Cellular Respiration Powerpoint
advertisement

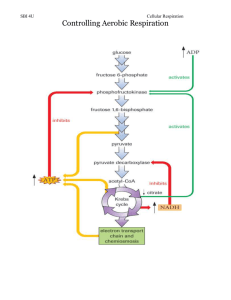
CELLULAR RESPIRATION YOU ARE WHAT YOU EAT CELLULAR RESPIRATION *Controlled process that releases ENERGY (in the bonds) of food in the presence of oxygen. *Main source of Energy- carbohydrates Broken down to glucose ATP – main source of energy WHAT ORGANISMS USE CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Humans • Bacteria • Protists • Plants!!! • Fungi • Remember photosynthesis makes glucose- not energy! Plants need energy to carry out all their wonderful plant functions. CHEMICAL ENERGY IN FOOD • The amount of energy in each type of food varies. • Measured in calories- the amount of energy needed to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water by 1 degree Celsius. • Calories on food labels- measured in kilocalories (1000 calories) • Generally 1 gram of carbohydrate or protein provides 4 Calories/gram; whereas 1 gram of fat (lipids) provides 9 Calories/gram • Also get vitamins and minerals from the food we eat Chemical Equation Glucose + oxygen ------ carbon dioxide + water + ATP (energy) HOW WE GET THE INGREDIENTS FOR CELLULAR RESPIRATION • Simple Diffusion – • higher to lower concentration Oxygen carried to all cells -enters into cell and travels to the mitochondria (organelle converts glucose and oxygen to energy) FOOD DIGESTION • Food ingested – digested to smaller molecules that can move into the red blood cells to be carried to cells GETTING THE GLUCOSE • GLUCOSE ENTERS THE CELL THROUGH Active Transport – insulin produced in the pancreas required as a signal molecule to let the glucose in. What happens when glucose builds up in the blood plasma? ATP • Adenosine triphosphate (ATP) • Made up of adenine, ribose sugar, and three phosphates • the high energy bond is between the phosphate groups between CREATING ATP ATP Charged ADP Uncharged THREE STEPS OF CELLULAR RESPIRATION 1)Glycolysis – 2)THE Kreb Cycle3)Electron Transport Chain and ATP Synthesis GLYCOLYSIS • Means sugar-breaking • Many steps that convert Glucose (6-carbon compound) into 2 molecules of pyruvic acid (3 – carbon compound) • Happens in the CYTOPLASM of the cell. • No Oxygen Required KREB CYCLE • HAPPENS IN THE MATRIX OF THE MITOCHONDRIA (POWERHOUSE OF THE CELL) • INPUT: PYRUVIC ACID FROM GLYCOLYSIS • OUTPUT: CO2, NADH, ATP, FADH2 From Glycolysis INPUT: pyruvic acid OUTPUT: CARBON DIOXIDE, NADH, FADH2 (electron carriers) and ATP ELECTRON TRANSPORT CHAIN ANAEROBIC RESPIRATION • Organisms still need energy when oxygen is not available • Occurs when oxygen is not available • Lactic Acid Fermentation • Alcoholic Fermentation EQUATIONS • Alcoholic Fermentation *Lactic Acid Fermentation ALCOHOLIC FERMENTATION • Biological process which converts sugars such as glucose, fructose and sucrose into cellular energy, produces ethanol and CO2. .Yeast – (example – bread dough- once the oxygen molecules are used up the yeast begins to use pyruvic acid and produces alcohol and CO2 *generates NAD+ (electron carrier) so ATP can continue to be made LACTIC ACID FERMENTATION • Lactic acid fermentation does not give off carbon dioxide, but does make NAD+ (electron carrier) so ATP can continue to be made. • Examples of organisms going through lactic acid fermentation certain bacteria that can produce yogurt, sour cream, buttermilk, kimchi, *Humans also use lactic acid fermentation for quick bursts of energy.