Telecommunications and Networks
advertisement

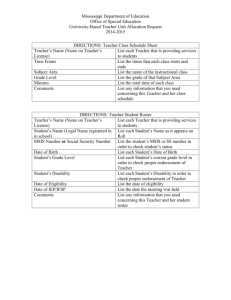
Telecommunications and Networks Chapter 6 MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 1 Principles and Learning Objectives • Effective communication is essential to organizational success. – Define the terms communication and telecommunications and describe the components of a telecommunications system. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 2 Principles and Learning Objectives • An unmistakable trend of communications technology is that more people are able to send and receive all forms of information over greater distances at a faster rate. – Identify three basic types of communications media and discuss the basic characteristics of each. – Identify several types of telecommunications hardware devices and discuss the role that each plays. – Identify the benefits associated with a telecommunications network. – Name three distributed processing alternatives and discuss their basic features. – Define the term network topology and identify five alternatives. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 3 Principles and Learning Objectives • The effective use of telecommunications and networks can turn a company into an agile, powerful, and creative organization, giving it a long-term competitive advantage. – Identify and briefly discuss several telecommunications applications. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 4 Overview of Telecommunications Systems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 5 Communications MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 6 Communications MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 7 Telecommunications MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 8 Telecommunications Media MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 9 Basic Communications Channel Characteristics • Simplex channel • Half-duplex • Full-duplex channel MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 10 Bandwidth • The range of frequencies that an electronic signal occupies on a given transmission medium. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 11 Broadband • Telecommunications in which a wide band of frequencies is available to transmit information, allowing more information to be transmitted in a given amount of time. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 12 Shannon’s Fundamental Law of Information Theory • The information carrying capacity of a channel is directly proportional to its bandwidth - the broader the bandwidth, the more information that can be carried. MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 13 Types of Media • • • • Twisted-Pair Coaxial Cable Fiber-Optic Cable Microwave Transmission MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 14 Twisted-Pair Wire Cable MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 15 Coaxial Cable MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 16 Fiber Optic Cable MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 17 Microwave Transmission MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 18 Satellite Transmission MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 19 Cellular Transmission MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 20 Telecommunications Devices MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 21 Devices • Modems: – Analog – Digital • Special-purpose modems • Multiplexers • Front-end processors MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 22 Modems MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 23 Multiplexers MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 24 Front-End Processors MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 25 Carriers and Services MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 26 Carriers and Services • • • • • • • • Common carriers Value-added carriers Switched and dedicated lines Private branch exchange (PBX) Wide-area telecommunications service (WATS) Phone and dialing services Digital subscriber line (DSL) T1 Carrier MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 27 Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN) MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 28 Carriers and Services MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 29 Networks & Distributed Processing MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 30 Basic Processing Strategies • Centralized processing • Decentralized processing • Distributed processing MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 31 Network Concepts and Considerations • Network topology – – – – – Ring network Bus network Hierarchical Star network Hybrid network • Network types – – – – Local Area Networks Wide Area Networks International networks Home and small business networks MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 32 Network Topology MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 33 Network Topology MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 34 Network Topology MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 35 Local Area Networks MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 36 Wide Area Networks MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 37 Home and Small Business Networks MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 38 Terminal-to-Host MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 39 File Server MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 40 Client/Server MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 41 Communications Software and Protocols MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 42 Communications Software • Network operating systems (NOS) • Network management software MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 43 Communications Protocols • Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) model • Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) • Systems Network Architecture (SNA) • Ethernet • Asynchronous Transfer Mode (TM) • Bluetooth MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 44 Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 45 Open Systems Interconnection (OSI) Model MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 46 Network Interconnectivity Technology MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 47 Bridge, Routers, and Gateways MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 48 Telecommunications and Applications MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 49 Telecommunications and Applications • • • • • Voice mail Electronic software distribution Telecommuting Videoconferencing Electronic data interchange (EDI) MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 50 Videoconferencing MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 51 Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 52 Public Network Services MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 53 Summary • Communications - any process that permits information to pass from a sender to one or more receivers • Telecommunications media - twisted-pair wire cable, coaxial cable, and fiber-optic cable • Modems - convert signals from digital to analog for transmission, then back to digital • Ethernet - the most widely installed local area network (LAN) technology MSIS 110: Introduction to Computers; Instructor: S. Mathiyalakan 54