Case Report DVT/PE - Lock Haven University

Case Report
DVT/PE
Brenda Mertsock, PA-S
Lock Haven University
September 2008
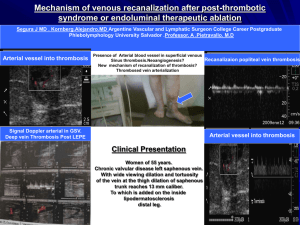
This is what we saw!
Presenting Symptoms
Patient drove herself to the ER
CC: Shortness of Breath
Tightness in her chest X a few hours.
VS: 148/95, 82, 20, 98.2 F
HPI: Included rt. leg was swollen, warm to touch, and painful X 12 days.
Pain was now a 3 out of 10, but it felt like a cutting, tight rope pressure behind the knee that was much more swollen and tender for the past 12 days.
HPI
Aug, 1 st , active doing yard work, felt pain behind the knee
Aug, 2 nd , hauling logs, trimming trees, more physical activity, swollen rt knee
Aug 3 rd , knee so swollen, she reclined most of the day with it elevated , also noticed an exacerbation of low back pain
Aug 4 th , her usual chiropractor out of town, went to someone new , showed him her leg and he agreed it was swollen and worked on her back
Aug 6 th , her chiropractor back in town, he attributed her swollen leg to her back pain
Aug 7 th , went to her primary care physician , he said her SI joint was out and that there was probably some pooling from that .
No one ever made a measurement .
By this time, she felt like her skin could not stretch anymore, she elevated it every night, but nothing helped.
She continued to walk daily, work in her very busy professional business, and do household chores.
Aug 9 th , her and her husband drove to North Carolina and then on Monday drove 10 hours back.
On Tuesday the 12 th , she went to work and that evening was in the ER with SOB .
Tests Ordered & PE
CBC, BMP, D-Dimer, PT, PTT, cardiac enzymes, EKG, venous duplex of right lower extremity, and a CT chest with IV contrast.
Right lower leg moderate to severe tenderness, swelling, and warmth to the post rt. knee, calf, and rt. popliteal.
Tenderness to a cord-like structure along the great saphenous vein post. to the knee medially along the thigh.
PE: no increased JVD or thyromegaly, lungs were CTA Bilat., RRR, S1 and S2 with no murmurs, + abd BS, soft, NT, no oganomegaly, no guarding or rigidity, portable chest x-ray was unremarkable.
Lungs were well expanded, unremarkable heart, hila, and mediastinum.
Recent Past Medical History
Past 6 mo. new onset of hypothyroidismtaking 25mg daily of Levothyroxine
Past 6 mo. New onset of menorrhagiataking Solia .15/.03mg
Past mo. skin rash- taking 5 mg prednisone
Takes multivitamin and Oyster-D
Allergic to Penicillin
DVT
Differential Diagnosis
Acute deep vein thrombosis of the right leg popliteal vein, great saphenous vein thrombosis- underlying etiology of Oral contraceptives
Chest pain ruling out PE or MI
Hypothyroidism
Test Results
Pertinent lab results:
White ct – 12,700
Neutrophils- 90.4%
Negative cardiac enzymes
D-dimer- over 5000 ug/ml (0-300 ref range)
Venous Doppler showed rt common femoral and femoral veins patent,
Rt popliteal vein was occluded and contained thrombus with minimal flow , posterior tibial vein appeared to be patent.
CT showed extensive pulmonary emboli through-out the pulmonary arteries bilaterally. This was so extensive there were only a few branches that were not involved.
Admit to hospital with BRP only…
For 6 days
Treatment
Sub-Q Lovenox 100 mg/ml q 12 hr
Use until therapeutic oral anticoagulation of
Coumadin is established with a level between 2 and 3.
Pt will be on anti-coagulant therapy for 9 mo to a year and monitor PT-INR.
Pt was informed of risks and benefits of treatment.
Pt will continue on thyroid med, vitamins, and discontinue OCP.
Why did it Happen?
Ethinyl estradiol and norgestrel
Brand Names:
Cryselle 28
Lo/Ovral- 28
Low-Ogestrel-28
Ogestrel-28
Patient had no previous history of any type of thrombolytic event.
Pt had no complications with previous oral contraceptive use.
