File
advertisement
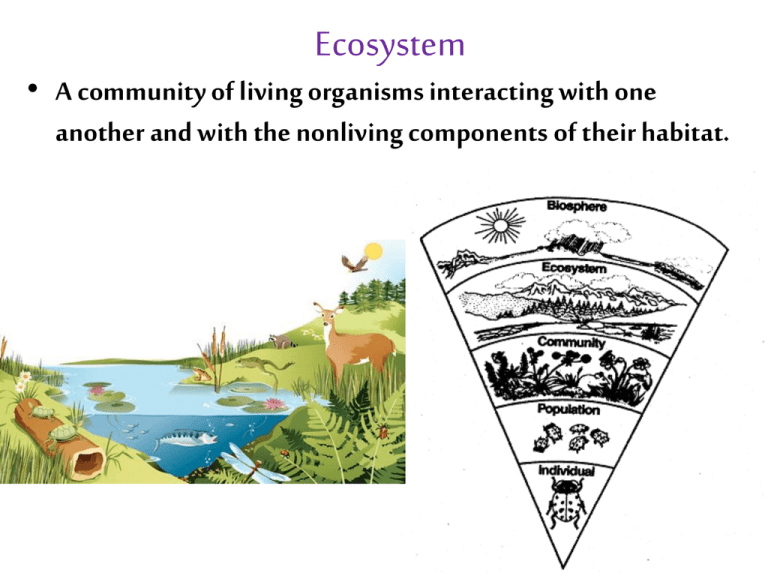
Ecosystem • A community of living organisms interacting with one another and with the nonliving components of their habitat. Ex: lake, forest, jungle, island, mountain.. Trophic Relationships • Trophic relationships are the feeding connections among the living organisms in an ecosystem. All living organisms need energy to survive and they obtain it by feeding on organisms in their environment. Trophic relationships are represented by a FOOD CHAIN Trophic Levels • Food chains contain the following trophic levels: 1) Producers 2) Consumers 3) Decomposers Producers • These organisms get the energy they need to survive by taking inorganic matter (matter not produced by living organisms such as rocks, sunlight, water, minerals) and turning it into organic matter (matter created by a living organism such as leaves, tree bark, flowers). Usually done through photosynthesis Can feed themselves without having to ingest other living organisms Also called autotrophs Introduce energy and matter into ecosystems Producers Biomass: Total mass of organic matter in an ecosystem Organic matter is made by producers. Producers are constantly turning inorganic matter into organic matter. Primary Productivity: Amount of new biomass created by producers in an ecosystem. This is the amount of energy available for primary consumers. As primary productivity increases, the number of organisms able to live in an ecosystem increases (more food available). Factors that Influence Primary Productivity • • • • Amount of light (for photosynthesis) Amount of water available (for photosynthesis) Amount of nutrients in the soil Temperature (warmer weather promotes the growth of producers) Rainforest Arctic Consumers • Consumers obtain the energy they need by feeding off of other living organisms. They are heterotrophs (incapable of producing food for themselves from inorganic matter) Can be separated into two types: primary consumers or second/third/fourth order consumers Types of Consumers • Primary (or first-order) Consumers: -Feed on producers -Are herbivores/frugivorous • Second/third/fourth order Consumers: - Feed off primary consumers - Are carnivores **Note: Omnivores are consumers of several orders at once. Ex: a bear can eat plants and fish** Decomposers • Organisms that feed on the waste and remains of other organisms (organic matter) and turn it into inorganic matter Feed off detritus (dead organic matter) Heterotrophs Also called detrivores Decomposers & Chemical Recycling Chemical Recycling: When decomposers make inorganic available for others in an ecosystem by breaking down organic matter Try This! 1. Which organism can be classified as a Primary Consumer? a) Red Tailed Hawk b) Shrew c) Willow d) Snowshoe Hare 2. Which organisms act both as a secondary and tertiary consumer depending on the individual food chain they are involved in? a) Shrew and Red Fox b) Lynx and Red Fox c) Lynx and Snowshoe Hare d) Red Tailed Hawk and Insects Try This! Using the above food web, indicate an example of a producer. Explain why producers can also be called autotrophs.








