chapter14
advertisement

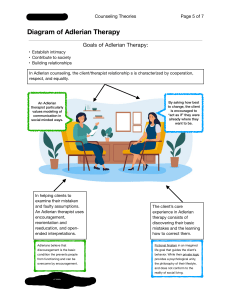
Theory and Practice of Counseling and Psychotherapy Psych422 Chapter14: Family System Therapy The Family Systems Perspective Individuals – are best understood through assessing the interactions within an entire family Symptoms – are viewed as an expression of a dysfunction within a family Problematic behaviors – Serve a purpose for the family Are a function of the family’s inability to operate productively Are symptomatic patterns handed down across generations A family – is an inter-actional unit and a change in one member effects all members Adlerian Family Therapy Alfred Adler Adlerians use an educational model to counsel families Emphasis is on family atmosphere, birth order, and family constellation Therapists function as collaborators who seek to join the family Understand the purposes of underlying children’s misbehavior Adlerian Family Therapy Therapy Goals Unlock mistaken goals and interactional patterns Engage parents in a learning experience and a collaborative assessment Emphasis is on the family’s motivational patterns (e.g., a desire to belong) Main aim is to initiate a reorientation of the family Multigenerational Family Therapy Murray Bowen The application of rational thinking to emotionally saturated systems With the proper knowledge the individual can change A well-articulated theory is considered to be essential Change occurs only with other family members Triangulation A pattern of interaction with two-against-one experience A third party is recruited to reduce anxiety and stabilize a couples’ relationship Multigenerational Family Therapy Make the most use of genograms Differentiation of the self A psychological separation from others Involve (1) psychological separation of intellect and emotions and (2) of independence of the self from others. The greater one’s differentiation, the better one’s ability to keep from being drawn into dysfunctional patterns with other family members. Multigenerational Family Therapy Therapy Goals To change the individuals within the context of the system To end generation-to-generation transmission of problems by resolving emotional attachments To lessen anxiety and relieve symptoms To increase the individual member’s level of differentiation Human Validation Process Model Virginia Satir Open communications Enhancement of self-esteem Family decisions are based on individual needs Encouragement of growth Individuals are allowed to honestly report their perceptions Differences are acknowledged and seen as opportunities for growth Transform extreme rules into useful and functional rules Families have many spoken and unspoken rules Experiential Family Therapy Therapy Goals (Carl Whitaker) Application of existential therapy to family systems Help individuals achieve more intimacy by increasing their awareness of their inner potential and opening channels for family interaction An interactive process between a therapist and a family Encourage members to be themselves by freely expressing what they are thinking and feeling Techniques grow out of the therapist’s intuitive and spontaneous reactions (Therapist use of self) to the present situation in therapy Structural Family Therapy Salvador Minuchin Focus is on family interactions to understand the structure, or organization of the family Symptoms: are a by-product of structural failings Structural changes must occur in a family before an individual’s symptoms can be reduced Structural Family Therapy Therapy Goals Reduce symptoms of dysfunction Bring about structural change by modifying the family’s transactional rules and developing more appropriate boundaries Strategic Family Therapy Jay Haley Focuses on solving problems in the present Presenting problems are accepted as “real” and not a symptom of system dysfunction Therapy is brief, process-focused, and solutionoriented The therapist designs strategies for change Change results when the family follows the therapist’s directions & change transactions Strategic Family Therapy Therapy Goals Resolve presenting problems by focusing on behavioral sequences Get people to behave differently Shift the family organization so that the presenting problem is no longer functional Move the family toward the appropriate stage of family development Problems often arise during the transition from one developmental stage to the next Family therapy as a whole Basic assumption An individual’s problematic behavior grows out of the interactional unit of the family, community, and societal systems Focus of family therapy Short term, solution-focused, action-oriented, and here-and-now interaction. Focus on how current family relationships contribute to the development and maintenance of symptoms. Family therapy as a whole Role of goals and values Specific goals are determined by family and therapist Global goal is to reduce family’s distress How family change Cognitive, emotional, or behavioral changes Change needs to happen in relationships, not just within the individual Family therapy as a whole Techniques of family therapy Techniques are tools for achieving therapeutic goals Personal characteristics (respect, empathy, sensitivity) are even more important Always consider what is in the best interests of the family. From a multicultural perspective Contributions Many ethnic and cultural groups place great value on the extended family Approach each family as unique culture Limitations Few limitations for multicultural counseling Summary and Evaluation Contributions Inclusion of all parts of the system rather than being limited to the “identified patient” Rather than blaming either “identified patient” or the family, the entire family has an opportunity (1) to examine the multiple perspectives and interactional patterns that characterize the unit and (2) participate in finding solutions. Limitations lose sight of the individual by focusing on the broader system