L/T 2
advertisement
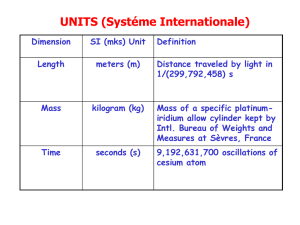
Chapter (1) Introduction What is physics? Units Dimensional Analysis What is physics? Physics is the most basic of all sciences. Underlying principles of all engineering fields. The goal of Physics is to explain on a fundamental level how our environment behaves. Physicists try to model the world mathematically. Physicists try to understand all the little pieces that make a physical system work. Classical physics (Between 1600 and 1900) Classical mechanics: The study of the motion of particles and fluids. Thermodynamics: The study of temperature, heat transfer, …… Electromagnetism: Electricity, magnetism, Electro- magnetic waves, and optics. Modern physics (After 1905) Special relativity: a theory of the behavior of particles moving at high speed. Quantum mechanics: A theory of submicroscopic world of the atom. General relativity: a theory that relates the force of gravity to the geometrical properties of space. Some Major Fields of Physics Astrophysics Atomic Physics Biophysics Chemical Physics Geophysics Nuclear Physics Optics Particle Physics Solid State Physics Units The value of physical quantity must be expressed in terms of some standard or units. Units are necessary to compare measurements and also to distinguish between different quantities. Different systems of units The international system of units (SI). The British system. The units of length is the foot. The units of time is the second. The units of Force is the pound. This system doesn’t use mass as a basic unit. o The units of temperature is F. The international system of units It uses seven base units: Length (m) Mass (kg) Time (s) Temperature (K) Electric current (A) Amount of substance (mol) Luminous intensity (cd) Dimensional Analysis Since equations must be dimensionally correct, dimensional analysis may be used to: Check the correctness of the form of the equation. Derive a relation between the physical quantities. Dimensional Analysis physical quantity Units (SI) Dimensions Length Mass Time Area Volume Force Velocity Acceleration m Kg S m2 m3 Kg m/S2 m/S m/S2 L M T L2 L3 M L / T2 L/T L / T2 Check the correctness of an equation. The speed of waves in shallow water depends only on the acceleration of gravity g, with dimensions L/T 2, and on the water depth h. Which of the following formulas for the wave speed v could be correct? 1 2 v gh v gh 2 L L 2 2L T T L L L 2 T T L L3 2 T T L L T T Terms do not match Terms match, this could be a valid formula. Limitations Dimensional analysis only checks the units. Numeric factors have no units and can’t be tested. gh v 3 is valid. v gh 4 is not valid. Example The period p of a simple pendulum is the time for one complete swing. How does p depends on the the mass m of the bob, the length L of the string, and the acceleration due to gravity g? P = K L a gb (K is constant) ---------------- (1) T = K [L]a [L/T2]b Equate the power of each dimension, thus L: 0 = a + b, then a = -b T: 1 = -2b then b = - 1/2, Sub. In (1) L pk g a = 1/2 Example The wavelength λ of a wave depends on the speed v of the wave and its frequency f. decide which of the following equations is correct, = v/f or = vf Assume that = va fb Solution [L] = [L/T]a.[1/T]b [L] = [L]a.[T]-a-b Equate the power of each dimension, thus L: 1 = a T: 0 = -a-b a = -b = v/f QUIZ (1) What are the dimensions of the following? [3] [sin (wt)] Show that the following equation is Dimensionally correct. 1 2 X vot at 2