Creating effective learning objectives and measures
advertisement

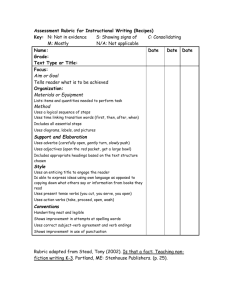
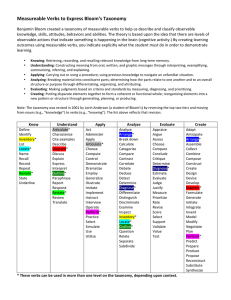
Dr. Barbara Wheeling Coordinator for Institutional Assessment Montana State University Billings September 1, 2010 Primary Concepts The learning objectives should clearly state what the learner should be able to do. The assessment should measure if they can, in fact, do that. Patti Shank, "Online Teaching Fundamentals: To Plan Good Instruction, Teach to the Test", Online Classroom, June, 2006, P. 4. Tips on Learning Objectives Learning Objectives have two parts: a verb and a content area. 2. Keep statements short and focused. 3. Avoid verbs that are vague or cannot be objectively assessed. 4. Learning objectives should be studentfocused. 1. http://captain.park.edu/facultydevelopment/writing_l earning_objectives.htm. Key Questions for Writing Learning Objectives 1. Is it specific? An objective is written too broadly if ○ It cannot be reasonably assessed with just one or two assessments ○ It covers several different elements of the subject matter from a course or semester 2. Is it observable and measurable? Examples, not measurable: ○ “Students will understand how to divide two-digit numbers.” ○ “Students will develop an appreciation of cultural diversity in the workplace.” Example, measurable: ○ “Students will correctly divide two-digit numbers.” ○ “Students will summarize in writing their feelings about cultural diversity in the workplace.” Avoid phrases such as, ○ “have an understanding”, “have an appreciation for”, “be knowledgeable about” Be careful of modifiers such as, ○ “will effectively”, “can accurately”, “should completely” ○ These can make measurement impossible 3. Is it actually a teaching outcome? Avoid phrases such as: ○ “will be taught”, “will learn how to”, “will be evaluated on” 4. Does the objective include action verbs? Overt behavior that can be observed and measured Examples: compile, create, plan, revise, analyze, design, select, utilize, apply, prepare, use, compute, discuss, explain, predict, assess, compare, rate, critique. Using Bloom’s Taxonomy The taxonomy provides a useful structure in which to develop learning objectives. Primarily useful for deciding on action verbs Assurance of Learning Blackboard site: The Assurance of Learning Initiative The Process Step 1: What should students be able to do? These are the objectives. Step 2: What indicates students have met the objective? These are authentic tasks. Step 3: What does good performance on the task look like? These are the criteria to assess. Step 4: How well did the students perform? Use a rubric with the criteria or Compile a score for each objective Step 5: How well should most students perform? The minimum level at which you would want students to perform is a benchmark. Step 6: What do students need to improve upon? Information from the rubric will provide feedback and ideas for improving instruction. Q&A