(PPT, Unknown)
advertisement

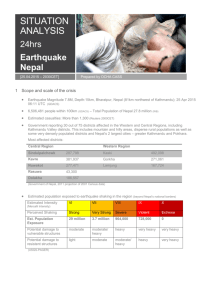
University of Guelph Ntokozo James Mpofu ESN for Nepal "one hectare at a time" Nepal • located in South Asia. • landlocked and bordered between China and India. • has a population of 27.8 Million people. • capital city is Kathmandu. Nepal Geography and Land use at a glance • Total area of the nation is 147,181 sq. km. - area consists of mountainous, hill and Terai terrain. • Land use: • arable land - 16% (land cultivated for crops like wheat, maize and rice that are replanted after each harvest.) • permanent crops - 0.8% (land cultivated for crops that are not replanted after each harvest such as citrus, coffee and rubber, as well as plants such as fruit trees and shrubs.) • other - 83.2% (all other land that is not arable or under permanent crops such as permanent meadows, pastures, forests and woodlands, buit-on areas, roads, barren land, etc.) Agriculture in Nepal Agriculture in Nepal • Agriculture is the mainstay of the economy. • Over 70% of the country's population is engaged in Agriculture for livelihood. • Agriculture accounts for at least one third of the GDP (Gross Domestic Product - value of all final goods and services produced within a nation in a given year) • Industrial activity mainly involves the processing of agricultural products, including pulses, jute, sugarcane, tobacco, and grain. Nitrogen Fertilizers • Nitrogen is a natural element found in the atmosphere. • Makes up 16% of proteins that plants need for growth and survival. • Increase in both population and food demands globally, have increased the use of nitrogen fertilizers by farmers. Enhanced Efficiency Nitrogen Fertilizers (EEF): Environmentally Smart Nitrogen Environmentally Smart Nitrogen • Created and developed by Agrium Advanced Technologies, headquartered in Calgary Alberta. • Uses polymer coated Nitrogen granules (patented!). • N release is controlled by soil moisture and temperature. How does it work...? ESN: how it works • Water moves into the polymer coated urea granules. • N dissolves in the solution inside the granule. • N exits through the polymer coating into the soil solution. Note - factors such as field location, soil type and weather conditions are to be considered when applying ESN. ESN Benefits to Nepal Benefits to Nepal • ESN could supply readily available N needed to grow paddy* with minimal N loss due to volatilization, and leaching. *Paddy (unmilled rice) is Nepal's highest produced cereal crop and is grown on more than a million hectares of arable land area. • ESN responds and releases N based on soil temperatures thus providing N to crops when needed. (suitable for a warm and wet climate such as that of Nepal) • A safe alternative to urea and other natural urea sources and can be top-dress applied to crops, with low burn potential. • Diversity of crops and increase in yields can boost agrisystems, create export opportunities to the growing neighbouring nations of China and India, and sustain the Nepalese economy. Benefits to Canada Benefits to Canada • Agrium Advanced Technologies can establish awareness and promote the eco-friendly benefits of using the Canadian made N fertilizer in Nepal. • Inclines in Nepal's agricultural production may result in increased demand of other agri-system inputs such as machinery made in Canada, and reinforce bilateral trade. - Canada mainly exports machinery as well as vegetables amongst other products to Nepal, and imports textile garments and apparel. • Other developing nations may be interested in importing ESN as well and boost Canadian revenue. Challenges • The cost of ESN to Nepalese farmers once import related charges are accounted for may be expensive. • Urea is a cheaper source of Nitrogen commonly used in Nepal and agronomists would need practical evidence of long term benefits of using ESN instead. • Competition from China and India in the supply of cheaper N fertilizers. However... Nepal could increase both the diversity of crop yields and profitablity in the nation's agricultural sector by using a Canadian product that is environmentally smart, in the light of current global warming concerns. References Agriculture and Agri-Food Canada. (2012). Canadian farm fuel and fertilizer: prices and expenses. Market Outlook Report, 4 (1). Retrieved from http://www.agr.gc.ca/eng/industry-markets-andtrade/statistics-and-market-information/by-product-sector/crops/crops-market-informationcanadian-industry/market-outlook-report/canadian-farm-fuel-and-fertilizerprices-and-expensesmarch-2012/?id=1378845446435 Agrium Inc. Smart Nitrogen. (2014). What is esn [Product information]. Available from http://www.smartnitrogen.com/what-is-esn Agrium Inc. Wholesale (2014). Agricultural specialties [Product information]. Available from http://www.agriumwholesale.com/about_us/agricultural_specialties.jsp Frink, C. R., Waggoner, P. E. & Ausubel, J. H., (1999). Nitrogen Fertilizer: Retrospect and Prospect. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 96, No. 4, 1175-1180. Index Mundi. (2014). Nepal economy - overview [Data]. Available from http://www.indexmundi.com/nepal/economy_overview.html Index Mundi. (2014). Nepal land use [Data]. Available from http://www.indexmundi.com/nepal/land_use.html Ntokozo James Mpofu University of Guelph in partnership with IDRC CIFSRF and DFAIT Faculty Sponsor: Prof. Manish Raizada (raizada@uoguelph.ca) Total presentation time: 5m30sec Thank you!!