Dr. Balbaa - BMC Dentists 2011
advertisement

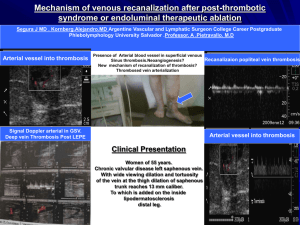
Dr. Balbaa By Mohammad Ashraf Balbaa, MD Associate Professor of Surgery Intrinsic pathway HMW kininogen XII Prekallikerin XIIa HMW kininogen XI Extrinsic pathway XIa TPL IX VIIa IXa PL VIII Ca++ PL VIIIa Ca++ X Xa TPL PL Ca++ V Prothrombin Va Thrombin Fibrinogen XIII VII XIIIa Fibrin Ca++ Dr. Balbaa Definition: A venous thrombus is the formation of a semi-solid coagulum within flowing blood in the venous system. Dr. Balbaa Types: Superficial Thrombophlebitis Deep vein thrombosis Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa The term “Superficial Thrombophlebitis” is customarily applied to any kind of thrombotic process in the superficial venous system. However, it implies existence inflammatory component, which always present. of an is not Dr. Balbaa Definition: Localized inflammation of the vein wall + thrombus formation in the lumen Dr. Balbaa Etiology: Direct trauma. A direct blow over a superficial vein can result in phlebitis. Venous intimal damage Infusion of hypertonic solutions, injurious compounds as antibiotics & chemotherapeutic agents and I.V. drug abuse. Cannula insertion. N.B. Traumatic thrombophlebitis can be put to clinical use in the form of sclerotherapy. Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa Clinical Picture: The vein becomes painful, tender, firm & cord-like. The overlying skin becomes dusky & edematous. Dr. Balbaa Clinical Picture: Embolization is rare as the thrombus is firmly adherent Sometimes, it is accompanied with DVT, especially if there is marked edema that can not be explained by simple or superficial Dr. Balbaa phlebitis alone. Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa Treatment: Prevention: The best R/ for traumatic thrombophlebitis is prevention by: Rotating IV sites every 3 days & changing IV tubing regularly under sterile conditions Diluting irritant infusions. Dr. Balbaa Treatment: Conservative Measures : Rest & elevation + elastic bandage. Warm compresses + non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or aspirin. antibiotics. Dr. Balbaa Treatment: Surgical Measures: If the thrombus propagates e.g. in the long saphenous vein above the knee ligation of the sapheno-femoral junction, under local anesthesia. Excision, in recurrent & symptomatizing phlebitis. Dr. Balbaa Types: Superficial Thrombophlebitis Deep vein thrombosis Dr. Balbaa INCIDENCE: Prevalence Site Side •Occurs for the first time in about 100 persons per 100,000 each year in the United States. This incidence increases with increasing age. •The recurrence rate with anticoagulation has been noted to be 6% to 7% in the ensuing 6 months. Dr. Balbaa INCIDENCE: Prevalence Site Side Upper limb: Axillary vein thrombosis. Lower limb: •venous plexus calf vein thrombosis. •Ilio-femoral thrombosis (phlegmasia alba dolens PAD). •Ilio-frmoral thrombosis + deep pelvic vien thrombosis (phegmasia cerulae dolans PCD). Dr. Balbaa INCIDENCE: Prevalence Site Side Ilio-femoral thrombosis occurs on the left side > right (3:1) due to: •It is more liable to be compressed by the overlying right common iliac artery against L5 •Left iliac vein is longer than the right. Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa Etiology A triad (posited by Virchow in 1856): Stasis Intimal damage Hypercoagulability Dr. -1902 Balbaa 1821 Etiology A triad (posited by Virchow in 1856): STASIS Intimal damage Hypercoagulability Dr. Balbaa STASIS: Stasis in the lower limb is associated with: Immobilization during anesthesia, after trauma and fractures, post operative recumbency & serious illness. Diminished cardiac function (heart failure). Previous DVT: cannot maintain uni-directional venous flow due to valvular incompetence. Dr. Balbaa Etiology A triad (posited by Virchow in 1856): Stasis INTIMAL DAMAGE Hypercoagulability Dr. Balbaa INTIMAL DAMAGE It caused by: Trauma & fractures. Infusions. Infection & toxemia. Dr. Balbaa Etiology A triad (posited by Virchow in 1856): Stasis Intimal damage HYPERCOAGULABILITY Dr. Balbaa HYPERCOAGULABILITY 1ry or familial causes: Anti-thrombin III deficiency Protein S or C deficiency Dr. Balbaa HYPERCOAGULABILITY 2ry or acquired causes: Malignancy, dehydration, toxemia and sepsis, polycythemia, D.M., smoking, pregnancy & post partum state. Dr. Balbaa RISK FACTORS Patient factors Disease or surgical procedure •Age ≥ 60 yr •Obesity •Immobility •Pregnancy •Puerperium •High-dose estrogen therapy •Previous deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism Dr. Balbaa RISK FACTORS Patient factors Disease or surgical procedure •Trauma or surgery, especially of procedure pelvis, hip and lower limb •Malignancy, •Heart failure •Paralysis of lower limb(s) •Polycythaemia Dr. Balbaa PATHOGENESIS 1ry platelet thrombus Mural Coralline thrombus Occluding thrombus Consecutive clot Propagated clot Dr. Balbaa PATHOGENESIS 1ry platelet thrombus Mural Coralline thrombus Occluded thrombus Consecutive clot Propagated clot Dr. Balbaa PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Dr. Balbaa