Pt had no contributory family history.
New onset of hypothyroidism and contributing symptom of menorrhagia?
Maybe.
Reinstated use of Oral contracptives?
Maybe.
Solia
Equivalent to:
Desogen
Ortho-cept
Apri
Reclipsen
Oral Contraceptive Use
The pt. took Cryselle (2 nd generation OCP) from Feb to May, could not tolerate it.
The pt. took Solia (3 rd generation OCP) from
May to Aug.
2 nd an 3 rd generation OCPs contain different levels of progestin.
2 nd - Norgestrel
3 rd - Desogestrel
What Happens?
Desogestrel causes resistance to activated protein C (APC)
Decreases total and free protein S
Causes more pronounced APC resistance.
When APC and protein S cannot perform their natural function of inhibiting coagulation, clots tend to form more easily.
Increasing the risk of venous thrombosis.
If a pre-existing pro-thrombotic condition exists, the risk increases 35-fold
What Happens
-600,000 episodes of PE in the US annually
-100,000 – 200,000 deaths
-Most not suspected or unrecognized
-Common cause of death a week to ten days after a thrombosis formed.
.
-Proximal lower extremity venous thrombosis has been reported to be the source of 90% of emboli.
-Symptoms of a PE could include; chest pain, dyspnea, hemoptysis, JVD, fever, tricuspid regurgitation, increased pulmonic heart tone, tachycardia, tachypnea, and pleural effusion.
Clinical Risk Factors for DVT/PE
Age greater than 40 - Renal failure
Previous DVT/PE - Nephrotic syndrome
Surgery requiring anesthesia - Central venous catherization for more than 30 min. - COPD
Prolonged immobilization - Long distance travel
Stroke - Genetic or acquired thrombophilia
Heart failure -Inflammatory bowel disease
Malignancy - Estsrogen therapy
Fractures of long bones or pelvis
Spinal cord injury
Obesity
Smoking
Pregnancy
Discussion
At this time there is a petition to the US Food and Drug
Administration to ban third generation oral contraceptives containing desogestrel. There have been documented case of women of all ages experiencing DVTs from taking OCPs that contain desogestrel.
Pro-thrombotic blood tests are not routinely checked, so prior knowledge is often unknown to the patient.
Need to consider history, physical, and risks, when prescribing
OCPs.
References
Demaria, Andrew (2001, February 5). Deep vein thrombosis explained. Retrieved September 4, 2008, from CNN.com Web site: http://archives.cnn.com/2001/WORLD/asiapcf/01/24/dvt.medical/
Drug Information Online. Retrieved September 5, 2008, from Drugs.com Web site: http://www.drugs.com/drug_interactions.php?action=allinteractions&drugid=d03780&grugname = desogestrel
Parkinson, MD, MPH, Jay, Park, MD, MPH, Sylvia, Wolfe, MD, Sidney M., & Rosendaal, MD, Frits (2007). Petition to the FDA to Ban Third Generation Oral Contraceptives Containing Desogestrel due to Increased Risk of
Venous Thrombosis (HRG Publication # 1799). Protecting Health, Safety & Democracy, Retrieved Sept, 1,
2008, from http://www.citizen.org/publications/release.cfm?ID=7503 .
Savelli, MD, Stephanie L., Kerliln, MD, Bryce A., Springer, MS, CGC, Michelle A., Monda, BSN, RN, Kay L., Thornton,
BSN, RN, Jennifer D., & Blanchong, MD, Carol A. (2006). Recommendations for screening for thrombophilic tendencies in teenage females prior to contraceptive initiation. Journal of Pediatric and Adolescent
Gynecology 19, 1-8
Test, MD, FCCP, Victor J. (2008). Pulmonary Embolism. In Rakel & Bope: Conn's Current Therapy 2008, 60th ed.
[Web]. Saunders, An Imprint of Elsevier. Retrieved Sept 1, 2008, from h ttp://www.mdconsult.com/das/book/body/10388708-
2 /0/1621/155.html?tocnode=54634409&fromURL=155.html#4-u1.0-B978-1-4160-4435-2..50081-9_1072
(2008, July 3). Cryselle 28. Retrieved September 5, 2008, from Consumer Drug Information Web site: http://www.drugs.com/mtm/cryselle-28.html