Overview of the cell structure Bacteria, animals and plants
advertisement

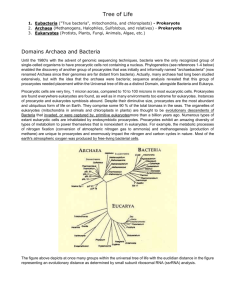
Overview of the cell structure Readings and Objectives • Reading – Russell: 2.5a, 21.2, 22 – Cooper: Chapter 1 • Objectives – – – – – Cell Theory Basic properties of cells Cell size Cell diversity Prokaryotic vs eukaryotic cells • Diversity • Structure Properties of Cells Basic properties of cells • Order and complexity – surrounded by a semi-permeable membrane, similar in composition and function – Similar chemical composition: similarity of structural patterns of macromolecules and their functions – Similar biochemical and regulatory processes – hierarchal complexity from molecules to supramolecular structures • Self replication by division: all cells come from existing cells by division, process of division share similarities among cells Properties of Cells Basic properties of cells • Cells are small (see module 3) 1200 S=6(X)^2 1000 V=(X)^3 800 S or V – Varied between ~0.5 to a few 100 um (eg E.coli ~0.6 um, RBC 8 um, skin epithelial cells ~30 nm and ameoba ~500 um) – Why cells are generally small? – Limiting factor: Surface to volume ratio (S/V) – Surface is the portal of supply for the volume of cell 600 400 200 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 X (side of cube) 7 8 9 10 Properties of Cells Basic properties of cells • Cells are small (see module 3) – S/V vs X in nonlinear – S/V exponentially reduced as X increases • Surface (size of cell) reaches a limit that cannot support the cell’s need (volume) • Eukaryotes: have increased the S/V by extending internal membrane surfaces 7.00 6.00 S/V 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 1.00 0.00 1 2 3 4 5 6 X (cube side) 7 8 9 10 Properties of Cells Properties… • Interaction with the environment • All have transmittable genetic program – DNA: similar structure and function, being inherited – Genes: units of genetic function, basic similarity – Evolution: plasticity of genetic information, functional divergence in response to environmental cues • Energy biogenesis • Similarity of metabolic pathways, eg. glycolytic pathway, Krebs cycle, adaptive variations on a general theme • Use of ATP as the universal cellular energy currency Chemical and mechanical activity • Similar enzymes carry out metabolic reactions → energy • Use of energy to do mechanical work Cell theory Early observations • Robert Hooke (1665): first to observe unit structures in cork, called them “cells” • Antone Van Leeuwenhoek: discovers microbial single “cells” • Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann (1839): Independently concurred that all living organisms, – All living organisms consist of unit structures called Cells (The Cell theory) • Rudolf Virchow (1855): expanded the cell theory, – Each cell is the result of division of previous cells • Modern cell biology addresses the question “how cells work” • To understand the molecular basis of cellular processes Cell diversity • Domains of life: cells are organized in three domains • Procaryotes- Eubacteria and Arhaebacteria • Eucaryotes- Protista, Fungi, Plants and Animals • Similarities: Procaryotes and eucaryotes – Cell membrane – energy metabolism – Genetic code • Differences: – Procaryotes are unicellular – Except for many members of protista the rest of eukaryotes are multicellular – Size: procaryotes 0.5-5 um, eucaryotes 5-500 um – Membrane bound organelles present in eucaryotes but not procaryotes – Reproduction: cell fission in procaryotes vs mitosis in eukarotes Procaryotes: Structure Bacterial cytoplasm is surrounded by a cell membrane, a cell wall, and for some with a polysaccharide capsule Cell wall: used for protection, shape, rigidity • Composed of peptidoglycan, a polysaccharide of alternating acetlylated muramic acid and glucoseamine • β14 glycosidic bond btw sugars • cross-linked by a short oligopeptide Two types of bacteria based on cell wall structure – Gram positive: multiple layers of peptidoglycan – Gram negative: few layers of peoptidoglycan G+ bacteria G- bacteria Procaryotes: Structure • Plasma membrane – Beneath the cell wall is the plasma membrane, a phospholipid bilayer with associated proteins – Steroid like molecules instead of cholesterol Procaryotes: Structure Cytoplasm: lacks membrane bound organelles • Ribosomes –70S; 3 rRNA + 55 proteins (in 2 subunits 50S and 30S) –Protein synthesis • Chromosome: single supercoiled chromosome that resides in a region called nucleoid (not membrane bound) Procaryotes: Structure • Bacteria have appendages with specific functions – Flagella, composed of flagellin helps bacteria move – Fimbriae are small bristlelike fibers that allow bacteria to attach themselves to surfaces – Sex pili (F pilus) used for conjugation to transfer DNA from one bacterium to another • Genes coding for F-pilus are on F plasmid Procaryotes: reproduction Reproduction • Fission instead of mitosis • Chromosomal DNA replication Cytokinesis • formation of divisome (several proteins that tag the centre of cell) • Cell wall peptidoglycan deposited • Chromosomes separated Eucaryotic cells Diversity • Protista: free-living marine unicellular, some photosynthetic • e.g. Giardia lamblia, dinoflagellates, Paramecium, Plasmodium • Multicellular organisms – Fungi, Plants, Animals – Differentiation – Model organisms (a) Saccharomyces cerevisiae (yeast) (b) Arabidopsis thaliana (c) Caenorhabditis elegans (d) Drosophila melanogaster (e) Mus musculus Eucaryotic cells Structure Characteristics: • Typically 10-30 um • Separation of DNA and cytoplasm by nuclear envelope • Presence of membrane-bound compartments with specialized functions: Mitochondria, chloroplasts, ER, Golgi complex • Highly specialized motor proteins • Nuclear envelope and internal membranes – Originated from cell membrane – differentiated and acquired special functions Eucaryotic cells • organelles can be divided into four categories – The nucleus and ribosomes – endomembrane system – energy-related organelles – cytoskeleton Can you meet these objectives? • Describe the cell theory • Describe the basic properties of cells • Outline the major advances leading to modern cell biology • Describe the properties of procaryotic cells • Contrast and compare prokaryotes and eukaryotes • Discuss the cellular structure of prokaryotes