PPT Semester Exam Review
advertisement

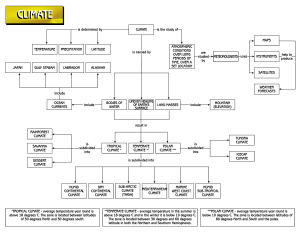
Fall Semester Exam Review By: Mr. Mora Basic Landforms Island – land area, smaller than a continent surrounded by water • Archipelago – a group or chain of islands Basic Landforms Cont’d • Plain - area of land, usually at low elevation and often covered with grasses • Plateau – area of flat or rolling land at high elevation Plate Tectonics • The process of continental drift and magma flow that creates the Earth physical features https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ryrXAGY1dmE Plate Tectonics (cont) • Subduction (or Convergent Plates) – Heavier sea plates dive under lighter continental plates • Creates volcanic mountains – Results in earthquakes and tsunamis Plate Tectonics (cont) • Faults – Occurs when plates grind past each other • As the plates slide, earthquakes are created “Ring of Fire” The Pacific ”Ring of Fire” (or just The Ring of Fire) is an area where large numbers of earthquakes and volcanic eruptions occur in the basin of the Pacific Ocean (responsible for creating places such as the Hawaiin islands). Mountain Ranges of North America The Rocky Mountains stretch from Texas up to Canada Appalachian Mountains are Mostly In the United States. The northern portion extends into Canada. The Appalachian Mountains are older than the Rocky Mountains. Ural Mountains • The Ural Mountain range separates Europe from Asia. Orographic (Rain Shadow Effect) Windward Side Leeward Side The higher the elevation, the temperature gets cooler. Rising air cools and condenses and creates precipitation. Landforms • Delta: A delta is an area of land in which a river divides into smaller rivers and empties into a larger body of water. •A tropical hurricane is caused by the very rapid evaporation of warm ocean water in the late summer months. Typhoon in Okinawa 2012 Typhoon is the same as a Hurricane. Eight Factors That Affect Climate Continental Latitude Location Air Pressure O cean Currents Mountain Barriers Elevation Wind Currents Storms (These 8 factors affect climate…nothing else) Climate Factors Use the map and your knowledge of social studies to answer the following question: • In the map above, the major influencing climatic factor are mountain barriers (i.e., coastal ranges, Sierra Nevada mountains). Remember, mountain barriers is one of the factors in LAMECOWS. The Seasons The seasons occur because of the tilt of the earth and our revolution around the sun Due to tilt of earth, not all places receive same amount of light at one time Tilt Definition: Axial tilt is the inclination angle of a planet's rotational axis in relation to its orbital plane What would happen If the earth’s tilt changed? Seasons would change Population Pyramids Less Developed More Developed Remember, countries with pyramid shapes, such as the Philippines, are less developed, whereas, countries with “honey-combed” shapes are more developed. X and Y Axis of Human Pyramid Y axis = age of people X axis = # of people of a certain age Human Pyramid, Cont. Use the graphs and your knowledge of social studies to answer the following questions. • In the population pyramids above, you can see that in 1950 Japan had a high birth rate and high death rate (i.e. developing country); in the 2007 population pyramid, Japan’s pyramid looks like a honey comb, which signifies a developed country with lower birth rates and lower death rates. In 2050, Japan is projected to have an even lower birth rate and high life expectancies for the elder populations…i.e. Japan will be a country of mostly old people, and few young people. North Africa As everyone can see, population density are in clusters, since this is North Africa, located in the Sahara desert, settlements are found in areas with reliable sources of water. Also, since the northern area of Africa receives less than 10 inches of annual rainfall, this area would be defined as a Desert. Region Characteristics • In the South American country of Brazil, the official language is Portuguese, which comes from Portugal. This thematic map would be most useful to a — • For these kind of questions, use your common sense. For example, since the thematic map above shows the average amount of rain in California, it can be inferred that a farmer would find this information more useful. Urban Buildup With the rise of the Industrial Revolution (i.e. factories, industrial facilities, etc.) an increased labor force in urban areas was needed in order to operate the factories/industry. This increase in human population in the cities has created what is now known as “urban sprawl .” Migration Chart Use the chart and your knowledge of social studies to answer question. Title: _____________________________________________________________________________ Push Factors Pull Factors Turkish authorities persecuted Christian Armenians Armenians with relatives in the United States were in their villages and drove many women and attracted by stories of economic opportunity and a children into the desert. life without persecution. Above, you will see a similar chart and a question asking what would be the best title for the chart. Use your common sense. Read both factors carefully and find a common feature among both to come up with a viable answer. Economics • High tech industry, service and manufacturing industries are an example of Market oriented economy • The European Union (EU) consists of countries that are physically located in Europe. • Subsistence Farming: Farmers grow just enough food crops to feed their own families. • Commercial Farming: Farmers grow food crops in order to sell and make a profit. Economics, Cont. Use the diagram below and your knowledge of social studies to answer the question Subsistence Agriculture Both Market Oriented Agriculture Small Scale Family produced Low Level of technology Type of Agriculture Depends on supply and demand; Common in developed countries; Farmers raise goods that give the most profit • In a market economy, supply and demand determines the prices of goods and services. Traditional Economy Early form, very primitive and basic Economic decisions