The Study of Bacteria
advertisement

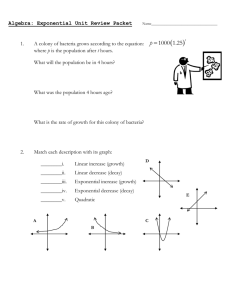
Susan Hollingsworth Aaron Kaiser Biology 110 Lab # smh092404 Purpose: To observe multiple environments that harbor bacterial growth and determine which environment under investigation is most conducive to bacterial growth Environments under investigation: air soil washed/unwashed hands door handle of men’s bathroom raw chicken pond water Hypothesis: Pond Water largest and most diverse population of bacteria due to a vast array of living and decomposing organisms that are vulnerable to bacterial colonization aquatic medium that receives sunlight (some bacteria are photosynthetic) exposed to air which transports bacterial spores. Materials: 7 sterile Petri dishes with nutrient agar Wax pencil 9 bacterial inoculating loops Sterile cotton swab Piece of raw chicken Soil sample Pond water sample Hand soap Sterile water Parafilm strips Light microscope Dissecting microscope incubator Method: 1. Label each Petri dish 2. “Air” sample 3. Use Streak Plate method to apply sample (a) (b) (c) Figure 1. Isolating bacterial colonies using the “Streak Plate” method. 4. Unwashed/Washed hand sample 5. Recover dish labeled “air.” 6. Wrap cultures with Parafilm and incubate upside down for 1 week. Data Interpretations: The Petri dishes will be analyzed by using colony morphology characteristics to see which one has the most species of bacteria. This will be accomplished by identifying and tabulating the number of different colonies present in each sample. Table 1. Bacteria colony morphology: Air Colony Size Shape Margin Surface Color a. 6mm Irregular Lobate Wrinkled Milky white b. 4mm Round Wavy Smooth White center, clear surrounding c. 13mm Irregular Lobate Smooth White center, milky white surrounding d. 5mm Irregular Wavy Smooth Yellow, gold, clear surrounding e. 9.5mm Irregular Wavy Smooth, contoured edges Tan center, white ring, clear ring Fig. 2 Bacteria present in Air environemnt Table 2. Bacteria colony morphology: Chicken Colony Fig 3. Bacteria found on Chicken environment Shape Margin Surface Color a. 1mm Round Lobate Wrinkled Creamy white to slightly yellow b. 5mm Round Smooth Smooth white Table 3. Bacteria colony morphology: Soil Colony Fig 4. Bacteria found on soil environment Size Size Shape Margin Surfac e Color a. 10mm No defined shape No defined margin Wrinkled Clear b. Less than 1mm Irregular Lobate Wrinkled Cream white Table 5. Bacteria colony morphology: washed hand Colony Shape Size Margin Surface Color a. 3mm Round Lobate Smooth Creamy white b. 4mm Round Lobate Smooth Clear c. Punctiform Round Smooth Smooth white Fig 5. Bacteria found on washed and unwashed hand environments Table 4. Bacteria colony morphology: unwashed hand Colony Size Shape Margin Surface Color a. 8mm Irregular Smooth Smooth Yellow b. 8mm Round Lobate Smooth Clear to creamy white c. 3mm Round Smooth Concentric White d. 2mm Round Lobate Smooth Clear to off white e. 3mm Round Lobate Wrinkled and smooth Clear f. Punctiform on e. Round Smooth Smooth Slightly white to clear g. 7mm Irregular Wavy Smooth Creamy white Table 6. Bacteria colony morphology: pond water Colony Size Shape Margin Surface Color a. 4mm Round Lobate Smooth Tan to white b. 1mm Round Smooth Smooth Orange c. 5mm Round Smooth Smooth Clear to off white d. 30mm Irregular Lobate Smooth trasparent Fig 7. Bacteria found on pond water environment Table 7. Bacteria colony morphology: Men’s bathroom door Colony Size Shape Margin Surface Color a. 3mm Round Lobate Smooth Clear b. 3mm Round Lobate Smooth Orange c. 10mm Round Smooth Smooth yellow d. 10mm Round Smooth Smooth white e. 6mm Round Wavy Mucoidal white Fig 8. Bacteria found on bathroom door environment Side Study: Effect of Antibiotics on E. coli growth Antibiotic Sensitivity Chloramphenicol30mg NS Penicillin-10mg NS Nalidixic Acid-30mg VS* Norobiocin-30mg NS Streptomycin-10mg VS Erythromycin-15mg S Tetracycline-30mg VS Kanamycin-30mg VS Fig 9. E coli growth among antibiotics