lecture 5 - cda college
advertisement

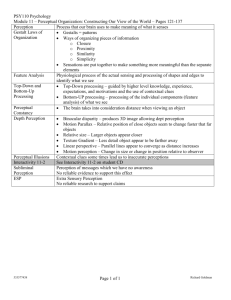
PERCEPTION LECTURE 5 WHAT IS PERCEPTION? What is Perception? Perception is a process by which individuals organize and interpret their sensory impressions in order to give meaning to their environment. IMPORTANCE OF PERCEPTION: WRITE DOWN HOW YOU PERCEIVE THE FOLLOWING IMAGES. Horizontal lines or do they slope? How many legs does this elephant have? Vase or two profiles? An old woman or a young lady? Content or skeptical? WE DON’T SEE THINGS AS THEY ARE…. WE SEE THINGS AS WE ARE…. The importance of Perception People’s perceptions influence how they behave in their organization. Perception describes the way people filter, organize and interpret sensory information. Accurate perception allows employees to interpret what they see and hear in the workplace effectively to make decisions, complete tasks and act in ethical manner. Faulty perceptions lead to problems in the organization, such as stereotyping, that lead people to erroneously make assumptions. MENTION SOME FACTORS YOU BELIEVE INFLUENCE PERCEPTION.. Factors Influencing Perception There are three main categories of factors influencing perception: Factors in the perceiver Factors in the situation Factors in the target Factors in the perceiver (personal characteristics of the individual perceiver for example if we except young people to be lazy, we may perceive them as such regardless of their behavior) Attitudes Motives Interests Experience Expectations Factors in the situation (the context in which we see objects or events for example you might not notice an extreme haircut in a club but you’ll probably notice it at school. The perceiver and the target are the same.) Time Work Setting Social Setting Factors in the target (Characteristics of the target we observe eg loud people will get more notice than quiet ones) Novelty Motion Sounds Size Background Proximity Similarity Selective perception Halo Effects Shortcuts for judging others Stereotyping Contrast Effects Frequently used Shortcuts in Judging Others Selective Perception: The tendency to selectively interpret what one sees on the basis of one’s interests, background, experience and attitudes. Halo Effects: The tendency to draw a general impression about an individual on the basis of a single characteristic. Frequently used Shortcuts in Judging Others Contrast Effects: Evaluation of a person’s characteristics that is affected by comparisons with other people recently encountered who rank higher or lower on the same characteristics. Stereotyping: Judging someone on the basis of one’s perception of the group to which that person belongs ( for example the police). What is your stereotype of a manager? Sensation Versus Perception Sensation is the information we pick up with the help from our sensory organs. Perception is the interpretation of this sensory information. Perceptual Selectivity Numerous stimuli constantly confront everyone. The noise of air conditioners, the sound of other people talking and moving, and outside noises from cars and vehicles, planes, and many other sounds are heard by us every minute but why and how people select a specific stimulus or a few stimuli at a given time? Perceptual Selectivity The answers can be found in the principles of perceptual selectivity. External Attention Factors Internal Set Factors Perceptual Selectivity External Attention Factors: Intensity: The more intense, the most likely will be t be perceived. Size: The larger the object, the more likely it will be perceived. Contrast: A stimulus which stands out against the background gets more attention (Stop sign-red with white). Repetition: More times, more attention. Motion: Moving object gets more attention than a stable one. Novelty and Familiarity: Novelty means something new and fresh and familiarity means something known and experienced. So, the principle of novelty and familiarity states that new objects in familiar settings and familiar objects in new settings get more attention. Perceptual Selectivity Internal Set Factors: Learning and Perception: Learning affects selectivity of perception, because the people read and see what they expect to see and hear (Turn of the the engine). Perceptual set in workplace: In organization life, some employees have learned to perceive the world around them in the same way. Motivation and Perception: a person who has a relatively high need for power or achievement will be more attentive to the relevant situation. Personality and Perception: Personality of the perceiver also affects what is attended to in confronting situations. Perceptual Organization The perceptual process organizes the incoming information into a meaningful whole. In other words, the perceivers’ mind organizes the information in such a way that it can give meaning and is understandable. Perceptual Organization Figure Ground: The figure ground principle means simply that perceived objects stand out separable from their background. Perceptual Organization Perceptual Grouping: It states that there is a tendency to group several stimuli together into a recognizable pattern. When people are presented with stimuli they tend to group them into closure, proximity and similarity. Perceptual Organization Impression Management: Is the process by which people attempt to manage or control the perceptions others form of them. There is often a tendency that people present themselves so as to impress others in a desirable way. Social Perception SOCIAL PERCEPTION Social perception is a term that defines an individual’s ability to create an impression or judgment of other individuals or social groups. Social Perception This is formed through observation and understanding existing information about an individual and drawing out conclusions from the information. Wrongful social perceptions when one person mistakes another person's characteristics as the cause of a negative event, can lead to problems in organizational behavior.