based on customs and beliefs Passed from one generation to the next by family, etc. Economic system where people produce what they need to survive Often centered around hunting and gathering, subsistence farming, or herding Example: A primitive tribe Communism • A system of government in which the state plans and controls the economy and citizens, claiming to make progress toward a higher social order in which all goods are equally shared by the people • A major goal of communism is to have a classless society Three types of Regions Formal, Functional, and Perceptual • Formal (uniform) – defined by a common characteristics such as a product produced there or climate experienced there • The Corn Belt – Iowa-Illinois area in the US – Common Characteristic? • Islamic World – Middle East – Common Characteristic? Functional Region • Functional - a central place and the surrounding area linked to it – Group of places that help each other function Examples: • Regional airport of Dallas/Fort Worth • Trade area of city Perceptual Region • Perceptual - defined by popular feelings and images rather than by objective data • “Heartland” • Its what YOU think an area is • Hollywood! Part 2 Climate Zones Based on Latitude • Climates in the world are organized into climate zones (based on latitudes): • • • Low Latitude Mid-Latitudes High Latitudes Climate Zones & Biomes (High Latitude) • Subarctic • Arctic • • • Grasslands • Humid Subtropical • Mediterranean Humid Continental Marine West Coast (Low Latitude) • Tropical Rainforest Warmest Avg. Temp • Tropical Grassland • Desert • • • Grasslands • Humid Subtropical • Mediterranean Humid Continental Marine West Coast (High Latitude) • Subarctic • Arctic • Highland (found in mountainous areas around the world) Climatic Zones & Biomes (Not all, there are more…) Biome Climatic Zone World Location Vegetation Seasons Tropical Rainforest Low Latitude Amazon basin, equatorial Africa, East Indies, from Sumatra to New Guinea A canopy of tall trees with layers of shorter trees and plants underneath Heavy rainfall in all months, no difference in seasons; very warm year round Arctic High Latitude Northern North America and Eurasia (Closest to North Pole) Short grasses, mosses, lichens, tundra Extremely cold and dry all year Desert Middle/Low latitudes Western North America (southwest U.S. southwest South America (Chili) north central Mexico, north Africa, southwest Africa, central Australia, north Asia (China, Mongolia) Scattered vegetation; short grasses and shrubs, cacti Warm or Cold, little to no precipitation year round Humid Continental Middle Latitudes North central North America; north central Asia (China); Korea; Japan; central and eastern Europe Mixed coniferous and deciduous forest Warm summer cold winters, moderate rainfall throughout the year Thematic Map Example Use the map and your knowledge of social studies to answer the question. Distribution of Muslim Populations Above is an example of Thematic Map showing the distribution of Muslims around the world. You will need to know to read a thematic map, and know the regions of the world (e.g. Southern Europe, Northern Africa, Northwest Europe, etc.). Climate Regions Use the map and your knowledge of social studies to answer the question. Remember, the climate regions of northern Europe are greatly influenced by the ocean currents from the Pacific, namely the Norwegian current, which started out as the Gulf Stream. Languages Use the map and your knowledge of social studies to answer the question. According to the map, people living in Belgium most likely speak French and German, since they are adjacent to France and Germany. Likewise, people living in Switzerland, most likely speak French, German, and Italian, due to their proximity to France, Germany , and Italy. Overseas Imperialism/Migration • In Africa, European powers exploited African natural resources for their benefit. • In Egypt, most of the population settled along the Nile River for access and availability of resources. • Diffusion is the spread of ideas, knowledge, and skills from their places of origin to other areas where they are adopted. • Economic pull factors caused the shift of population (i.e. urbanization) in 19th century England, and you can see this type of urbanization today in developing nations…i.e. people are being pulled by the possibility of work in the cities. Human & Physical Geography • Deforestation is defined as the depletion or loss of the forest by human activity such as logging, farming, etc. • Based on what you know about LAMECOWS, do lines of longitude dictate or influence climate? No…longitude is not a part of LAMECOWS, hence, not considered a climatic factor. • Conquest and colonization caused the Indo-European language family to be spoken by approximately half of the world. • The effect of the Columbian exchange on European society was an increase in human population due to the introduction of new foods such as, potatoes, corn, etc. Human & Physical Geography, Cont. • The development of the steam engine in the 1800s revolutionized transportation (e.g. steam ships, locomotives). • The mountainous terrain of the Balkan peninsula directly influenced the development of Greek city-states. • In Southern Europe, the Iberian Peninsula is made up of Portugal and Spain Human & Physical Geography, Cont. • The “Old South” of the United States is a good example of a perceptual region, since the term is based on people’s attitudes and perceptions. • European “Imperialism” affected most of the entire continent of Africa. • France and Britain were the two main imperialist power(s) that controlled Africa. • The European Union was created in 1993 with the signing of the Treaty on European Union, commonly referred to as the Maastricht Treaty. • A savannah is an area that has common landforms, soils, climate, and vegetation. Which biome is paired with its correct climatic zone? • Christianity is the predominant religion in Europe, which means that most Europeans are Christians. Democracy • leaders are usually elected by the people • Citizens who are eligible to vote have a say in how the government works.