Work-related learning
advertisement

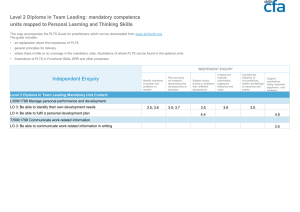
Additional Applied Science Rationale, Assessment and Resources 1 Some figures Bottom 40% of UK workplace earn less than 2/3 of the pay of German counterparts Why? Lower percentage in education post-16 National Commission on Education Follow-up Group (Dec 2003) 2 Applied Science courses Motivate potential school leavers success at all levels meaningful hands-on experiences assessment – larger % coursework real employment prospects 3 Work-related learning A statutory requirement at KS4 rationale – – learning … – – – The student: ‘a broad and balanced education … ‘part of fully preparing for an adult life’ The economy: ‘the country’s economic well-being’ through work about work for work audited 4 Applied Science courses Major challenges authenticity, as employment patterns change perceptions of students, parents, teachers and employers 5 C21 Additional Applied Science Aim: To meet the needs of students who wish to develop their scientific understanding through authentic, work-related contexts. 6 1993 study - CSTI Occupational group number (000s) Category Nurses & midwives 467 Agriculture/horticulture/forestry/fisheries 329 Engineers (all types) 311 Chem/gas/petroleum process operatives 161 Medical doctors & dentists 156 Lab science technicians 130 Medically related occupations 128 Food processing operatives 113 Secondary school science teachers 106 Product, works and maintenance managers 86 Marketing sales managers 73 University/HE/FE teaching professionals 64 Engineering technicians 60 Biological scientists and biochemists 49 Chemists 39 Physicists, geologists, meteorologists etc 28 critical enhanced/significant critical enhanced critical main main/critical enhanced significant significant significant main critical main main main 7 Additional Applied Science Choose any 3 modules from: Life care Agriculture and food Scientific detection Harnessing chemicals Communications Materials and performance 8 Key features of the course 1 Cluster of related workplace contexts 2 Authentic procedures and techniques 3 Underpinning science knowledge 4 Employers, regulators, social values 5 Problem-solving - applying knowledge 9 Key features of the course 1 Cluster of related contexts in which people apply science in their work - but with freedom to adapt to local circumstances – assessment: Work-related report 2 Authentic procedures and techniques ‘where the results matter’ - adapted as necessary for school labs – assessment: Standard procedures 10 Key features of the course 3 Underpinning knowledge - with a degree of coherence and including some big ideas of potential value for progression – assessment: Module Test 4 Framework within which people apply science (organisations, employers, regulators, social values) – assessment: Work related report, Module Test 5 Applying knowledge and techniques to solve a practical problem – assessment: Suitability test 11 Internally assessed skills Authentic and manageable Work-related Portfolio – – – Six standard procedures (2 per module) - 12% One suitability test - 21% One work-related report - 17% Additional Applied modules have been developed to take 36 hours, leaving time for skills assessment Teachers arrange coursework differently to suit their curriculum and students 12 Module structure Example: Ap2 Agriculture and food Ap2.1 The agriculture and food industries Ap2.2 Ap2.3 Ap2.4 Growing plants for food Animal farming for food Biotechnology and food Ap6.5 Quality, value and sustainability 13 Scheme of work (each module) 35 hours of guided classroom activities +10 hours for skills assessment + FLEXIBILITY through work: science-related work experience placements about work: practitioner focus, visits from & to local workplaces for work: work-related portfolio, underpinning knowledge 14 Video sequences for the course Locations A1: Human performance lab, Middlesex Uni Diagnosis and treatment – from GP to hospital A2: Longley farm - from cow to yoghurt A3: National Gallery – examining paint Food standards officer, Haringey Environmental Agency – monitoring a stream Cape Farewell – gathering data about life in the Arctic seas A4: Manufacturing agrochemicals A5: Ferraris Respiratory – testing baby monitors A6: Rolls Royce – testing turbine blades National Physical Laboratory – measuring temperature Funded by Gatsby SEP 15 Student books Referenced from the scheme of work – Case studies – People – The and organisations science – Procedures and techniques Coursework overview – Glossary and index – 16 Progression routes AS/A Applied Science BTEC Nationals in Science Other vocational courses and vocationallyrelated qualifications AS/A courses in Biology, Chemistry or Physics (top students, with suitable choice of modules) 17 Challenges for technicians volume of practical work ordering new apparatus and consumables storage providing for varied tasks in the classroom e.g. Suitability tests maintenance of frequently-used kit 18 Challenges for teachers Addressing perceptions of students & parents Capitalising on the freedom, not letting it be a burden Meeting the diverse demands for equipment, materials and ICT Making connections with the working world of science Managing the assessment Offering progression to post-16 courses 19 What do teachers say? “Pupils enjoy the practical work involved” “Attitudes, motivation and achievement in science improve during the applied course” “It is a genuine pleasure to be working with pupils in these lessons” “The grades that students achieve are typically one grade higher than we might expect from previous science courses” 20 Websites General information: www.21stcenturyscience.org Publications from OUP: www.twentyfirstcenturyscience.org Specifications, assessment and training: www.ocr.org.uk 21