access). • It is very popular because it is usually relatively cheap, well tested, and has wide support (e.g. easy to use manuals and tutorials). General Purpose Software • General purpose software is also known as ‘content free software’. Generic Software • e.g. word processing, spreadsheet and database. • This simply implies that any of the dozens of spreadsheet packages, for example, can be made to do many different tasks, and is not designed specifically for one type of application Word processor Program or set of programs used to enter, edit, format, store and print documents. A document may be anything from a simple memo to a complete book. Word processors have several important features: • Spelling and grammar checker • Each word in a document can be checked against words held in the package’s dictionary. • Automatic creation of index and table of contents • Any word in the text can be marked for inclusion in an index, which can be updated at any time. • Import files • Tables, photographs, graphics and even video and sound files can be imported from other sources and inserted in a document. Word processor (cont.) • Mail Merge • A document and a list of names and addresses can be merged to produce personalised letters. • Creation of templates • with preset text styles, margins, formatting, letterheading, etc. • WYSIWYG capability • ‘What You See Is What You Get’ Spreadsheet features • Format cells, rows and columns • specifying for example, the alignment of text, number of decimal points, height and width of cell; • Copy cell contents to other locations • with automatic adjustment of formulae; • Determine effect of changes of data • this facility is termed ‘what-if’ calculation; • Insert, move or delete rows and columns • Use functions • such as SUM, AVERAGE, MAX, MIN in formulae; Spreadsheet features (cont.) • Create a simple database • and sort or query the data to produce report of, say, all females earning over £20,000; • Write macros • to automate common procedures; • Create templates • spreadsheets with formats and formulae already entered, into which new figures may be inserted; • Create ‘multi-dimensional’ spreadsheets • using several sheets, copy data between sheets; • Create many different types of charts and graphs Presentation Graphics • e.g. PowerPoint. Useful for putting together a presentation which can be delivered using a computer attached to a projection device. • slides with text, graphics and pictures • animation or sound effects • ‘transition’ effects between slides Web Browser • Shows a web page for which you have either entered the URL or clicked on a ‘hot’ link; • Browses back and forward; • ‘Bookmarks’ pages for quick reference; • Keeps a ‘History’ list of pages visited; • Saves pages for viewing off-line; • Shows animation sequences in Java script; • Plays back sound, video clips and multimedia; • Downloads files to a local hard disk; • Submits on-line forms by e-mail; • Allows access to some personal e-mail.