Point of Difference 1. Major cause: 2. Clinical Presentation: Thrombophlebitis Inflammation of the vein wall Pain + signs of inflammation Phlebothrombosis Stasis & hypercoagulability Silent few signs & symptoms 3. Size of propagated Short & fixed Large & easy detachable clot: liable to 4. Emboli: Less liable to embolization. More embolization. Dr. Balbaa CONSEQUENCES OF THROMBOSIS Dr. Balbaa Locally Distally Proximally Dr. Balbaa LOCALLY Lysis: Organization and fibrosis: Results from fibrinolytic action of blood → retraction post-phlebitic leg (CVI), i.e. recanalization with valve destruction Infection: High virulence emboli. organisms → septic Dr. Balbaa Distally: A varying degree of edema after which venous collateral circulation soon opens up tortuous superficial veins, i.e. 2ry VV. Phlegmasia alba and cerula. Post-phlebetic syndrome Dr. Balbaa Proximally: Detachment pulmonary embolism pulmonary infarction up to death. Dr. Balbaa CLINICAL PICTURE Dr. Balbaa CLINICAL PRESENTATION DVT can be completely asymptomatic in about 30-50% of cases. Passed unnoticed Detectable PE, which may be sometimes fatal. Low grade fever which fails to settle after operation. By the occurrence of local signs of in the limb. Dr. Balbaa Swelling the extent of which depends on the site of the thrombus → (frog-leg position): Leg is externally rotated The knee is flexed) Dr. Balbaa Aching pain and heaviness on moving the calf and thigh. Tenderness on pressure on the instep of the sole of the foot and along the affected veins. Dr. Balbaa Increase warmth of the affected limb. Varicose veins due to distension of the superficial veins (late sign). Dr. Balbaa Certain tests: Homan's sign: Dorsiflexion of the foot → resistance or pain of the calf muscles to forcible dorsiflexion – is not discriminatory and should be abandoned. Dr. Balbaa Certain tests: Pratt's sign: Compression of the calf against tibia → pain. Moses's sign: Compression of the calf from side to side → pain. Dr. Balbaa Phlegmasia alba (white) dolens (pain) (White Leg; Milk Leg) Phlegmasia cerulae (blue) dolens Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa COMPLICATIONS Dr. Balbaa 2ry varicose veins: Venous gangrene: 2ry collaterals develop when the deep system is occluded. In PCD. Pulmonary embolism: When a thrombus becomes dislodged form its attachment to the venous wall & is carried into the pulmonary arteries Dr. Balbaa INVESTIGATIONS: Dr. Balbaa NON INVASIVE INVESTIGATIONS Doppler Ultrasonography Duplex Imaging Doppler Color Flow. Magnetic Resonance Venography (MRV) Dr. Balbaa NON INVASIVE INVESTIGATIONS Blood Tests Breakdown products of complexed fibrin (fibrin acted on by factor XIII) generated during physiologic fibrinolysis (D-Dimer). A negative D-dimer test in patients with suspected DVT has a high negative predictive value. A normal D-dimer reliably excludes DVT. Dr. Balbaa MANAGEMENT : Prophylaxis of DVT Treatment of established DVT Conservative (non-operative) treatment Operative surgical treatment Dr. Balbaa PROPHYLAXIS OF DVT Preoperative measures: Mechanical prophylaxis: Elastic compression stockings. Intermittent pneumatic compression (IPC) devices: Dr. Balbaa PROPHYLAXIS OF DVT Preoperative measures: Pharmacologic prophylaxis: Low-dose unfractionated heparin: 5000 unites, CS, beginning 2 hours preoperatively Low-molecular weight heparin (LMWH): Dose is drug dependent, SC, twice daily, no monitoring or dose adjustment. Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa PROPHYLAXIS OF DVT Operative measures: Reduction of trauma to the calf muscles during surgery; the operating table should be well padded to decrease the pressure on the buttocks, calves and heel. Elevation and massage of the leg at the end of the operation is a good plan. Dr. Balbaa PROPHYLAXIS OF DVT Postoperative measures: Early ambulation after surgery. Maintenance of adequate hydration. Pharmacologic prophylaxis. Daily examination of the calves & feet for local signs of thrombosis & on suspicion or history, anticoagulants should be considered. Dr. Balbaa MANAGEMENT : Prophylaxis of DVT Treatment of established DVT Conservative (non-operative) treatment Operative surgical treatment Dr. Balbaa Bed rest and foot elevation Anti-coagulants Thrombolytic (fibrinolytic) & defibrinating agents Post treatment compression to control leg edema: Dr. Balbaa Dose duration 1. Parentral (Heparin) and 5000-10,000 units/6 hours, 7 days, in calf thrombosis and for 14 days in Iliofemoral thrombosis. Low dose MW: 1 mg/kg/12 hrs. 2. Oral (Dendivan) 3 tablets/day reduced to 2 tabs, then one tab for 6 months, started before we stop heparin by 3 days (as it takes 3 days to start its action) Dr. Balbaa Bed rest and foot elevation Anti-coagulants Thrombolytic (fibrinolytic) & defibrinating agents Post treatment compression to control leg edema: Dr. Balbaa Tissue palsmingen activators : streptokinase & human urokinase. Dr. Balbaa Indications: Most effective when given to thrombi of 5-7 days duration. For patients whose clot extends proximally beyond the origin of the deep femoral vein. Dr. Balbaa Dr. Balbaa