ERCP Presentation
advertisement

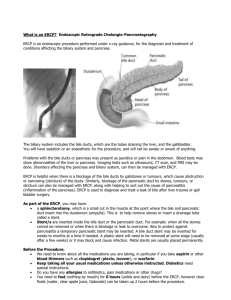
ERCP: Our Initial Attempts Dr.Jimma Hossain MBBS; MD Trained in Advanced Endoscopy, India. Asstt.Professor- Gastroenterology, Rangpur Medical College, Rangpur. Definition of ERCP • Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography • The technique that combines the use of endoscopy and fluoroscopy to diagnose and treat certain problems of biliary and pancreatic ductal systems. Since its initial inception four decades ago ERCP has evolved from a diagnostic to therapeutic procedure. Such an evolution required developments in technology, techniques and training. Brief History of ERCP • The first endoscope was developed in 1806 by Philipp Bozzini ‘for the examinations of canals and cavities of the human body’. Brief History of ERCP • H/o four decades, spanning the 1970s to 2000s. • 1970s-diagnosis and therapy-first reports of sphincterotomy. Brief History of ERCP 1980s-refinement and reporting- in accessories, radiographic imazing. Reporting of adverse events. Stent placement. Acceptance of ERCP by medical community. Brief History of ERCP 1990s-Training and expanding therapy. Emphasis on advanced training. endoscopic photography, videography. Therapy of pancreatic disorders. Safer sphincterotomy- computer assisted blended current. SEMS. Complementary techniques-EUS,MRCP. Brief History of ERCP 2000s-Prevention,pulverizng. Pancreatitis Pancreatic Pulvarizing stents lagre stones Diagnostic ERCP Diagnostic ERCP largely been supplanted by noninvasive imazing – Abdominal MRI-MRCP EUS CT Diagnostic ERCP To define etiology of acute relapsing pancreatitis Divisum, anomalous PB union, annular pancreas, SOD. To differentiate chronic pancreatitis from intraductal neoplasm. To define presence or absence of CBD stones in jaundice, cholangitis or acute pancreatitis. Distinguish benign from malignant biliary stricture. Diagnostic ERCP To define etiology of acute relapsing pancreatitis Divisum, anomalous PB union, annular pancreas, SOD. To differentiate chronic pancreatitis from intraductal neoplasm. To define presence or absence of CBD stones in jaundice, cholangitis or acute pancreatitis. Distinguish benign from malignant biliary stricture. Therapeutic ERCP Endoscopic sphincterotomy was first described by Classen and Kawai independently in Germany and Japan respectively. That was beginning of therapeutic ERCP. Therapeutic ERCP Biliary endotherapy Obstructing calculi in biliary tree Obstructing worms Obstructing strictures Ductal disruption Senting for malignant obstruction. Therapeutic ERCP Pancreatic endotherapy Obstructing caculi-50% requires ESWL Obstructing strictures Treatment of ductal disruption Pancreato-cutaneous fistula Internal fistulas Pseudocysts Pancreatic ascites Pl effusion Pancreato-biliary fistula. Required logistics and manpower ERCP room-300 square feet ERCP table -30 inch in width Manpower Endoscopist Two assistant Nurse anaesthetist/ anaesthesiologist C-arm operator Required logistics and manpower Core equipments Side –viewing duodenoscope with wide channels C-arm X-ray Accessories Essential ERCP Accessories Electro-surgery generator Guidewires Cannulas Sphincterotomes Stone retrieval balloons and baskets Lithotriptors Dilating balloons and catheters Snares and FB forceps Stents with delivery systems etc. Sedation and analgesia for ERCP ERCP requires moderate to deep sedation Can be administered by nurse anaesthetist or anaesthesiologst. Should have ability to recue from any level of sedation. Complications of ERCP Overall short-term complication rate-5-10% Death from ERCP is rare,<0.5% Most often related to cardio-pulmonary complications. Complications of ERCP Pancreatitis Haemorrhage Perforation Cholangitis Stent related Cardio-pulmonary ERCP –Our first case Mrs. Archana Rani Roy, 60 yrs of age, a house wife, non-diabetic, normotensive lady Presented with h/o recurrent episodes of upper abdominal pain, fever and jaundice for 2 months H/o Lap chole 6 months back Physical examination showed mild firm hepatomegaly Imazing showed biliary dilatation and a stone in lower CBD We planned for therapeutic ERCP. ERCP –Our first case We tried ERCP with a therpeutic intend. But diagnostic ERCP could be possible only. Selective CBD cannulation was done. Cholangiogram showed dilated intra & extra hepatic biliary tree and a large stone in lower part of CBD. Therapeutic procedures Endoscopic esophageal variceal band ligation Haemorrhoidal band ligation Endoscopic polypectomy Achalasia balloon dilatation. Liver abscess drainage. Case- Haemorrhoids Mr AMM Alam ,50 yrs,Banker,normotensive ,non-diabetic. Presented to us with h/o intermittent painless fresh p/r bleeding since 2010 Anoscopy showed 3 columns of 2nd degree internal haemorrhoids. We planned for banding treatment for haemorrhoids. Aspiration of liver abscess Amoebic liver abscess ◦ >90% respond dramatically to metronidazole ◦ Decreases pain and fever within 72 hrs. Indications for aspiration ◦ To rule out pyogenic,particularly with multiple lesions. ◦ Failure to respond clinically in 3 to 5 days ◦ Threat of imminent rupture ◦ Rupture of lt lobe-abscess into pericardium