Cause and effect The U.S.
advertisement

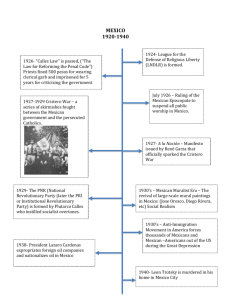
Cause and Effect The Mexican-American War Objective : Determining the causes of the Mexican American War U.S.-Mexico Disputes • The Annexation of Texas by the U.S. angered the Mexican Government. • Mexico never acknowledged Texas as independent and felt the U.S. had no right to take its territory. • Mexico also did not acknowledge the Treaty of Velasco which set the southern border of Texas as the Rio Grande. • The loss of Texas will inevitably result in the loss of New Mexico and the Californias. Little by little our territory will be absorbed until only an insignificant part is left to us.... Our national existence... will end like those weak meteors that, from time to time, shine fitfully in the firmament (sky) and disappear. -José Maria Tornel y Mendivil The U.S. and Texas considered the Rio Grande as the Southern border. For Mexico it was the Nueces Area in Dispute Nueces River Rio Grande River • Why would the Mexican government not accept the treaty of Velasco? – Santa Anna only signed the treaty of Velasco because his life was in danger. Manifest Destiny • Another issue with Mexico was Manifest Destiny. • The land that the United States desired out west (California especially) was all controlled by Mexico. The U.S. Perspective • Most Americans sympathized with Texas during the Texas revolution and republic days because most Texans were former Americans. • As a result of the brutal fighting (at the Alamo, Massacre at Goliad, and other times) the American public developed negative stereotypes against the Mexican people and Stereotype: A belief that is incorrectly government attributed to an entire group of people Effort to ease the tensions • After Texas Annexation, Mexico threatened war. • U.S. President James K. Polk sent John Slidell to Mexico to work for better relations between the two countries. John Slidell Slidell’s Mission 1) Get Mexican recognition of the Rio Grande as the border between Mexico and the United States 2) To forgive about $4.5 million owed to U.S. citizens by Mexico from the Mexican War of Independence 3) To discuss the purchase of the New Mexico and California • The Mexican government refused to talk with Slidell which angered the U.S. • A company of U.S. Calvary by Captain Seth The Thornton Affair commanded Thornton got into a skirmish with Mexican forces near the Rio Grande. • Thornton was ordered to scout an area about twenty miles northwest of what later became Brownsville, Texas. In April 1846, the Calvary, investigated an abandoned hacienda (Ranch). • Some two thousand Mexican soldiers were encamped in and around the hacienda, and a firefight occurred. Both sides Thornton was outnumbered fought ferociously, but the greatly By about 1900 men. outnumbered U.S. force was forced to surrender after several hours of Skirmish: A small battle skirmishing. Presidents Polk’s Response • President Polk asked for a declaration of war before a joint session of the United States Congress, summing up the need for war by famously stating: – "American blood has been shed on American soil". • Congress declared war on Mexico, despite protests by the Mexican government that Thornton had crossed the border into Mexican Texas — a border that Mexico claimed as the Nueces River. the ensuing Mexican-American War was waged from 1846-1848 and witnessed the loss of many thousands of lives and nearly half of the territory of Mexico. • US Problems with Mexico 1) Americans had a negative view of Mexico because of the Texas Revolution 2) Mexico owed the U.S. money for the Mexican Revolution against Spain • Mexican Problems with US. 1) Mexico felt that Texas was being stolen from them. 2) Mexico didn’t believe in Manifest Destiny and didn’t want to give away their land. Vote Yes-Declare War • Treaty of Velasco is valid • Belief in Manifest Destiny • Texas Annexation is legal Vote no-not to Declare War • Will expand slavery • Manifest Destiny is unfair to Mexico • Treaty of Velasco is a sham and not valid • Annexation is illegal without Mexico approval. POLK’s Speech Video